Americas Headquarters
Text Part Number OL-9775-02
Page
N T E N T S
Iii
Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
Understanding Cisco Configuration Engine Software
Clustering Switches
Catalyst 1900 and Catalyst 2820 CLI Considerations
Vii
Creating a Banner
Viii
Changing the Default Privilege Level for Lines
Device Roles
Bypass
Routed Ports
Xii
Monitoring and Maintaining the Interfaces
Xiii
Encapsulation Types
Xiv
Domain Names
Private-VLAN Configuration Guidelines
Xvi
Disabled State
Xvii
Boundary Ports
Xviii
Xix
19-25
Dhcp Server
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
Xxi
Configuring MVR
Xxii
Understanding Storm Control
Xxiii
Understanding Udld Modes of Operation
Xxiv
Creating an Rspan Source Session
Xxv
Snmp Agent Functions
Xxvi
Creating a Numbered Extended ACL
Xxvii
Interaction with Other Features and Switches
Xxviii
Xxix
Port-Channel Interfaces
Xxx
Configuring IP Addressing
Xxxi
Nonstop Forwarding Awareness
Xxxii
IPv6 Addresses
Xxxiii
Configuring Hsrp Priority
Xxxiv
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
Xxxv
Configuring Basic Dvmrp Interoperability Features
Xxxvi
Using a Filter
Xxxvii
Xxxviii
45-14
Configuring Online Diagnostics
Xxxix
Unsupported Route-Map Configuration Commands C-1
Hsrp
Xli
VTP
Xlii
Preface
Audience
Purpose
Conventions
Related Publications
Xliv
Xlv
Xlvi
Features
Overview
Deployment Features
Availability and Redundancy Features, Vlan Features,
Overview Features
Performance Features
Management Options
Manageability Features
Availability and Redundancy Features
Vlan Features
Security Features
Overview Features
QoS and CoS Features
Layer 3 Features
Power over Ethernet Features
Default Settings After Initial Switch Configuration
Monitoring Features
Vlan
Overview Default Settings After Initial Switch Configuration
Overview Default Settings After Initial Switch Configuration
Network Configuration Examples
Design Concepts for Using the Switch
Network Demands Suggested Design Methods
Cost-Effective Wiring Closet
High-Performance Wiring Closet
High-Performance Workgroup Gigabit-to-the-Desktop
Redundant Gigabit Backbone
Server Aggregation
Linux Server Cluster
Cisco SoftPhone Software Gigabit servers
Internet Cisco 2600 or 3700 routers Catalyst 3560-E switches
Large Network Using Catalyst 3750-E and 3560-E Switches
Cisco 7x00 routers Catalyst
Catalyst 3560-E
Multidwelling Network Using Catalyst 3750-E Switches
Long-Distance, High-Bandwidth Transport Configuration
11 Catalyst 3750-E Switches in a MAN Configuration
Where to Go Next
Access layer Aggregation layer
OL-9775-02
Using the Command-Line Interface
Understanding Command Modes
Mode Access Method Prompt Exit Method About This Mode
Configure
Quit
Ctrl-Z
Console command
Command Purpose
Understanding the Help System
Line vty or line
Understanding Abbreviated Commands
Understanding no and default Forms of Commands
Command ?
Command keyword ?
Understanding CLI Error Messages
Using Configuration Logging
Error Message Meaning How to Get Help
Using Command History
Changing the Command History Buffer Size
Recalling Commands
Action1 Result
Using Editing Features
Disabling the Command History Feature
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Switch# terminal editing
Editing Commands through Keystrokes
Capability Keystroke1 Purpose
Editing Command Lines that Wrap
Return and Space bar
Press Ctrl-L or Ctrl-R
Accessing the CLI
Command begin include exclude regular-expression
Switch# show interfaces include protocol
Using the Command-Line Interface Accessing the CLI
OL-9775-02
Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
Understanding the Boot Process
Assigning Switch Information
Default Switch Information
Understanding DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration
Feature Default Setting
Dhcp Client Request Process
Dhcp Client and Server Message Exchange
Configuring DHCP-Based Autoconfiguration
Dhcp Server Configuration Guidelines
Configuring the Tftp Server
Configuring the DNS
Configuring the Relay Device
Obtaining Configuration Files
Routerconfig-if#ip helper-address
Example Configuration
Tftpserver
Switch a Switch B Switch C Switch D
DNS Server Configuration
Tftp Server Configuration on Unix
Dhcp Client Configuration
Manually Assigning IP Information
Checking and Saving the Running Configuration
Switch# show running-config
Switch# copy running-config startup-config
Modifying the Startup Configuration
Default Boot Configuration
Automatically Downloading a Configuration File
Booting Manually
Boot config-file flash/ file-url
Show boot
Configure terminal Enter global configuration mode
Booting a Specific Software Image
Boot system filesystem /file-url
Boot system switch number all
Controlling Environment Variables
Set Manualboot yes Boot manual
Set Switchnumber
Switch current-stack-member-number renumber
Set Switchpriority
Configuring a Scheduled Reload
Scheduling a Reload of the Software Image
Variable Description
Reload in hhmm text
Switch# reload at
Switch# reload at 0200 jun
Displaying Scheduled Reload Information
Configuring Cisco IOS CNS Agents
Understanding Cisco Configuration Engine Software
Configuration Service
Configuration Engine Architectural Overview
Event Service
ConfigID
What You Should Know About the CNS IDs and Device Hostnames
NameSpace Mapper
Using Hostname, DeviceID, and ConfigID
DeviceID
Hostname and DeviceID
Initial Configuration
Understanding Cisco IOS Agents
Configuring Cisco IOS Agents
Incremental Partial Configuration
Synchronized Configuration
Enabling Automated CNS Configuration
Device Required Configuration
Backup init-retry retry-count keepalive seconds
Show running-config
Enabling the CNS Event Agent
Show cns event connections
Enabling an Initial Configuration
Enabling the Cisco IOS CNS Agent
Cns config initial ip-address hostname
Cns id interface num dns-reverse ipaddress
Mac-address event
Cns id hardware-serial hostname string string
Enabling a Partial Configuration
Show running-config Verify your entries
Cns config partial ip-address hostname
Show cns config stats
Displaying CNS Configuration
Show cns config connections
Show cns event stats
Show cns event subject
Managing Switch Stacks
Understanding Switch Stacks
Managing Switch Stacks Understanding Switch Stacks
Switch Stack Membership
Creating a Switch Stack from Two Standalone Switches
Adding a Standalone Switch to a Switch Stack
Stack Master Election and Re-Election
Switch Stack Bridge ID and Router MAC Address
Stack Member Numbers
Stack Member Priority Values
Switch Stack Offline Configuration
Effects of Adding a Provisioned Switch to a Switch Stack
Scenario Result
Scenario Result
Switch Stack Software Compatibility Recommendations
Effects of Replacing a Provisioned Switch in a Switch Stack
Major Version Number Incompatibility Among Switches
Minor Version Number Incompatibility Among Switches
Stack Protocol Version Compatibility
Understanding Auto-Upgrade and Auto-Advise
Auto-Upgrade and Auto-Advise Example Messages
Switch
Directory
Mar 1 000422.537%IMAGEMGR-6-AUTOADVISESW
Incompatible Software and Stack Member Image Upgrades
Switch Stack Configuration Files
Switch Stack Management Connectivity
Connectivity to the Switch Stack Through an IP Address
Connectivity to the Switch Stack Through an SSH Session
Connectivity to Specific Stack Members
Switch Stack Configuration Scenarios
Use the switch stack-member-number
Priority new-priority-number global
Current-stack-member-number Renumber new-stack-member-number
Configuring the Switch Stack
Default Switch Stack Configuration
Enabling Persistent MAC Address
Stack-mac persistent timer
Show switch
Switchconfig# stack-mac persistent timer
Time-value
Setting the Stack Member Priority Value
Assigning Stack Member Information
Assigning a Stack Member Number
Provisioning a New Member for a Switch Stack
Accessing the CLI of a Specific Stack Member
Displaying Switch Stack Information
Command Description
Show switch stack-member-number
Show switch stack-ports
Show switch stack-ring activity
Detail
OL-9775-02
Clustering Switches
Understanding Switch Clusters
Switch Cisco IOS Release Cluster Capability
Cluster Command Switch Characteristics
Standby Cluster Command Switch Characteristics
Planning a Switch Cluster
Candidate Switch and Cluster Member Switch Characteristics
Automatic Discovery of Cluster Candidates and Members
Discovery Through CDP Hops
Discovery Through CDP Hops
Discovery Through Different VLANs
Discovery Through Different Management VLANs
Discovery Through Different VLANs
Discovery Through Routed Ports
Discovery of Newly Installed Switches
New out-of-box
Hsrp and Standby Cluster Command Switches
Virtual IP Addresses
Other Considerations for Cluster Standby Groups
Automatic Recovery of Cluster Configuration
IP Addresses
Hostnames
Passwords
Snmp Community Strings
Switch Clusters and Switch Stacks
Switch Stack Switch Cluster
Members Other cluster member switches
TACACS+ and Radius
LRE Profiles
Using the CLI to Manage Switch Clusters
Switch# rcommand
Catalyst 1900 and Catalyst 2820 CLI Considerations
Using Snmp to Manage Switch Clusters
Snmp Management for a Cluster
OL-9775-02
Administering the Switch
Managing the System Time and Date
Understanding the System Clock
Understanding Network Time Protocol
NTP
Configuring NTP
Typical NTP Network Configuration
Default NTP Configuration
Configuring NTP Authentication
Ntp authenticate
Configuring NTP Associations
Configuring NTP Broadcast Service
Switchconfig# ntp server 172.16.22.44 version
Ntp peer ip-address version number
Key keyid source interface prefer
Interface interface-id
Ntp broadcast version number key keyid
Destination-address
Ntp broadcast client
Configuring NTP Access Restrictions
Ntp broadcastdelay microseconds
Ntp access-group query-only
Serve-onl y serve peer
Command Purpose
Configuring the Source IP Address for NTP Packets
Interface interface-id
Configuring Time and Date Manually
Displaying the NTP Configuration
Setting the System Clock
Fundamentals Command Reference, Release
Displaying the Time and Date Configuration
Configuring the Time Zone
Clock timezone zone hours-offset
Minutes-offset
Configuring Summer Time Daylight Saving Time
Clock summer-time zone recurring
Week day month hh mm week day month
Hh mm offset
Configuring a System Name and Prompt
Clock summer-time zone date month
Clock summer-time zone date date
Default System Name and Prompt Configuration
Configuring a System Name
Copy running-config startup-confi g
Understanding DNS
Default DNS Configuration
Setting Up DNS
Ip domain-name name
Ip name-server server-address1
Default Banner Configuration
Displaying the DNS Configuration
Creating a Banner
Configuring a Message-of-the-Day Login Banner
Banner motd c message c
Unix telnet
Configuring a Login Banner
Banner login c message c
Managing the MAC Address Table
Building the Address Table
MAC Addresses and VLANs
MAC Addresses and Switch Stacks
Default MAC Address Table Configuration
Changing the Address Aging Time
Configuring MAC Address Notification Traps
Removing Dynamic Address Entries
Mac address-table aging-time
Show mac address-table aging-time
String by using the snmp-server community
Snmp-server enable traps mac-notification
Snmp-server host host-addr traps informs version
Mac address-table notification
Adding and Removing Static Address Entries
Configuring Unicast MAC Address Filtering
Mac address-table static mac-addr
Vlan vlan-id interface interface-id
Show mac address-table static
Vlan vlan-id drop
Managing the ARP Table
Displaying Address Table Entries
OL-9775-02
Configuring SDM Templates
Understanding the SDM Templates
Resource Access Default Routing
Dual IPv4 and IPv6 SDM Templates
SDM Templates and Switch Stacks
IPv4-and-IPv6 Resource Default Routing
Configuring the Switch SDM Template
Default SDM Template
SDM Template Configuration Guidelines
Setting the SDM Template
Sdm prefer access default
Dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default routing
Vlan routing vlan
Switchconfig# sdm prefer routing
Switchconfig# sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default
Displaying the SDM Templates
Policy based routing aces 25K
OL-9775-02
Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
Preventing Unauthorized Access to Your Switch
Protecting Access to Privileged Exec Commands
Default Password and Privilege Level Configuration
Setting or Changing a Static Enable Password
Enable password password
Switchconfig# enable password l1u2c3k4y5
Enable password level level password
Encryption-type encrypted-password
Enable secret level level password
Service password-encryption
Disabling Password Recovery
No service password-recovery
Show version
Setting a Telnet Password for a Terminal Line
Configuring Username and Password Pairs
Password password
Switchconfig-line#password let45me67in89
Configuring Multiple Privilege Levels
Username command
Login local
Username name privilege level
Setting the Privilege Level for a Command
Privilege mode level level command
Show privilege
Changing the Default Privilege Level for Lines
Command
Logging into and Exiting a Privilege Level
Controlling Switch Access with TACACS+
Understanding TACACS+
Typical TACACS+ Network Configuration
Configuring TACACS+
TACACS+ Operation
Default TACACS+ Configuration
Tacacs-server host hostname port
Aaa new-model
Aaa group server tacacs+ group-name
Configuring TACACS+ Login Authentication
Aaa new-model Enable AAA
Show tacacs Verify your entries
Aaa authentication login default
Login authentication default
Authentication login command
Line console tty vty line-number
Show running-config Verify your entries
Controlling Switch Access with Radius
Displaying the TACACS+ Configuration
Starting TACACS+ Accounting
Understanding Radius
Transitioning from Radius to TACACS+ Services
Radius Operation
Configuring Radius
Default Radius Configuration
Identifying the Radius Server Host
Page
Acct-port port-number timeout
Radius-server host hostname
Ip-address auth-port port-number
Seconds retransmit retries key
Configuring Radius Login Authentication
Switchconfig# radius-server host host1
Server Host section on
Defining AAA Server Groups
Aaa group server radius group-name
Aaa authorization network radius
Radius
Starting Radius Accounting
Configuring Settings for All Radius Servers
Radius-server timeout seconds
Radius-server key string
Radius-server retransmit retries
Authentication
Radius-server vsa send accounting
Cisco-avpair=shellpriv-lvl=15
Cisco-avpair=ipoutacl#2=deny ip 10.10.10.10 0.0.255.255 any
Controlling Switch Access with Kerberos
Displaying the Radius Configuration
Radius-server host hostname ip-address non-standard
Understanding Kerberos
Term Definition
KDC
Authenticating to a Boundary Switch
Kerberos Operation
Keytab
Srvtab
Configuring Kerberos
Authenticating to Network Services
Obtaining a TGT from a KDC
Aaa authentication login default local
Aaa authorization exec local
Aaa authorization network local
Configuring the Switch for Secure Shell
Username command
Username name privilege level
Understanding SSH
SSH Servers, Integrated Clients, and Supported Versions
Configuring SSH
Configuration Guidelines
Limitations
Setting Up the Switch to Run SSH
Displaying the SSH Configuration and Status
Configuring the SSH Server
Ip ssh timeout seconds
Authentication-retries number
Configuring the Switch for Secure Socket Layer Http
Understanding Secure Http Servers and Clients
Certificate Authority Trustpoints
Rsakeypair TP-self-signed-3080755072
Configuring Secure Http Servers and Clients
Default SSL Configuration
CipherSuites
SSL Configuration Guidelines
Configuring a CA Trustpoint
Configuring the Secure Http Server
Configuring the Secure Http Client
Ip http timeout-policy idle seconds life
Show ip http server secure status
Ip http client secure-trustpoint name
Configuring the Switch for Secure Copy Protocol
Displaying Secure Http Server and Client Status
Ip http client secure-ciphersuite
Show ip http client secure status
Information About Secure Copy
Html
OL-9775-02
Configuring Ieee 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
Understanding Ieee 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
10-1
Device Roles
10-2
Authentication Process
10-3
Authentication Flowchart
10-4
Authentication Initiation and Message Exchange
10-5
10-6
EAPOL-Start
Ieee 802.1x Authentication and Switch Stacks
Ports in Authorized and Unauthorized States
10-7
Ieee 802.1x Host Mode
10-8
Ieee 802.1x Accounting
Ieee 802.1x Accounting Attribute-Value Pairs
Attribute Number AV Pair Name
10-9
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Vlan Assignment
10-10
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Per-User ACLs
10-11
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Guest Vlan
10-12
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Restricted Vlan
10-13
10-14
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Voice Vlan Ports
10-15
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Port Security
10-16
Using Ieee 802.1x Authentication with Wake-on-LAN
10-17
10-18
Using Multidomain Authentication
Network Admission Control Layer 2 Ieee 802.1x Validation
10-19
Using Web Authentication
For example
10-20
Configuring Ieee 802.1x Authentication
10-21
Default Ieee 802.1x Authentication Configuration
AAA
10-22
Ieee 802.1x Authentication Configuration Guidelines
Ieee 802.1x Authentication
10-23
10-24
Configuring Ieee 802.1x Authentication
MAC Authentication Bypass
10-25
Configuring the Switch-to-RADIUS-Server Communication
10-26
Ip-address auth-port port-number key
10-27
Configuring the Host Mode
Dot1x host-mode multi-host
Multi-domain
Show dot1x interface interface-id
Configuring Periodic Re-Authentication
Manually Re-Authenticating a Client Connected to a Port
10-29
Changing the Switch-to-Client Retransmission Time
Dot1x timeout tx-period seconds
Changing the Quiet Period
Show dot1x interface interface-id Verify your entries
Setting the Switch-to-Client Frame-Retransmission Number
Switchconfig-if#dot1x timeout tx-period
Show dot1xinterface interface-id Verify your entries
Dot1x max-reauth-req count
Setting the Re-Authentication Number
Configuring Ieee 802.1x Accounting
Switchconfig-if#dot1x max-reauth-req
10-32
Configuring a Guest Vlan
10-33
Configuring a Restricted Vlan
Switchport mode private-vlan host
Switchconfig# interface gigabitethernet2/0/2
Dot1x guest-vlan vlan-id
Dot1x auth-fail vlan vlan-id
Dot1x auth-fail max-attempts max
Attempts
10-35
Configuring the Inaccessible Authentication Bypass Feature
Switchconfig-if#dot1x auth-fail max-attempts
Radius-server dead-criteria time time
Tries tries
10-37
Configuring Ieee 802.1x Authentication with WoL
Dot1x critical recovery action
Reinitialize vlan vlan-id
Show dot1x interface interface-id
Configuring MAC Authentication Bypass
Switchconfig-if#dot1x control-direction both
Switchconfig-if#dot1x mac-auth-bypass
Dot1x control-direction both
Configuring NAC Layer 2 Ieee 802.1x Validation
10-40
Configuring Web Authentication
10-41
10-42
Disabling Ieee 802.1x Authentication on the Port
No dot1x pae Disable Ieee 802.1x authentication on the port
Dot1x fallback fallback-profile
10-43
Displaying Ieee 802.1x Statistics and Status
10-44
Configuring Interface Characteristics
Understanding Interface Types
11-1
Switch Ports
Port-Based VLANs
11-2
Access Ports
Trunk Ports
11-3
Routed Ports
Tunnel Ports
11-4
Switch Virtual Interfaces
EtherChannel Port Groups
11-5
Power over Ethernet Ports
Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
Supported Protocols and Standards
11-6
Powered-Device Detection and Initial Power Allocation
Class
11-7
Power Management Modes
11-8
Power Monitoring and Power Policing
11-9
Maximum Power Allocation Cutoff Power on a PoE Port
11-10
Connecting Interfaces
11-11
Ethernet Management Port
11-12
Connecting a Switch Stack to a PC
11-13
Tftp
11-14
Using Interface Configuration Mode
Mgmtinit
Mgmtshow
Mgmtclr
Procedures for Configuring Interfaces
11-16
Configuring a Range of Interfaces
Interface range port-range macro
Macroname
Show interfaces interface-id
11-18
Configuring and Using Interface Range Macros
Show running-config include define
Define interface-range macroname
Interface range macro macroname
Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
Switch# show running-config include define
Switch# show run include define
11-20
Default Ethernet Interface Configuration
11-21
Configuring Interface Speed and Duplex Mode
Speed and Duplex Configuration Guidelines
11-22
Setting the Interface Speed and Duplex Parameters
Speed 10 100 1000 auto 10
Nonegotiate
Duplex auto full half
Configuring Ieee 802.3x Flow Control
Flowcontrol receive on off desired
11-24
Configuring Auto-MDIX on an Interface
Local Side Auto-MDIX
With Correct Cabling
11-25
Configuring a Power Management Mode on a PoE Port
Interface-id phy
11-26
Budgeting Power for Devices Connected to a PoE Port
Power inline auto max max-wattage
Show power inline i nterface-id
Neve r static max max-wattage
Wattage
11-28
Configuring Power Policing
11-29
Adding a Description for an Interface
11-30
Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
Configuring Ethernet Management Ports
Switch# show interfaces gigabitethernet1/0/2 description
11-31
No switchport
Interface gigabitethernet interface-id vlan vlan-id
No shutdown
11-32
Configuring the System MTU
11-33
Use the system mtu jumbo Use the system mtu routing
System mtu jumbo bytes
System mtu routing bytes
11-34
Configuring the Cisco Redundant Power System
System mtu bytes
Reload
Show system mtu
Power rps switch-number name string serialnumber
Power rps switch-number port rps-port-id mode active
Standby
11-36
Configuring the Power Supplies
Power supply switch-numberoff on
Show env power
Show env rps
Monitoring and Maintaining the Interfaces
Monitoring Interface Status
11-38
Clearing and Resetting Interfaces and Counters
11-39
Shutting Down and Restarting the Interface
Interface vlan vlan-id gigabitethernet interface-id
Shutdown
11-40
Configuring Smartports Macros
Understanding Smartports Macros
12-1
Configuring Smartports Macros
Default Smartports Macro Configuration
Macro Name Description
12-2
Smartports Macro Configuration Guidelines
12-3
Creating Smartports Macros
Macro name macro-name
Name Sample-Macro and macro name sample-macro will result
Show parser macro name macro-name
Applying Smartports Macros
12-5
Applying Cisco-Default Smartports Macros
Show parser macro
Show parser macro macro-name
12-6
Switch# show parser macro cisco-desktop
Switchconfig-if#macro apply cisco-desktop $AVID
12-7
Displaying Smartports Macros
Show parser macro brief
Show parser macro description interface
12-8
Configuring VLANs
Understanding VLANs
13-1
13-2
Supported VLANs
Vlan Port Membership Modes
13-3
Configuring Normal-Range VLANs
13-4
Vlan ID
13-5
Normal-Range Vlan Configuration Guidelines
Token Ring VLANs
13-6
Vlan Configuration Mode Options
Saving Vlan Configuration
Vlan Configuration in config-vlan Mode
Vlan Configuration in Vlan Database Configuration Mode
Default Ethernet Vlan Configuration
Parameter Default Range
VLANxxxx, where
13-8
Copy running-config startup config
Creating or Modifying an Ethernet Vlan
Remote-span
13-9
Deleting a Vlan
Vlan database
13-10
Assigning Static-Access Ports to a Vlan
Switchport access vlan vlan-id
No vlan vlan-id
Show vlan brief
Configuring Extended-Range VLANs
Default Vlan Configuration
Show interfaces interface-id switchport
Vlan fields of the display
Extended-Range Vlan Configuration Guidelines
13-13
Vtp mode transparent
Creating an Extended-Range Vlan
Show vlan id vlan-id
13-14
Switchconfig# vtp mode transparent
Switch# copy running-config startup config
Creating an Extended-Range Vlan with an Internal Vlan ID
Show vlan internal usage
Configuring Vlan Trunks
Command Command Mode Purpose
Displaying VLANs
Trunking Overview
Switches in an ISL Trunking Environment
13-17
Mode Function
Encapsulation Types
Encapsulation Function
13-18
Default Layer 2 Ethernet Interface Vlan Configuration
Configuring an Ethernet Interface as a Trunk Port
Ieee 802.1Q Configuration Considerations
13-19
Interaction with Other Features
Configuring a Trunk Port
Dot1q negotiate
13-20
Defining the Allowed VLANs on a Trunk
13-21
Switchport trunk allowed vlan add
Changing the Pruning-Eligible List
All except remove vlan-list
13-22
Configuring the Native Vlan for Untagged Traffic
Switchport trunk pruning vlan add
Except none remove vlan-list
Vlan ,vlan
Configuring Trunk Ports for Load Sharing
Load Sharing Using STP Port Priorities
Switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id
13-24
13-25
Load Sharing Using STP Path Cost
Or switch stack
Connect to the trunk ports configured on Switch a
Exit Return to global configuration mode
Switchport trunk encapsulation
Interface gigabitethernet1/0/1
Isl dot1q negotiate
Spanning-tree vlan 2-4 cost
Configuring Vmps
Understanding Vmps
13-28
Default Vmps Client Configuration
Vmps Configuration Guidelines
Dynamic-Access Port Vlan Membership
13-29
Configuring the Vmps Client
Entering the IP Address of the Vmps
13-30
Configuring Dynamic-Access Ports on Vmps Clients
Switchport access vlan dynamic
Reconfirming Vlan Memberships
Vmps reconfirm
Changing the Reconfirmation Interval
Changing the Retry Count
Vmps reconfirm minutes
13-32
Troubleshooting Dynamic-Access Port Vlan Membership
Vmps Configuration Example
Switch# show vmps
Monitoring the Vmps
Dynamic Port Vlan Membership Configuration
13-34
Configuring VTP
Understanding VTP
14-1
VTP Domain
14-2
VTP Mode Description
VTP Modes
VTP Advertisements
14-3
VTP Version
VTP Pruning
14-4
14-5
Vlan
Configuring VTP
VTP and Switch Stacks
14-6
Default VTP Configuration
VTP Configuration Options
VTP Configuration in Global Configuration Mode
14-7
VTP Configuration Guidelines
VTP Configuration in Vlan Database Configuration Mode
Passwords
Domain Names
Configuring a VTP Server
Configuration Requirements
VTP Version
14-9
Vtp password password
Vtp password password
Show vtp status
Vtp server
Configuring a VTP Client
Vtp mode client
Switch# vlan database
14-11
Disabling VTP VTP Transparent Mode
14-12
Enabling VTP Version
Vtp version
14-13
Adding a VTP Client Switch to a VTP Domain
Enabling VTP Pruning
Vtp pruning
14-14
14-15
Monitoring VTP
14-16
Configuring Voice Vlan
Understanding Voice Vlan
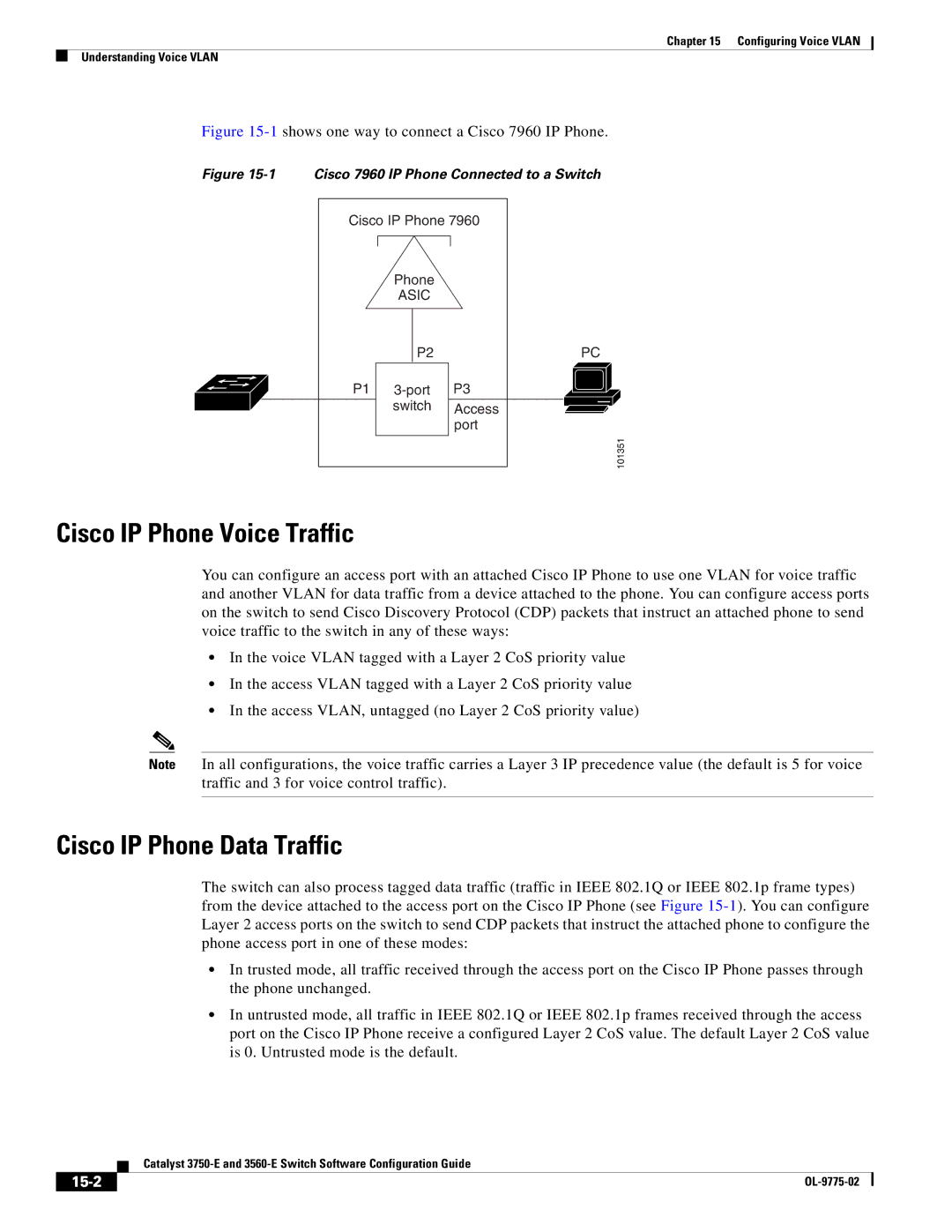
15-1
Cisco IP Phone Voice Traffic
Cisco IP Phone Data Traffic
15-2
Configuring Voice Vlan
Default Voice Vlan Configuration
Voice Vlan Configuration Guidelines
15-3
Configuring a Port Connected to a Cisco 7960 IP Phone
15-4
Configuring Cisco IP Phone Voice Traffic
15-5
Configuring the Priority of Incoming Data Frames
15-6
Displaying Voice Vlan
15-7
15-8
Configuring Private VLANs
Understanding Private VLANs
16-1
16-2
Private-VLAN Domain
IP Addressing Scheme with Private VLANs
16-3
Private VLANs across Multiple Switches
Private-VLAN Interaction with Other Features
16-4
Private VLANs and Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast Traffic
Private VLANs and SVIs
16-5
Configuring Private VLANs
Tasks for Configuring Private VLANs
Private VLANs and Switch Stacks
16-6
Default Private-VLAN Configuration
Private-VLAN Configuration Guidelines
Secondary and Primary Vlan Configuration
16-7
Private-VLAN Port Configuration
16-8
Limitations with Other Features
16-9
Configuring and Associating VLANs in a Private Vlan
16-10
Show vlan private-vlan type
Show interfaces status
16-11
Configuring a Layer 2 Interface as a Private-VLAN Host Port
Switchport private-vlan host-association
Switch# show interfaces gigabitethernet1/0/22 switchport
Primaryvlanid secondaryvlanid
Switchport mode private-vlan promiscuous
Switchport private-vlan mapping primaryvlanid
Add remove secondaryvlanlist
16-13
Switch# show interfaces private-vlan mapping
Interface vlan primaryvlanid
Private-vlan mapping add remove
Show interface private-vlan mapping
Monitoring Private VLANs
16-15
16-16
Configuring Ieee 802.1Q and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
Understanding Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling
17-1
Ieee 802.1Q Tunnel Ports in a Service-Provider Network
17-2
17-3
Configuring Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling
Default Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling Configuration
Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling Configuration Guidelines
Native VLANs
System MTU
17-5
Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling and Other Features
17-6
Configuring an Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling Port
Vlan dot1q tag native
Show dot1q-tunnel
Show vlan dot1q tag native
Understanding Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
17-8
17-9
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
17-10
Default Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Configuration
17-11
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Configuration Guidelines
17-12
Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
17-13
Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling for EtherChannels
Configuring the SP Edge Switch
L2protocol-tunnel point-to-point
Pagp lacp udld
17-15
Configuring the Customer Switch
17-16
Switchconfig-if#channel-group 1 mode desirable
Switchconfig# interface port-channel
17-17
Monitoring and Maintaining Tunneling Status
17-18
Configuring STP
Understanding Spanning-Tree Features
18-1
STP Overview
18-2
Spanning-Tree Topology and BPDUs
18-3
Bridge ID, Switch Priority, and Extended System ID
18-4
Switch Priority Value
Spanning-Tree Interface States
Bit
32768 16384 8192 4096 2048 1024 512 256 128
2illustrates how an interface moves through the states
18-6
Blocking State
Listening State
Learning State
Forwarding State
How a Switch or Port Becomes the Root Switch or Root Port
Disabled State
18-8
Spanning Tree and Redundant Connectivity
Spanning-Tree Address Management
Accelerated Aging to Retain Connectivity
18-9
Spanning-Tree Modes and Protocols
Supported Spanning-Tree Instances
18-10
Spanning-Tree Interoperability and Backward Compatibility
STP and Ieee 802.1Q Trunks
VLAN-Bridge Spanning Tree
Rapid PVST+
Configuring Spanning-Tree Features
Spanning Tree and Switch Stacks
18-12
Default Spanning-Tree Configuration
Spanning-Tree Configuration Guidelines
18-13
18-14
Changing the Spanning-Tree Mode
18-15
Configuring the Root Switch
Disabling Spanning Tree
Show spanning-tree vlan vlan-id Verify your entries
18-16
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id root primary
Diameter net-diameter hello-time seconds
Show spanning-tree detail
18-17
Configuring a Secondary Root Switch
Configuring Port Priority
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id root secondary
Diameter net-diameter hello-time
Spanning-tree port-priority priority
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id port-priority priority
Show spanning-tree interface interface-id
Show spanning-tree vlan vlan-id
Configuring Path Cost
Port-channel-number
Spanning-tree cost cost
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id cost cost
Configuring the Switch Priority of a Vlan
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id priority priority
18-21
Configuring Spanning-Tree Timers
Configuring the Hello Time
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id hello-time seconds
18-22
Configuring the Forwarding-Delay Time for a Vlan
Configuring the Maximum-Aging Time for a Vlan
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-id forward-time
Spanning-tree vlan vlan-idmax-age seconds
Configuring the Transmit Hold-Count
Displaying the Spanning-Tree Status
Show spanning-tree detail Verify your entries
18-24
Configuring Mstp
19-1
Understanding Mstp
Multiple Spanning-Tree Regions
19-2
IST, CIST, and CST
Operations Within an MST Region
19-3
Operations Between MST Regions
19-4
Hop Count
Ieee 802.1s Terminology
Cisco Prestandard Cisco Standard
19-5
Boundary Ports
Ieee 802.1s Implementation
19-6
Interoperation Between Legacy and Standard Switches
Port Role Naming Change
19-7
Mstp and Switch Stacks
Detecting Unidirectional Link Failure
19-8
Understanding Rstp
Interoperability with Ieee 802.1D STP
Port Roles and the Active Topology
19-9
Rapid Convergence
19-10
Synchronization of Port Roles
19-11
Bridge Protocol Data Unit Format and Processing
Bit Function
19-12
Topology Changes
Processing Superior Bpdu Information
Processing Inferior Bpdu Information
19-13
Configuring Mstp Features
19-14
Default Mstp Configuration
Mstp Configuration Guidelines
19-15
Specifying the MST Region Configuration and Enabling Mstp
Spanning-tree mst configuration
Instance instance-id vlan vlan-range
Name name
Spanning-tree mode mst
Revision version
Show pending
Exit
Spanning-tree mst instance-id root primary
19-18
19-19
Spanning-tree mst instance-id port-priority priority
Show spanning-tree mst interface interface-id
19-20
Spanning-tree mst instance-id cost cost
19-21
Configuring the Switch Priority
Configuring the Hello Time
Spanning-tree mst instance-id priority priority
19-22
Configuring the Forwarding-Delay Time
Show spanning-tree mst Verify your entries
Spanning-tree mst forward-time seconds
Show spanning-tree mst
Configuring the Maximum-Aging Time
Configuring the Maximum-Hop Count
Specifying the Link Type to Ensure Rapid Transitions
Spanning-tree mst max-age seconds
Designating the Neighbor Type
19-25
Displaying the MST Configuration and Status
Restarting the Protocol Migration Process
19-26
Configuring Optional Spanning-Tree Features
Understanding Optional Spanning-Tree Features
20-1
Understanding Port Fast
Understanding Bpdu Guard
20-2
Understanding Bpdu Filtering
Understanding UplinkFast
20-3
Switches in a Hierarchical Network
20-4
Understanding Cross-Stack UplinkFast
20-5
How Csuf Works
20-6
Understanding BackboneFast
Events that Cause Fast Convergence
20-7
20-8
BackboneFast Example Before Indirect Link Failure
Adding a Switch in a Shared-Medium Topology
20-9
Understanding EtherChannel Guard
Understanding Root Guard
20-10
Understanding Loop Guard
20-11
Default Optional Spanning-Tree Configuration
Optional Spanning-Tree Configuration Guidelines
Enabling Port Fast
20-12
Spanning-tree portfast trunk interface configuration
Enabling Bpdu Guard
Spanning-tree portfast trunk
Portfast
Spanning-tree portfast Enable the Port Fast feature
Enabling Bpdu Filtering
20-14
Enabling UplinkFast for Use with Redundant Links
20-15
Spanning-tree uplinkfast max-update-rate
Uplinkfast command
Enabling Cross-Stack UplinkFast
Enabling BackboneFast
Spanning-tree backbonefast Enable BackboneFast
Enabling EtherChannel Guard
Show spanning-tree summary Verify your entries
20-17
Enabling Root Guard
Enabling Loop Guard
20-18
20-19
20-20
Flex Links
21-1
Switchport backup interface preemption delay commands
Vlan Flex Link Load Balancing and Support
21-2
MAC Address-Table Move Update
21-3
MAC Address-Table Move Update Example
21-4
Configuration Guidelines
Default Configuration
21-5
Configuring Flex Links
Switchport backup interface interface-id
Show interface interface-id switchport backup
Switch# show interface switchport backup
Switchport backup interface interface-id preemption
Mode forced bandwidth off
Delay delay-time
21-7
Configuring Vlan Load Balancing on Flex Links
Switchport backup interface interface-id prefer vlan
Show interfaces interface-id switchport backup
Switch#show interfaces switchport backup
Configuring the MAC Address-Table Move Update Feature
Switchport backup interface interface-idmmu
Primary vlan vlan-id
21-9
End Return to global configuration mode
Switchconf# mac address-table move update transmit
Switch# show mac-address-table move update
21-10
Monitoring Flex Links and the MAC Address-Table Move Update
21-11
21-12
Configuring Dhcp Features and IP Source Guard
Understanding Dhcp Features
22-1
Dhcp Server
Dhcp Relay Agent
Dhcp Snooping
22-2
Option-82 Data Insertion
22-3
22-4
Dhcp Relay Agent in a Metropolitan Ethernet Network
Remote ID Suboption Frame Format
22-5
Cisco IOS Dhcp Server Database
Dhcp Snooping Binding Database
Release
22-6
22-7
Configuring Dhcp Features
Dhcp Snooping and Switch Stacks
Default Dhcp Configuration
22-8
Dhcp Snooping Configuration Guidelines
22-9
Configuring the Dhcp Server
Dhcp Server and Switch Stacks
22-10
Configuring the Dhcp Relay Agent
Specifying the Packet Forwarding Address
Ip helper-address address
22-11
Switchport mode access
Switchport access vlan vlan-id
Enabling Dhcp Snooping and Option
Interface range port-range
22-13
Enabling Dhcp Snooping on Private VLANs
Enabling the Cisco IOS Dhcp Server Database
Enabling the Dhcp Snooping Binding Database Agent
Ip dhcp snooping database
Displaying Dhcp Snooping Information
22-15
Understanding IP Source Guard
Source IP Address Filtering
22-16
Configuring IP Source Guard
Default IP Source Guard Configuration
IP Source Guard Configuration Guidelines
Source IP and MAC Address Filtering
Enabling IP Source Guard
22-18
Displaying IP Source Guard Information
22-19
22-20
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
Understanding Dynamic ARP Inspection
23-1
23-2
ARP Cache Poisoning
Interface Trust States and Network Security
23-3
Rate Limiting of ARP Packets
Relative Priority of ARP ACLs and Dhcp Snooping Entries
23-4
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
Default Dynamic ARP Inspection Configuration
Logging of Dropped Packets
23-5
Dynamic ARP Inspection Configuration Guidelines
23-6
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection in Dhcp Environments
Show cdp neighbors
Ip arp inspection vlan vlan-range
23-7
Configuring ARP ACLs for Non-DHCP Environments
23-8
23-9
Show arp access-list acl-name
Limiting the Rate of Incoming ARP Packets
No ip arp inspection trust
Specified with the ip arp inspection vlan logging
Performing Validation Checks
23-11
Configuring the Log Buffer
Ip arp inspection validate
Src-mac dst-mac ip
Show ip arp inspection vlan
Ip arp inspection log-buffer entries
Number logs number interval
23-13
Displaying Dynamic ARP Inspection Information
23-14
Clear ip arp inspection statistics
Show ip arp inspection statistics vlan
Clear ip arp inspection log
Show ip arp inspection log
23-16
Configuring Igmp Snooping and MVR
24-1
Understanding Igmp Snooping
24-2
Igmp Versions
Joining a Multicast Group
24-3
224.1.2.3
24-4
Leaving a Multicast Group
24-5
Igmp Configurable-Leave Timer
Immediate Leave
Igmp Report Suppression
24-6
Configuring Igmp Snooping
Igmp Snooping and Switch Stacks
Default Igmp Snooping Configuration
PIM-DVMRP
Enabling or Disabling Igmp Snooping
Ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id
24-8
Setting the Snooping Method
Ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id mrouter
Learn cgmp pim-dvmrp
Show ip igmp snooping
Configuring a Multicast Router Port
Show ip igmp snooping mrouter vlan vlan-id
24-10
Configuring a Host Statically to Join a Group
Enabling Igmp Immediate Leave
Ip igmp snooping vlan vlan-id static ipaddress
Show ip igmp snooping groups
Configuring the Igmp Leave Timer
24-12
Configuring TCN-Related Commands
Recovering from Flood Mode
Controlling the Multicast Flooding Time After a TCN Event
Count
Disabling Multicast Flooding During a TCN Event
No ip igmp snooping tcn flood
24-14
Configuring the Igmp Snooping Querier
24-15
Disabling Igmp Report Suppression
No ip igmp snooping report-suppression
24-16
Displaying Igmp Snooping Information
24-17
Understanding Multicast Vlan Registration
24-18
Using MVR in a Multicast Television Application
24-19
Configuring MVR
Default MVR Configuration
MVR
24-20
MVR Configuration Guidelines and Limitations
Configuring MVR Global Parameters
Mvr Enable MVR on the switch
24-21
Configuring MVR Interfaces
24-22
Mvr type source receiver
Mvr immediate
Show mvr
Show mvr interface Show mvr members
Configuring Igmp Filtering and Throttling
Displaying MVR Information
24-24
Default Igmp Filtering and Throttling Configuration
Configuring Igmp Profiles
24-25
Ip igmp profile profile number
Permit deny
Range ip multicast address
Show ip igmp profile profile number
Setting the Maximum Number of Igmp Groups
Switch# show ip igmp profile
Applying Igmp Profiles
Ip igmp filter profile number
Configuring the Igmp Throttling Action
Show running-config interface Verify the configuration
EtherChannel group or a EtherChannel interface
Interface-id
Displaying Igmp Filtering and Throttling Configuration
Ip igmp max-groups action deny
Replace
Show ip igmp profile profile
24-30
Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
Understanding MLD Snooping
25-1
25-2
MLD Messages
MLD Queries
Multicast Client Aging Robustness
25-3
Multicast Router Discovery
MLD Reports
MLD Done Messages and Immediate-Leave
25-4
Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
MLD Snooping in Switch Stacks
Topology Change Notification Processing
25-5
Default MLD Snooping Configuration
MLD Snooping Configuration Guidelines
25-6
Enabling or Disabling MLD Snooping
Ipv6 mld snooping
Ipv6 mld snooping vlan vlan-id
25-7
Configuring a Static Multicast Group
Ipv6 mld snooping vlan vlan-id static
Show ipv6 mld snooping multicast-address user
Show ipv6 mld snooping multicast-address vlan
Enabling MLD Immediate Leave
Ipv6 mld snooping vlan vlan-id mrouter
Show ipv6 mld snooping mrouter vlan vlan-id
25-9
Configuring MLD Snooping Queries
25-10
Displaying MLD Snooping Information
Disabling MLD Listener Message Suppression
25-11
Show ipv6 mld snooping querier vlan vlan-id
Vlan-id count dynamic user
Vlan-id ipv6-multicast-address
25-12
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
Configuring Storm Control
Understanding Storm Control
26-1
26-2
Broadcast Storm Control Example
Default Storm Control Configuration
Configuring Storm Control and Threshold Levels
26-3
Storm-control broadcast multicast
Unicast level level level-low bps bps
Bps-low pps pps pps-low
Storm-control action shutdown trap
Configuring Protected Ports
Default Protected Port Configuration
Show storm-control interface-id broadcast
Multicast unicast
Configuring Port Blocking
Protected Port Configuration Guidelines
Configuring a Protected Port
26-6
Configuring Port Security
Default Port Blocking Configuration
Blocking Flooded Traffic on an Interface
26-7
Understanding Port Security
Secure MAC Addresses
26-8
Security Violations
26-9
Default Port Security Configuration
Port Security Configuration Guidelines
Forwarded1 Trap Message Message2 Increments
26-10
26-11
Enabling and Configuring Port Security
26-12
Switchport port-security violation
Protect restrict shutdown
Shutdown vlan
26-13
26-14
Switchconfig-if#switchport port-security
Switchconfig-if#switchport port-security maximum
Switchconfig-if#switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Switchconfig-if#switchport port-security violation restrict
Enabling and Configuring Port Security Aging
26-16
Port Security and Switch Stacks
Switchconfig# interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/8
Port Security and Private VLANs
26-17
Displaying Port-Based Traffic Control Settings
Show port-security interface interface-idaddress
Show port-security interface interface-idvlan
26-18
Configuring CDP
Understanding CDP
27-1
Configuring CDP
CDP and Switch Stacks
Default CDP Configuration
Configuring the CDP Characteristics
Disabling and Enabling CDP
Cdp holdtime seconds
Cdp advertise-v2
Show cdp
No cdp enable Disable CDP on the interface
Cdp enable Enable CDP on the interface after disabling it
Disabling and Enabling CDP on an Interface
27-4
Monitoring and Maintaining CDP
27-5
27-6
Configuring Lldp and LLDP-MED
Understanding Lldp and LLDP-MED
Understanding Lldp
28-1
Understanding LLDP-MED
28-2
Configuring Lldp and LLDP-MED
Default Lldp Configuration
Configuring Lldp Characteristics
28-3
Disabling and Enabling Lldp Globally
28-4
Disabling and Enabling Lldp on an Interface
28-5
Configuring LLDP-MED TLVs
TLV, and enter interface configuration mode
No lldp med-tlv-select tlv Specify the TLV to disable
Lldp med-tlv-select tlv Specify the TLV to enable
Monitoring and Maintaining Lldp and LLDP-MED
28-7
28-8
Configuring Udld
Understanding Udld
Modes of Operation
29-1
Methods to Detect Unidirectional Links
29-2
Configuring Udld
29-3
Default Udld Configuration
29-4
Udld aggressive enable message time
Message-timer-interval
Enabling Udld Globally
Show udld
Resetting an Interface Disabled by Udld
Udld reset Show udld
Enabling Udld on an Interface
Udld port aggressive
Displaying Udld Status
29-7
29-8
Configuring Span and Rspan
Understanding Span and Rspan
30-1
Local Span
30-2
Remote Span
30-3
Span and Rspan Concepts and Terminology
Span Sessions
30-4
Monitored Traffic
30-5
Source Ports
30-6
Source VLANs
Vlan Filtering
30-7
Destination Port
30-8
Span and Rspan Interaction with Other Features
Rspan Vlan
30-9
Configuring Span and Rspan
Span and Rspan and Switch Stacks
30-10
Default Span and Rspan Configuration
Configuring Local Span
Span Configuration Guidelines
30-11
Creating a Local Span Session
30-12
Monitor session sessionnumber
Destination interface interface-id
Encapsulation replicate
Show monitor session sessionnumber
30-14
Specifying VLANs to Filter
Monitor session sessionnumber filter vlan
30-15
Configuring Rspan
Rspan Configuration Guidelines
Be a Vlan
30-16
Configuring a Vlan as an Rspan Vlan
30-17
Creating an Rspan Source Session
Interfaces port-channelport-channel-number. Valid
Destination remote vlan vlan-id
30-18
Creating an Rspan Destination Session
Remote vlan vlan-id
30-19
30-20
Ingress dot1q vlan vlan-id isl untagged
Untagged vlan vlan-id or vlan vlan-id- Forward incoming
30-21
Show monitor session sessionnumber
30-22
Displaying Span and Rspan Status
30-23
30-24
Configuring Rmon
Understanding Rmon
31-1
Configuring Rmon
31-2
Default Rmon Configuration
Configuring Rmon Alarms and Events
31-3
Rmon event number description string log owner string
Add an event in the Rmon event table that is
31-4
Collecting Group History Statistics on an Interface
Collecting Group Ethernet Statistics on an Interface
Rmon collection history index
Show rmon history
Displaying Rmon Status
Rmon collection stats index owner ownername
Show rmon statistics
31-6
Configuring System Message Logging
Understanding System Message Logging
32-1
Configuring System Message Logging
System Log Message Format
32-2
Hhmmss short uptime
Text string that uniquely describes the message
32-3
Default System Message Logging Configuration
No logging console Disable message logging
Show running-config Verify your entries Show logging
Disabling Message Logging
Setting the Message Display Destination Device
Logging buffered size
Logging host
32-5
Synchronizing Log Messages
Logging file flash filename
Terminal monitor
Session to see the debugging messages
Line console vty line-number
Line vty
Logging synchronous level severity-level
All limit number-of-buffers
Enabling and Disabling Time Stamps on Log Messages
Enabling and Disabling Sequence Numbers in Log Messages
32-8
Defining the Message Severity Level
Logging console level
Logging monitor level
Logging trap level
Level Description Syslog Definition
32-10
Enabling the Configuration-Change Logger
Logging history level
Logging history size number
32-11
Configuring Unix Syslog Servers
Logging Messages to a Unix Syslog Daemon
32-12
Configuring the Unix System Logging Facility
Logging facility facility-type
Facility-type keywords
32-13
Displaying the Logging Configuration
Facility Type Keyword Description
32-14
Configuring Snmp
Understanding Snmp
33-1
Snmp Versions
33-2
Model Level Authentication Encryption Result
Snmp Manager Functions
DES
Operation Description
Using Snmp to Access MIB Variables
Snmp Agent Functions
33-4
Snmp Notifications
33-5
Configuring Snmp
Snmp ifIndex MIB Object Values
IfIndex Range
SVI
Default Snmp Configuration
Snmp Configuration Guidelines
33-7
Configuring Community Strings
No snmp-server Disable the Snmp agent operation
Disabling the Snmp Agent
33-8
View-name ro rw access-list-number
Access-list access-list-number deny
Snmp-server community string view
Permit source source-wildcard
Configuring Snmp Groups and Users
Snmp-server engineID local engineid-string
Snmp-server engineID local
33-10
Write writeview notify notifyview access
Snmp-server group groupname v1 v2c
Auth noauth priv read readview
33-11
Configuring Snmp Notifications
Remote host udp-port port v1 access
Encrypted access access-list auth md5
Notification Type Keyword Description
33-13
33-14
Setting the Agent Contact and Location Information
33-12 , or enter snmp-server enable traps ?
Enable traps command for each trap type
Notification-types
Switchconfig# snmp-server community public
Limiting Tftp Servers Used Through Snmp
Snmp Examples
Snmp-server tftp-server-list
Displaying Snmp Status
33-17
33-18
Configuring Network Security with ACLs
Understanding ACLs
34-1
Supported ACLs
34-2
Port ACLs
34-3
Router ACLs
34-4
Handling Fragmented and Unfragmented Traffic
Vlan Maps
34-5
ACLs and Switch Stacks
34-6
Configuring IPv4 ACLs
34-7
Access List Numbers
Access List Number Type Supported
Creating Standard and Extended IPv4 ACLs
34-8
ACL Logging
34-9
Access-list access-list-number deny permit
Show access-lists number name
Creating a Numbered Standard ACL
Source source-wildcard log
Creating a Numbered Extended ACL
34-11
34-12
34-13
34-14
Resequencing ACEs in an ACL
Creating Named Standard and Extended ACLs
34-15
Ip access-list standard name
Ip access-list extended name
Any log
Tos tos established log time-range
Using Time Ranges with ACLs
34-17
Absolute start time date
Periodic weekdays weekend daily
Show time-range
34-18
Switch# show ip access-lists
Applying an IPv4 ACL to a Terminal Line
Including Comments in ACLs
34-19
Access-class access-list-number
Applying an IPv4 ACL to an Interface
Out
34-20
Ip access-group access-list-number
34-21
IPv4 ACL Configuration Examples
Hardware and Software Treatment of IP ACLs
34-22
Switchconfig# access-list 6 permit 172.20.128.64
Switchconfig# access-list 106 permit ip any 172.20.128.64
34-23
Numbered ACLs
Extended ACLs
34-24
Named ACLs
Time Range Applied to an IP ACL
Commented IP ACL Entries
34-25
Switch# show logging
Switchconfig-if#ip access-group ext1
34-26
Creating Named MAC Extended ACLs
34-27
Applying a MAC ACL to a Layer 2 Interface
34-28
Configuring Vlan Maps
Mac access-group name
Show mac access-group interface interface-id
ACL
Vlan Map Configuration Guidelines
34-30
Vlan access-map name number
Creating a Vlan Map
Action drop forward
Match ip mac address name
Examples of ACLs and Vlan Maps
34-32
34-33
Using Vlan Maps in Your Network
Wiring Closet Configuration
Applying a Vlan Map to a Vlan
Vlan filter mapname vlan-list list
Denying Access to a Server on Anothera Vlan
Switchconfig# vlan access-map map2
Switchconfig# ip access-list extended matchall
Switchconfig# vlan filter map2 vlan
Using Vlan Maps with Router ACLs
34-36
Vlan Maps and Router ACL Configuration Guidelines
34-37
ACLs and Switched Packets
Examples of Router ACLs and Vlan Maps Applied to VLANs
ACLs and Bridged Packets
34-38
ACLs and Routed Packets
34-39
Displaying IPv4 ACL Configuration
Show ip access-lists number name
ACLs and Multicast Packets
34-40
Show running-config interface interface-id
Show mac access-group interface interface-id
Show ip interface interface-id
34-41
34-42
Configuring IPv6 ACLs
35-1
Understanding IPv6 ACLs
35-2
Supported ACL Features
IPv6 ACLs and Switch Stacks
IPv6 ACL Limitations
35-3
Configuring IPv6 ACLs
Default IPv6 ACL Configuration
Interaction with Other Features and Switches
35-4
Ipv6 access-list access-list-name
Creating IPv6 ACLs
35-5
Dscp value fragments log
Log-input routing sequence
Value time-range name
35-6
35-7
Ipv6 traffic-filter access-list-name
Applying an IPv6 ACL to an Interface
Ipv6 address ipv6-address
35-8
Show access-lists
Show ipv6 access-list access-list-name
Displaying IPv6 ACLs
35-9
35-10
Configuring QoS
36-1
Understanding QoS
36-2
Basic QoS Model
36-3
36-4
Basic QoS Model
Classification
36-5
36-6
Check if packet came with CoS label tag Yes
Classification Based on QoS ACLs
Classification Based on Class Maps and Policy Maps
36-7
Policing and Marking
36-8
Policing on Physical Ports
36-9
Policing on SVIs
36-10
Policing and Marking Flowchart on SVIs
36-11
Mapping Tables
36-12
Queueing and Scheduling Overview
36-13
Weighted Tail Drop
SRR Shaping and Sharing
36-14
Queueing and Scheduling on Ingress Queues
36-15
Queue Type Function
36-16
WTD Thresholds
36-17
Queueing and Scheduling on Egress Queues
36-18
36-19
Buffer and Memory Allocation
36-20
Packet Modification
36-21
Configuring Auto-QoS
36-22
Generated Auto-QoS Configuration
36-23
Description Automatically Generated Command
36-24
36-25
Switch automatically configures the egress queue buffer
Sizes. It configures the bandwidth and the SRR mode shaped
If you entered the auto qos voip trust command, the switch
Or shared on the egress queues mapped to the port
Effects of Auto-QoS on the Configuration
Auto-QoS Configuration Guidelines
36-27
Enabling Auto-QoS for VoIP
Auto qos voip cisco-phone
Cisco-softphone trust
Show auto qos interface interface-id
36-29
Auto-QoS Configuration Example
36-30
Cdp enable
Debug auto qos
Auto qos voip trust
Show auto qos
Configuring Standard QoS
Displaying Auto-QoS Information
36-32
Default Standard QoS Configuration
Default Ingress Queue Configuration
36-33
Default Egress Queue Configuration
Dscp Value Queue ID -Threshold ID
36-34
Standard QoS Configuration Guidelines
Default Mapping Table Configuration
QoS ACL Guidelines
Applying QoS on Interfaces
Policing Guidelines
General QoS Guidelines
36-36
Enabling QoS Globally
Enabling VLAN-Based QoS on Physical Ports
36-37
Configuring Classification Using Port Trust States
Configuring the Trust State on Ports within the QoS Domain
36-38
36-39
15 Port Trusted States within the QoS Domain
Configuring the CoS Value for an Interface
Mls qos trust cos dscp ip-precedence
Show mls qos interface
36-40
Configuring a Trusted Boundary to Ensure Port Security
Mls qos cos default-cos override
36-41
Enabling Dscp Transparency Mode
Mls qos trust dscp
Mls qos trust device cisco-phone
36-42
No mls qos rewrite ip dscp
36-43
Mls qos map dscp-mutation
Mls qos dscp-mutation
Show mls qos maps dscp-mutation
36-44
Configuring a QoS Policy
Switchconfig-if#mls qos dscp-mutation gi1/0/2-mutation
36-45
Classifying Traffic by Using ACLs
36-46
Switchconfig# access-list 100 permit ip any any dscp
Switchconfig# access-list 102 permit pim any 224.0.0.2 dscp
Permit protocol source source-wildcard
Source-wildcard
Mac access-list extended name
36-48
Classifying Traffic by Using Class Maps
Class-map match-all match-any
Is match-all
Match-any keywords
Match access-group acl-index-or-name
Ip dscp dscp-list ip precedence
Ip-precedence-list
Show class-map
36-51
Policy-map policy-map-name
Class class-map-name
36-52
36-53
Service-policy input policy-map-name
Show policy-map policy-map-nameclass
36-54
Switchconfig# policy-map macpolicy1
Switchconfig-pmap#class macclass2 maclist2
Switchconfig-if#service-policy input macpolicy1
36-55
Traffic by Using Class Maps section on
36-56
36-57
Police rate-bps burst-byte exceed-action
Drop policed-dscp-transmit
Exceed-action policed-dscp-transmit keywords to mark down
36-58
Service-policy policy-map-name
36-59
Service-policy input policy-map-name
Show policy-map policy-map-nameclass
Show mls qos vlan-based
Mls qos aggregate-policer
Aggregate-policer-name rate-bps burst-byte
Exceed-action drop
Policed-dscp-transmit
Only one policy map per ingress port is supported
Show mls qos aggregate-policer
Aggregate-policer-name
Configuring Dscp Maps
Configuring the CoS-to-DSCP Map
Switchconfig-pmap-c#police aggregate transmit1
CoS Value Dscp Value
Configuring the IP-Precedence-to-DSCP Map
Mls qos map cos-dscp dscp1...dscp8
IP Precedence Value Dscp Value
36-64
Configuring the Policed-DSCP Map
36-65
Configuring the DSCP-to-CoS Map
Dscp Value CoS Value
36-66
Show
Configuring the DSCP-to-DSCP-Mutation Map
Mls qos map dscp-cos dscp-list to cos
Show mls qos maps dscp-to-cos
36-67
Switchconfig-if#mls qos dscp-mutation mutation1
Switch# show mls qos maps dscp-mutation mutation1
36-68
Configuring Ingress Queue Characteristics
36-69
Mls qos srr-queue input dscp-map
Mls qos srr-queue input cos-map
Mls qos srr-queue input threshold
Show mls qos maps
Allocating Buffer Space Between the Ingress Queues
Allocating Bandwidth Between the Ingress Queues
Mls qos srr-queue input buffers
Show mls qos interface buffer
Configuring the Ingress Priority Queue
Weight1 weight2
Mls qos srr-queue input bandwidth
Show mls qos interface queueing
Configuring Egress Queue Characteristics
Weight
Mls qos srr-queue input
Priority-queue queue-id bandwidth
36-74
Mls qos queue-set output qset-id
Queue-set qset-id
36-75
36-76
Mls qos srr-queue output dscp-map
Mls qos srr-queue output cos-map
36-77
Configuring SRR Shaped Weights on Egress Queues
Srr-queue bandwidth shape weight1
Weight2 weight3 weight4
Queueing
Configuring SRR Shared Weights on Egress Queues
Configuring the Egress Expedite Queue
Srr-queue bandwidth share weight1
36-79
Mls qos Enable QoS on a switch
Srr-queue bandwidth limit weight1
Limiting the Bandwidth on an Egress Interface
36-80
Displaying Standard QoS Information
36-81
Show running-config include rewrite
36-82
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
Understanding EtherChannels
37-1
EtherChannel Overview
37-2
Single-Switch EtherChannel
37-3
Port-Channel Interfaces
37-4
Port Aggregation Protocol
37-5
PAgP Interaction with Other Features
Mode Description
PAgP Modes
Auto
Lacp Interaction with Other Features
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Lacp Modes
37-7
EtherChannel On Mode
Load-Balancing and Forwarding Methods
37-8
37-9
EtherChannel and Switch Stacks
37-10
Configuring EtherChannels
Default EtherChannel Configuration
37-11
EtherChannel Configuration Guidelines
37-12
Configuring Layer 2 EtherChannels
37-13
Auto non-silent desirable non-silent on
Active passive
37-14
Configuring Layer 3 EtherChannels
Switchconfig-if-range#channel-group 5 mode active
Creating Port-Channel Logical Interfaces
37-15
Configuring the Physical Interfaces
Interface port-channel port-channel-number
Show etherchannel channel-group-number detail
No ip address
Partner that is PAgP capable, configure the switch port for
For channel-group-number, the range is 1 to 48. This number
Must be the same as the port-channel-number logical port
37-17
Configuring EtherChannel Load-Balancing
Port-channel load-balance dst-ip dst-mac
Src-dst-ip src-dst-mac src-ip src-mac
37-18
Configuring the PAgP Learn Method and Priority
Show etherchannel load-balance Verify your entries
37-19
Configuring Lacp Hot-Standby Ports
Pagp learn-method physical-port
Pagp port-priority priority
Show pagp channel-group-number internal
Configuring the Lacp System Priority
Show running-config Verify your entries Show lacp sys-id
37-21
Configuring the Lacp Port Priority
Lacp port-priority priority
Show lacp channel-group-number
Internal
Displaying EtherChannel, PAgP, and Lacp Status
Understanding Link-State Tracking
37-23
37-24
Configuring Link-State Tracking
37-25
Default Link-State Tracking Configuration
Link-State Tracking Configuration Guidelines
Configuring Link-State Tracking
37-26
Switch show link state group
Switch show link state group detail
Displaying Link-State Tracking Status
37-27
37-28
Configuring IP Unicast Routing
38-1
Understanding IP Routing
Types of Routing
38-2
IP Routing and Switch Stacks
38-3
38-4
Steps for Configuring Routing
Configuring IP Addressing
38-5
Default Addressing Configuration
ARP
Irdp
38-6
Show running-config Verify your entry
Assigning IP Addresses to Network Interfaces
Use of Subnet Zero
38-7
Classless Routing
38-8
Configuring Address Resolution Methods
No ip classless Disable classless routing behavior
38-9
Define a Static ARP Cache
Arp ip-address hardware-address type
38-10
Set ARP Encapsulation
38-11
Routing Assistance When IP Routing is Disabled
Enable Proxy ARP
Default Gateway
Proxy ARP
Icmp Router Discovery Protocol Irdp
38-13
Configuring Broadcast Packet Handling
38-14
Ip directed-broadcast access-list-number
Ip forward-protocol udp port nd sdns
38-15
Forwarding UDP Broadcast Packets and Protocols
38-16
Establishing an IP Broadcast Address
Flooding IP Broadcasts
Ip broadcast-address ip-address
38-17
Monitoring and Maintaining IP Addressing
Clear arp-cache
Clear host name
Clear ip route network mask
Enabling IP Unicast Routing
38-19
Configuring RIP
38-20
Default RIP Configuration
Configuring Basic RIP Parameters
Router rip
Network network number
38-22
Configuring RIP Authentication
Configuring Summary Addresses and Split Horizon
Ip rip authentication key-chain name-of-chain
Ip rip authentication mode text md5
Configuring Split Horizon
Switchconfig-router#neighbor 2.2.2.2 peer-group mygroup
Ip summary-address rip ip address ip-network mask
No ip split horizon
Configuring Ospf
No ip split-horizon
38-25
Default Ospf Configuration
38-26
Ospf Nonstop Forwarding
38-27
Ospf NSF Awareness
38-28
Configuring Basic Ospf Parameters
Configuring Ospf Interfaces
38-29
38-30
Configuring Ospf Area Parameters
38-31
Configuring Other Ospf Parameters
38-32
38-33
Configuring a Loopback Interface
Changing LSA Group Pacing
Ip address address mask
38-34
Configuring Eigrp
Monitoring Ospf
38-35
38-36
Default Eigrp Configuration
38-37
Eigrp Nonstop Forwarding
38-38
Configuring Basic Eigrp Parameters
Router eigrp autonomous-system
Network network-number
Eigrp log-neighbor-changes
Configuring Eigrp Interfaces
No auto-summary
Ip summary-address eigrp
38-40
Configuring Eigrp Route Authentication
Ip hello-interval eigrp autonomous-system-number
No ip split-horizon eigrp autonomous-system-number
Show ip eigrp interface
Eigrp Stub Routing
38-42
Configuring BGP
Monitoring and Maintaining Eigrp
38-43
38-44
EBGP, IBGP, and Multiple Autonomous Systems
Default BGP Configuration
38-45
38-46
Nonstop Forwarding Awareness
38-47
Enabling BGP Routing
Router bgp autonomous-system
Network network-number mask network-mask
Route-map route-map-name
38-49
Switchconfig-router#neighbor 192.208.10.2 remote-as
Switch# show ip bgp neighbors
Managing Routing Policy Changes
38-50
Type of Reset Advantages Disadvantages
Show ip bgp neighbors
Clear ip bgp * address
Show ip bgp
Configuring BGP Decision Attributes
38-52
38-53
Configuring BGP Filtering with Route Maps
Configuring BGP Filtering by Neighbor
38-54
Ip as-path access-list access-list-number
Out weight weight
Route-map map-tag in out
Show ip bgp neighbors paths
Configuring Prefix Lists for BGP Filtering
38-56
Configuring BGP Community Filtering
Ip community-listcommunity-list-number
Permit deny community-number
Send-community
Configuring BGP Neighbors and Peer Groups
Set comm-list list-num delete
Ip bgp-community new-format
Show ip bgp community
38-59
Configuring Aggregate Addresses
38-60
Configuring Routing Domain Confederations
Configuring BGP Route Reflectors
38-61
Configuring Route Dampening
Route-reflector-client
Bgp cluster-id cluster-id
No bgp client-to-client reflection
Monitoring and Maintaining BGP
38-63
Configuring Multi-VRF CE
38-64
Understanding Multi-VRF CE
38-65
38-66
Default Multi-VRF CE Configuration
Multi-VRF CE Configuration Guidelines
VRF
38-67
Configuring VRFs
Route-target export import both
Import map route-map
Ip vrf forwarding vrf-name
Configuring a VPN Routing Session
Show ip vrf brief detail interfaces
Log-adjacency-changes
Redistribute bgp
Configuring BGP PE to CE Routing Sessions
Multi-VRF CE Configuration Example
38-70
38-71
VPN2 CE1
Configuring Switch a
38-72
Switchconfig-router-af#network 8.8.2.0 mask
Switchconfig-router-af#network 8.8.1.0 mask
Switchconfig-if#ip address 208.0.0.20
38-73
Router# configure terminal
38-74
Configuring Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding
Displaying Multi-VRF CE Status
38-75
Configuring Protocol-Independent Features
Configuring Distributed Cisco Express Forwarding
38-76
Configuring the Number of Equal-Cost Routing Paths
38-77
Configuring Static Unicast Routes
Router bgp rip ospf eigrp
Maximum-paths maximum
Show ip route
Specifying Default Routes and Networks
Route Source Default Distance
Ip default-network network number Specify a default network
38-79
Using Route Maps to Redistribute Routing Information
38-80
38-81
38-82
Configuring Policy-Based Routing
38-83
PBR Configuration Guidelines
38-84
Enabling PBR
38-85
Ip policy route-map map-tag
Ip route-cache policy
Ip local policy route-map map-tag
38-86
Setting Passive Interfaces
Filtering Routing Information
38-87
Controlling Advertising and Processing in Routing Updates
Filtering Sources of Routing Information
Router bgp rip eigrp
38-88
Managing Authentication Keys
Distance weight ip-address ip-address mask
Ip access list
38-89
Monitoring and Maintaining the IP Network
38-90
38-91
38-92
Configuring IPv6 Unicast Routing
Understanding IPv6
39-1
IPv6 Addresses
39-2
Supported IPv6 Unicast Routing Features
Bit Wide Unicast Addresses
39-3
DNS for IPv6
Path MTU Discovery for IPv6 Unicast
ICMPv6
Neighbor Discovery
IPv6 Applications
39-5
Unsupported IPv6 Unicast Routing Features
Dual IPv4 and IPv6 Protocol Stacks
39-6
IPv6 and Switch Stacks
Limitations
39-7
39-8
SDM Templates
Dual IPv4-and IPv6 SDM Templates
39-9
Configuring IPv6
39-10
Default IPv6 Configuration
Configuring IPv6 Addressing and Enabling IPv6 Routing
39-11
39-12
Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Protocol Stacks
Ip routing Enable routing on the switch
Switchconfig-if#ipv6 address 20010DB8c181/64 eui
39-13
39-14
Configuring IPv6 Icmp Rate Limiting
Configuring CEF and dCEF for IPv6
Ipv6 icmp error-interval interval bucketsize
Show ipv6 interface interface-id
Configuring Static Routing for IPv6
39-16
Administrative distance
Ipv6 route ipv6-prefix/prefix length
Ipv6-address interface-id ipv6-address
39-17
Configuring RIP for IPv6
Show ipv6 route static updated
Show ipv6 static ipv6-address
Interface-id recursive detail
39-19
Configuring Ospf for IPv6
39-20
39-21
Switch# show ipv6 interface
Displaying IPv6
39-22
Switch# show ipv6 cef /0
Switch# show ipv6 protocols
Switch# show ipv6 rip
39-23
Switch# show ipv6 neighbors
Switch# show ipv6 static
Switch# show ipv6 route
Switch# show ipv6 traffic
39-25
39-26
Configuring Hsrp and Enhanced Object Tracking
Understanding Hsrp
40-1
40-2
Multiple Hsrp
40-3
Configuring Hsrp
Hsrp and Switch Stacks
40-4
Default Hsrp Configuration
Hsrp Configuration Guidelines
Enabling Hsrp
40-5
Switch# show standby
Standby group-number ip ip-address
Secondary
Show standby interface-id group
Configuring Hsrp Priority
40-7
Priority preempt delay delay
Standby group-number priority
Standby group-number track
40-8
Configuring Mhsrp
Configuring Hsrp Authentication and Timers
Switchconfig-if#standby 2 ip
40-9
Standby group-number authentication string
Standby group-number timers hellotime
Switchconfig-if#standby 1 authentication word
Holdtime
Displaying Hsrp Configurations
Configuring Hsrp Groups and Clustering
Enabling Hsrp Support for Icmp Redirect Messages
Show standby interface-idgroup brief detail
Configuring Enhanced Object Tracking
Understanding Enhanced Object Tracking
40-12
Configuring Enhanced Object Tracking Features
Tracking Interface Line-Protocol or IP Routing State
Track object-number interface
40-13
Configuring a Tracked List
Switch# show track 33 Track
Track track-numberlist boolean
Object object-number not
Weight
Threshold weight up number
Track track-numberlist threshold
40-15
Track track-number list threshold
Percentage
Object object-number
Threshold percentage up number
Configuring Hsrp Object Tracking
40-17
Configuring Other Tracking Characteristics
Show standby
40-18
Configuring Web Cache Services By Using
Understanding Wccp
41-1
Wccp Message Exchange
41-2
Packet Redirection and Service Groups
Wccp Negotiation
MD5 Security
41-3
Wccp and Switch Stacks
41-4
Configuring Wccp
Unsupported Wccp Features
Default Wccp Configuration
Wccp Configuration Guidelines
Enabling the Web Cache Service
41-6
41-7
41-8
Switchconfig# interface range gigabitethernet1/0/3
Switchconfig-if-range#switchport access vlan
Monitoring and Maintaining Wccp
41-9
Enabled / disabled
41-10
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
42-1
42-2
IP Multicast Routing Protocols
Understanding Igmp
Igmp Version
42-3
Understanding PIM
PIM Versions
PIM Modes
42-4
PIM Stub Routing
42-5
Auto-RP
42-6
Bootstrap Router
Multicast Forwarding and Reverse Path Check
42-7
Understanding Dvmrp
Network Port
42-8
Multicast Routing and Switch Stacks
Understanding Cgmp
42-9
Configuring IP Multicast Routing
Default Multicast Routing Configuration
Multicast Routing Configuration Guidelines
42-10
Auto-RP and BSR Configuration Guidelines
PIMv1 and PIMv2 Interoperability
42-11
Configuring Basic Multicast Routing
Ip multicast-routing distributed
42-12
Configuring PIM Stub Routing
Ip pim version 1
Ip pim dense-mode sparse-mode
Sparse-dense-mode
Configuring a Rendezvous Point
Manually Assigning an RP to Multicast Groups
Ip pim passive
42-14
Access-list-number override
Ip pim rp-address ip-address
42-15
Configuring Auto-RP
42-16
Scope ttl group-list access-list-number
Ip pim send-rp-announce interface-id
Interval seconds
42-17
Ip pim send-rp-discovery scope ttl
Show ip pim rp mapping
Show ip pim rp
42-18
Access-list-number group-list
Ip pim rp-announce-filter rp-list
42-19
Configuring PIMv2 BSR
Ip pim bsr-border
42-20
Ip multicast boundary
42-21
Ip pim bsr-candidate interface-id
Hash-mask-length priority
42-22
Group-list access-list-number
Ip pim rp-candidate interface-id
42-23
Using Auto-RP and a BSR
Show ip pim rp group-name
Group-address mapping
Show ip pim rp-hash group
Configuring Advanced PIM Features
Troubleshooting PIMv1 and PIMv2 Interoperability Problems
Monitoring the RP Mapping Information
Understanding PIM Shared Tree and Source Tree
42-26
Shared Tree and Source Tree Shortest-Path Tree
Delaying the Use of PIM Shortest-Path Tree
Ip pim spt-threshold kbps infinity
42-27
Configuring Optional Igmp Features
Modifying the PIM Router-Query Message Interval
Ip pim query-interval seconds
Show ip igmp interface interface-id
Default Igmp Configuration
Configuring the Switch as a Member of a Group
Ip igmp join-group group-address
42-29
Controlling Access to IP Multicast Groups
Ip igmp access-group access-list-number
Show ip igmp interface interface-id Verify your entries
42-30
Changing the Igmp Version
Modifying the Igmp Host-Query Message Interval
Ip igmp version 1
Query-interval or the ip igmp query-max-response-time
Changing the Igmp Query Timeout for IGMPv2
Ip igmp querier-timeout seconds
Ip igmp query-interval seconds
42-32
Configuring the Switch as a Statically Connected Member
Changing the Maximum Query Response Time for IGMPv2
Ip igmp query-max-response-time
42-33
Configuring Optional Multicast Routing Features
Enabling Cgmp Server Support
Ip igmp static-group group-address
42-34
Configuring sdr Listener Support
Ip cgmp proxy
42-35
Ip sdr listen Enable sdr listener support
Enabling sdr Listener Support
Limiting How Long an sdr Cache Entry Exists
42-36
Configuring an IP Multicast Boundary
42-37
Configuring Basic Dvmrp Interoperability Features
42-38
Configuring Dvmrp Interoperability
42-39
Ip dvmrp metric metric list
42-40
Configuring a Dvmrp Tunnel
42-41
Access-list-number distance
Neighbor-list access-list-number
Advertising Network 0.0.0.0 to Dvmrp Neighbors
Ip dvmrp accept-filter
Configuring Advanced Dvmrp Interoperability Features
Ip dvmrp default-information
Responding to mrinfo Requests
Originate only
Enabling Dvmrp Unicast Routing
42-44
Rejecting a Dvmrp Nonpruning Neighbor
42-45
Enter interface configuration mode
42-46
By default, 7000 routes are advertised. The range is 0 to
Controlling Route Exchanges
Limiting the Number of Dvmrp Routes Advertised
Changing the Dvmrp Route Threshold
Configuring a Dvmrp Summary Address
Default is 10,000 routes. The range is 1 to
Route-count
42-48
42-49
Disabling Dvmrp Autosummarization
Ip dvmrp summary-address address
Mask metric value
No ip dvmrp auto-summary
Adding a Metric Offset to the Dvmrp Route
Ip dvmrp metric-offset in out
Increment
42-51
Monitoring and Maintaining IP Multicast Routing
Clearing Caches, Tables, and Databases
Displaying System and Network Statistics
42-52
Monitoring IP Multicast Routing
42-53
42-54
Configuring Msdp
Understanding Msdp
43-1
Msdp Operation
43-2
Msdp Benefits
43-3
Configuring Msdp
Default Msdp Configuration
Configuring a Default Msdp Peer
43-4
Ip msdp default-peer ip-address name
Prefix-list list
43-5
Caching Source-Active State
Ip prefix-list name description string
Seq number permit deny network
Ip msdp description peer-name
Ip msdp cache-sa-state list
43-7
Switchconfig# ip msdp sa-request
Requesting Source Information from an Msdp Peer
Ip msdp sa-request ip-address name
43-8
Controlling Source Information that Your Switch Originates
Redistributing Sources
Ip msdp redistribute list
43-9
43-10
Name list access-list-number
Filtering Source-Active Request Messages
Ip msdp filter-sa-request ip-address
43-11
Controlling Source Information that Your Switch Forwards
Using a Filter
Ip msdp sa-filter out ip-address name
Route-map map-tag
43-13
Controlling Source Information that Your Switch Receives
Using TTL to Limit the Multicast Data Sent in SA Messages
Ip msdp ttl-threshold ip-address name
Ttl
Switchconfig# ip msdp sa-filter in switch.cisco.com
Ip msdp sa-filter in ip-address name
43-15
Configuring an Msdp Mesh Group
Shutting Down an Msdp Peer
Ip msdp mesh-group name ip-address
43-16
Including a Bordering PIM Dense-Mode Region in Msdp
Ip msdp shutdown peer-name peer
Ip msdp border sa-address interface-id
43-17
Configuring an Originating Address other than the RP Address
43-18
Monitoring and Maintaining Msdp
Clear ip msdp peer peer-addressname
Clear ip msdp statistics peer-addressname
Clear ip msdp sa-cache group-addressname
43-20
Configuring Fallback Bridging
Understanding Fallback Bridging
Fallback Bridging Overview
44-1
44-2
Configuring Fallback Bridging
Fallback Bridging and Switch Stacks
44-3
Default Fallback Bridging Configuration
Fallback Bridging Configuration Guidelines
Creating a Bridge Group
44-4
Bridge bridge-group protocol
Vlan-bridge
Bridge-group bridge-group
44-5
Adjusting Spanning-Tree Parameters
Switchconfig# bridge 10 protocol vlan-bridge
44-6
Changing the VLAN-Bridge Spanning-Tree Priority
Changing the Interface Priority
Bridge bridge-group priority number
Bridge-group bridge-grouppriority
Assigning a Path Cost
Bridge-group bridge-group path-cost
Cost
44-8
Adjusting Bpdu Intervals
Switchconfig# bridge 10 hello-time
Bridge bridge-group hello-time seconds
44-9
Switchconfig# bridge 10 forward-time
Switchconfig# bridge 10 max-age
Bridge bridge-group forward-time
Bridge bridge-group max-age seconds
Monitoring and Maintaining Fallback Bridging
Disabling the Spanning Tree on an Interface
Clear bridge bridge-group
Show bridge bridge-group group
44-12
Troubleshooting
45-1
Recovering from a Software Failure
45-2
Recovering from a Lost or Forgotten Password
Switch flashinit
Switch loadhelper
Switch copy xmodem flashimagefilename.bin
45-4
Procedure with Password Recovery Enabled
45-5
Copy the configuration file into memory
45-6
Procedure with Password Recovery Disabled
Switch dir flash
45-7
Preventing Switch Stack Problems
45-8
Recovering from a Command Switch Failure
45-9
Replacing a Failed Command Switch with a Cluster Member
Switchconfig# no cluster commander-address
45-10
Replacing a Failed Command Switch with Another Switch
45-11
45-12
Recovering from Lost Cluster Member Connectivity
Troubleshooting Power over Ethernet Switch Ports
Preventing Autonegotiation Mismatches
45-13
Disabled Port Caused by Power Loss
Disabled Port Caused by False Link Up
Show controllers power inline privileged Exec command
SFP Module Security and Identification
Monitoring Temperature
Using Ping
Monitoring SFP Module Status
Understanding Ping
Switch# ping
Executing Ping
Character Description
45-16
Using Layer 2 Traceroute
Understanding Layer 2 Traceroute
Usage Guidelines
45-17
Using IP Traceroute
Displaying the Physical Path
Understanding IP Traceroute
45-18
Switch# traceroute ip
Executing IP Traceroute
Traceroute ip host
Trace the path that packets take through the network
Using TDR
Understanding TDR
45-20
Using Debug Commands
Enabling Debugging on a Specific Feature
Running TDR and Displaying the Results
45-21
Enabling All-System Diagnostics
Redirecting Debug and Error Message Output
45-22
Using the show platform forward Command
45-23
Udp 10
45-24
Using the crashinfo Files
Basic crashinfo Files
45-25
Using On-Board Failure Logging
Extended crashinfo Files
Understanding Obfl
45-26
Configuring Obfl
45-27
Displaying Obfl Information
Show logging onboard module
45-28
Configuring Online Diagnostics
Understanding Online Diagnostics
46-1
Configuring Online Diagnostics
Scheduling Online Diagnostics
Diagnostic schedule switch
Non-disruptive daily hhmm
Configuring Health-Monitoring Diagnostics
Diagnostic monitor interval switch
Diagnostic content command output
Diagnostic monitor syslog
Diagnostic monitor threshold switch
Diagnostic monitor switch number test
Show diagnostic content post result
Schedule status switch
Running Online Diagnostic Tests
Starting Online Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic start switch number
All basic non-disruptive
Displaying Online Diagnostic Tests and Test Results
46-6
Supported MIBs
MIB List
CISCO-FTP-CLIENT-MIB CISCO-HSRP-MIB
CISCO-IGMP-FILTER-MIB
CISCO-RTTMON-MIB CISCO-SMI-MIB
ETHERLIKE-MIB IEEE8021-PAE-MIB IEEE8023-LAG-MIB
IGMP-MIB INET-ADDRESS-MIB IPMROUTE-MIB
TCP-MIB UDP-MIB
Using FTP to Access the MIB Files
Working with the Flash File System
Switch# show file systems
Displaying Available File Systems
Setting the Default File System
Field Value
Cd newconfigs
Displaying Information about Files on a File System
Changing Directories and Displaying the Working Directory
Pwd
Mkdir oldconfigs
Creating and Removing Directories
Copying Files
Switch# delete myconfig
Deleting Files
Creating, Displaying, and Extracting Files
Archive /create destination-url
Flash
Archive /table source-url
Archive /xtract source-url
Extract a file into a directory on the flash file system
Directories are extracted
More /ascii /binary /ebcdic
Working with Configuration Files
Guidelines for Creating and Using Configuration Files
Configuration File Types and Location
Creating a Configuration File By Using a Text Editor
Copying Configuration Files By Using Tftp
Downloading the Configuration File By Using Tftp
Uploading the Configuration File By Using Tftp
Copying Configuration Files By Using FTP
Downloading a Configuration File By Using FTP
Ip ftp password password
Ip ftp username username
Uploading a Configuration File By Using FTP
Ftp // username password @ location /directory
Filename systemrunning-config
Filename nvramstartup-config
Copying Configuration Files By Using RCP
Copy systemrunning-config
Copy nvramstartup-config
Ftp // username password @ location /directory Filename
Hostname Switch1 Ip rcmd remote-username User0
Downloading a Configuration File By Using RCP
Systemrunning-config
Nvramstartup-config
Ip rcmd remote-username username
Clearing Configuration Information
Uploading a Configuration File By Using RCP
Switch# copy nvramstartup-config rcp
Clearing the Startup Configuration File
Deleting a Stored Configuration File
Working with Software Images
Image Location on the Switch
File Format of Images on a Server or Cisco.com
Copying Image Files By Using Tftp
Field Description
Preparing to Download or Upload an Image File By Using Tftp
Downloading an Image File By Using Tftp
Allow-feature-upgrade /directory
Archive download-sw
Overwrite /reload
Archive download-sw /directory
Uploading an Image File By Using Tftp
Archive upload-sw
Tftp //location /directory /image-name .tar
Copying Image Files By Using FTP
Preparing to Download or Upload an Image File By Using FTP
Downloading an Image File By Using FTP
Archive download-sw /allow-feature-upgrade
Directory /overwrite /reload
For /directory /image-name1 .tar
Directory /image-name2 .tar image-name3 .tar
Uploading an Image File By Using FTP
Copying Image Files By Using RCP
Preparing to Download or Upload an Image File By Using RCP
Downloading an Image File By Using RCP
File By Using RCP section on page B-31
Or Upload an Image File By Using RCP section on
Uploading an Image File By Using RCP
Copying an Image File from One Stack Member to Another
Rcp // username @ location /directory /image-na
Me.tar
Archive copy-sw /destination-system
Destination-stack-member-number /force-reload
Source-stack-member-number
For /destination-system destination-stack-member-number
Unsupported Commands Cisco IOS Release 12.237SE
Access Control Lists
Unsupported Privileged Exec Commands
Unsupported Global Configuration Commands
Archive Commands
ARP Commands
Boot Loader Commands
Debug Commands
Fallback Bridging
Bridge bridge-groupacquire
Bridge crb
Bridge bridge-group domain domain-name bridge irb
Hsrp
X25 map bridge x.121-address broadcast options-keywords
Igmp Snooping Commands
Interface Commands
IP Multicast Routing
Ip pim accept-rpaddress auto-rpgroup-access-list-number
Show ip pim vc group-address name type number
Show ip rtp header-compression type number detail
Ip multicast-routing vrf vrf-name
Unsupported Privileged Exec or User Exec Commands
IP Unicast Routing
Unsupported BGP Router Configuration Commands
Unsupported VPN Configuration Commands
Unsupported Route Map Commands
MAC Address Commands
Show cable-diagnostics prbs Test cable-diagnostics prbs
Miscellaneous
Set tag tag-value
NetFlow Commands
Msdp
Network Address Translation NAT Commands
Unsupported Global Configuration Command
Unsupported Policy-Map Configuration Command
QoS
Unsupported Interface Configuration Command
Unsupported User Exec Commands
Unsupported Privileged Exec Command
Spanning Tree
Numerics
IN-1
ACLs
IN-2
CDP Lldp RIP
Eigrp
Hsrp
TACACS+
BGP
Cidr
IN-4
Bpdu
IN-5
CDP
CEF
Cgmp
CLI
CNS
IN-7
IN-8
Dhcp
DNS
IN-9
Snmp
TACACS+ Udld
Vmps
Wccp
Dhcp option
IN-11
DTP
IN-12
Dvmrp
IN-13
Dynamic ARP inspection
IN-14
Lacp
IN-15
STP
FIB
IN-16
Mstp STP
FTP
IN-17
Https
Icmp
IN-18
Igmp
IN-19
IN-20
IP addresses
IN-21
Mbone
IN-22
IGP
IN-23
IP unicast routing
IN-24
ISL
IN-25
LLDP-MED
IN-26
IN-27
MDA
Mhsrp
IN-28
Msdp
IN-29
CST
IST
MTU
IN-30
NAC
IN-31
NSSA, Ospf
IN-32
Obfl
PBR
IN-33
PIM
IN-34
Port-based authentication
IN-35
Pvid
Vvid
IN-36
Private VLANs
IN-37
QoS
IN-38
IN-39
RCP
IN-40
Radius TACACS+
RFC
Rmon
IN-41
RPS
Rspan
Rstp
IN-42
SDM
IN-43
Snmp
IN-44
Span
SRR
IN-45
SSL
VTP
IN-46
Stacks, switch
IN-47
LLDP-MED Ospf
IN-48
STP
IN-49
IN-50
System message logging
IN-51
IN-52
IN-53
IN-54
VLANs
IN-55
VPN
VQP
IN-56
WTD
IN-57
IN-58