! Caution
There is a risk of accident
There is a risk of fire
Electric shock may result
Electric shock may occur
Accident may result
Failure may result
Electric shock or injury may result
Treat as industrial waste when disposing it
Electrical shock may result
Never modify the product
DCR
DCR FRNF50G11S-4UX
Tightening torque and wire range
Use the following power supply to the inverter
General instructions
Contents
Appearance
Before Using This Product
Receiving Inspections
Type Inverter type
Handling the Product Removing the surface cover
1 Removing the surface cover for inverter of 30HP or less
1 Storage environment
1 Operating environment
Installation and Connection
Installation Method
2 Output current reduction rate based on altitude
Removing the ventilating covers
Voltage Inverter type Bracket screws Case mounting
Always connect a ground wire
Electric shock or fire may result
Basic Connection Diagram Sink Logic
Basic Connection Diagram to PLC Sink Logic
Gfci
THR
Inverter output terminals U, V, W
Connecting the main circuit and ground terminals
Main circuit power terminals L1/R, L2/S, L3/T
1 Functions of main circuit terminals and ground terminals
DC link circuit terminals P + and N
Auxiliary control-power input terminals R0 and T0
DC reactor connecting terminals P1 and P +
Fire may result
Frequency Hz Power voltage range VAC
Inverter ground terminal
9 Fan power switching
Cnux U1 Cnrxtx L1/R-L3/T
Connecting the control terminals
FWD
13 Example of noise prevention
Transistor output terminals Y1 to Y4, CME
Wiring of control circuit inverter of 40HP or more
Digital input terminals FWD, REV, X1 to X9 and CM
Others
L2/S L3/T Screw size M4
Terminal arrangement
Main circuit terminals
L3/T L1/R L2/S
Y5C FWD REV
Control circuit terminals
30C 30B
P24 DX − DX + 30A
FRNF50G11S-2UX
Applicable equipment and wire size for main circuit
FRNF25G11S-2UX
FRNF50G11S-4UX
Auxiliary power input Supplied Magnetic contactor
Phase
Power supply
108
Operation Method
Operation
Inspection and Preparation before Operation
Trial Run
Keypad Panel
Appearance of Keypad Panel
Keypad panel operating system during normal operation
Alarm occurrence
Keypad Panel Operation System LCD screen, Level Structure
1 Overview of contents displayed for each level
Digital keypad panel settings F01=0 or C30=0
Operating Keypad Panel Operation Mode
Setting digital frequency
Other than digital setting
To switch to LED monitor display When power is turned on,
Switching the LED monitor
Setting function data
Menu screen
Display Reason for no modification Release method
To scroll Function Select screen rapidly , use alphabet
To move the screen in a unit grouped by
Screen
Checking function data
Monitoring operating status
PRG⇒PRG Menu F/D ⇒LED Shift
Data Setting 2.DATA Check 3.OPR Mntr ⇒4.I/O Check
8 I/O check
Maintenance information
NRK=xxxxx NRR=xxxxx NRO=xxxxx
Load rate measurement
EDC=
Alarm information
TRQ=
Alarm history and factors
Maintenanc 6.LOAD Fctr 7.ALM INF ⇒8.ALM Cause
Data copy
Verify error
Change disabled during operation
Memory error
Data protection
Alarm detection order
Alarm mode
Alarm detection order
PRG⇒PRG Menu RESET⇒RESET
Function select Function select list FFundamental Functions
Name
EExtension Terminal Functions
CControl Functions of Frequency
PMotor Parameters
HHigh Performance Functions
AAlternative Motor Parameters
UUser Functions
1 The factory setting value details
Function code
FRN001G11S-4UX FRN002G11S-4UX FRN003G11S-4UX
Function Explanation
Frequency setting block diagram
C33
F04 Base frequency
Setting range 230 V series 80 to Series
F03 Maximum frequency
F05 Rated voltage
F09 Torque boost
F10 Electric thermal O/L relay Select F11 Level F12
S T
F13 Electric thermal O/L relay for breaking resistor
U59
F14 Restart mode after momentary power failure
Accident may result
Power failure
F18Bias frequency
Setting range Inactive
F15 Frequency limiter High F16 Low
F17Gain
Setting range 0 to 200%
Setting range 0.0 to 60.0Hz
Voltage adjust
F26 Motor sound carrier frequency
Pulse rate
F36 30Ry operation mode
F33
F34
Set value
Accident may result F42 Torque vector control
P01, P09 2 T R Q
Off
Frequency selected
E01 X1 Terminal function E09 X9 Terminal function
Motor
Motor selected Related function
Torque limit Related function F41 Value selected F40
Set value Input signal Function Off →on
Disable PID control
On →off
F14 Off
Alarm
Inverse operation when forward
H18
E16 Torque limiter 2 driving E17 Torque limiter 2 braking
Settings when shipped from the factory
E10 Acceleration time E11 Deceleration time E12 E13 E14 E15
E20 Y1 terminal function E24
AL4 AL8
STG1 STG2 STG4
AL1
E25 Y5 Ry operation mode
E30 FAR function signal Hysteresis
Output current
Set value
E45 LCD monitor function
Display item
E46Language
C05 Multistep frequency C19
Setting range G11S 0.00 to 400.00Hz
C01 Jump frequency C02 C03 C04 Jump frequency Hysteresis
‹Setting example 100 F
C31 Bias terminal12 C32Gain terminal12
C30 Frequency command
Related functions E01 to E09 Set value11 F01
Bias -100 to +100% GAIN0.0 to 200%
C33 Analog setting signal filter
T E R
Tuning procedure
Set value Operation
P05 Motor 1 On-line Tuning
As injury may result
Inactive Active
Hen retry succeeded
Retry failed
Related functions U02 to U05
H08 Rev. phase sequence lock
H07 ACC/DEC (Mode select) pattern
FWD-CM
H10 Energy-saving operation
H09 Start mode
H11 DEC mode
1 D E C M O D E
‹This Function controls motor torque according to a
H13 Auto-restart Restart time H18 Torque control
To 5.0 seconds
Related functions
100% feedback amount
H20 PID control Mode select H25 PID controlFeedback filter
H21 PID control Feedback signal
Set value Descriptions
3 I G a I N
Deviation Time Operation amount
2 P G a I N
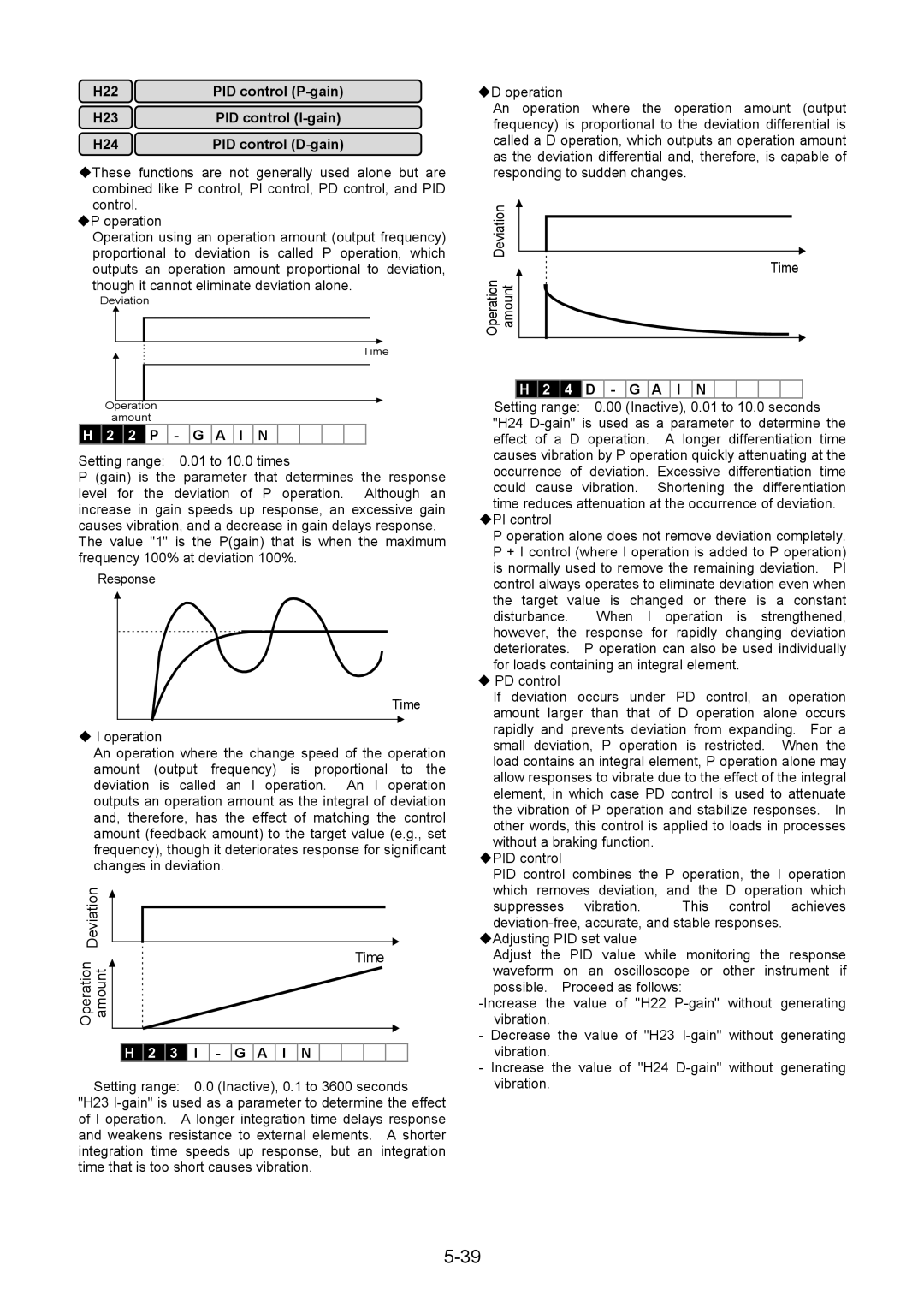
4 D G a I N
H25 PID control Feedback filter
Setting range 0.0 to 60.0 seconds
H26 PTC thermistor Mode select
Value Inactive
H31
Setting range 0 to Set value
H30 Serial link Function select
H39 RS-485 Response interval
Slippage = Synchronous speed-Rated speed
Set value 15 becomes 1Hz. The set value 1 becomes 1/15Hz
‹100% value of this function means maximum frequency fmax
U23
U15 Slip compensation filter time constant
Filter time constant of Slip compensation is set
Failure may result
U48 Input phase loss protection
U59 Braking resistor function select
U49 RS-485 protocol selection
Voltage detect offset adjustment
00 OH1 alarm at DC fan broken No alarm at DC fan broken
U61 Voltage detect offset and gain adjustment
Voltage detect gain adjustment
U89
Motor overload memory retention
Protective Operation
List of Protective Operations
Keypad panel display Alarm display
Alarm Reset
Reset command
Trip -2-1
Protective function activation
Trouble shooting
Ground fault
Overcurrent
Overvoltage
Low voltage
Overtemperature inside air
Overheating
Memory error Er1
Output wiring error
Abnormal motor rotation
If motor does not rotate
If the motor rotates but the speed does not change
UP/DOWN
If the motor stalls during acceleration
If the motor generates abnormal heat
1 Periodical inspection list
Maintenance and Inspection
Check parts Check items How to inspect Evaluation Criteria
Environment
Estimate life
Power is off Tighten
Use this function as follows
Is there discoloration due to overheating?
Page
Meter Moving-iron
Digital Moving-iron Digital power Moving-coil
1 Meters for measuring main circuit
Rectifier type
Inquiries about Products and Product Guarantee
Applicable Scope of Service
Free of Charge Warranty Period and Warranty Range
Service Contents
Exclusion of Liability for Loss of Opportunity, etc
Three-phase 230V series
Specifications
Standard Specifications
Three-phase 460V series
Common Specifications
Transport 70 to 106 kPa
Inch mm
Outline Dimensions
Outline Dimensions 30HP or less
460V Series
Outline Dimensions G11S 40HP to 350HP, P11S 40HP to 450HP
230V Series
Outline Dimensions G11S 400HP or more ,P11S 500HP or more
W3 W4
Outline Dimensions Reactor Accessories for 100HP or more
Fig図. C
RS-485 Modbus RTU Serial Communications
Transmission Specification
Serial Interface Configuration
Connection
Frequency Setting Registers
Inverter Function Code Access
Command and Monitor Data Registers
Operation command data Registers
Monitoring parameter registers
Data Format Specification
Bits binary data
Data format Index data ACC/DEC time, display coefficient
Data format Alarm Code
Data format Capacity code
All bit are on or active by
Inverter fault
Data format Pattern operation
Forward operation Current limiting
USA
Data format Code setting 1-4 figures
Data format Type code
NAK
Data format Auto tuning
Built-in Options
Options
10-1
Motor
Separately Installed Options Name Type Explanation
10-2
FAB
General
Electromagnetic compatibility EMC
11-1
EMC product standard EN61800-3/1997 +A11/2000
Applied Inverter Filter Type
Recommended Installation Instructions
11-2
Filters
Outline Dimensions RF3100-F11, RF3180-F11
11-3
Mccb
11-4
RCD or RFI filter Inverter
11-5
Harmonics restriction in Europe Union EU
2007-11 K07/K07 10CM


 Time Operation amount
Time Operation amount