www.ti.com
EMAC Control Module Registers
3 EMAC Control Module Registers
3.1Introduction
Table 11 lists the
Table 11. EMAC Control Module Registers
Offset | Acronym | Register Description | Section |
4h | EWCTL | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Control Register | Section 3.2 |
8h | EWINTTCNT | EMAC Control Module Interrupt Timer Count Register | Section 3.3 |
3.2EMAC Control Module Interrupt Control Register (EWCTL)
The EMAC control module interrupt control register (EWCTL) is used to enable and disable the central interrupt from the EMAC and MDIO modules.
It is expected that any time the EMAC and MDIO interrupt is being serviced, the software disables the INTEN bit in EWCTL. This ensures that the interrupt line goes back to zero. The software reenables the INTEN bit after clearing all the pending interrupts and before leaving the interrupt service routine. At this point, if the EMAC control module monitors any interrupts still pending, it reasserts the interrupt line, and generates a new edge that the DSP can recognize.
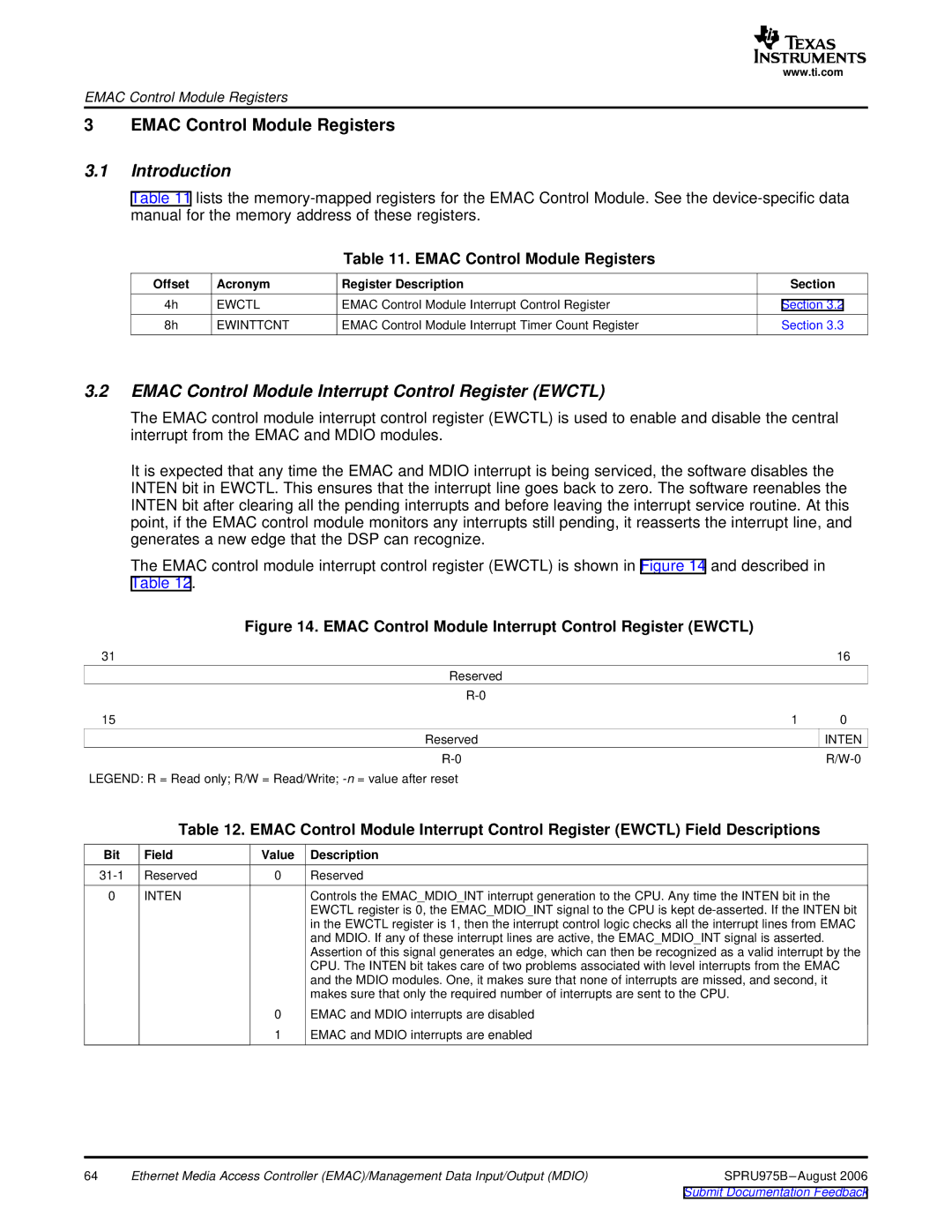
The EMAC control module interrupt control register (EWCTL) is shown in Figure 14 and described in Table 12.
Figure 14. EMAC Control Module Interrupt Control Register (EWCTL)
31 |
| 16 |
Reserved |
|
|
|
| |
15 | 1 | 0 |
Reserved |
| INTEN |
|
LEGEND: R = Read only; R/W = Read/Write;
Table 12. EMAC Control Module Interrupt Control Register (EWCTL) Field Descriptions
Bit | Field | Value | Description |
Reserved | 0 | Reserved | |
0 | INTEN |
| Controls the EMAC_MDIO_INT interrupt generation to the CPU. Any time the INTEN bit in the |
|
|
| EWCTL register is 0, the EMAC_MDIO_INT signal to the CPU is kept |
|
|
| in the EWCTL register is 1, then the interrupt control logic checks all the interrupt lines from EMAC |
|
|
| and MDIO. If any of these interrupt lines are active, the EMAC_MDIO_INT signal is asserted. |
|
|
| Assertion of this signal generates an edge, which can then be recognized as a valid interrupt by the |
|
|
| CPU. The INTEN bit takes care of two problems associated with level interrupts from the EMAC |
|
|
| and the MDIO modules. One, it makes sure that none of interrupts are missed, and second, it |
|
|
| makes sure that only the required number of interrupts are sent to the CPU. |
|
| 0 | EMAC and MDIO interrupts are disabled |
|
| 1 | EMAC and MDIO interrupts are enabled |
64 | Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)/Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) | SPRU975B |