www.ti.com
EMAC Functional Architecture
2.8EMAC Module
Section 2.8 discusses the architecture and basic functions of the EMAC module.
2.8.1EMAC Module Components
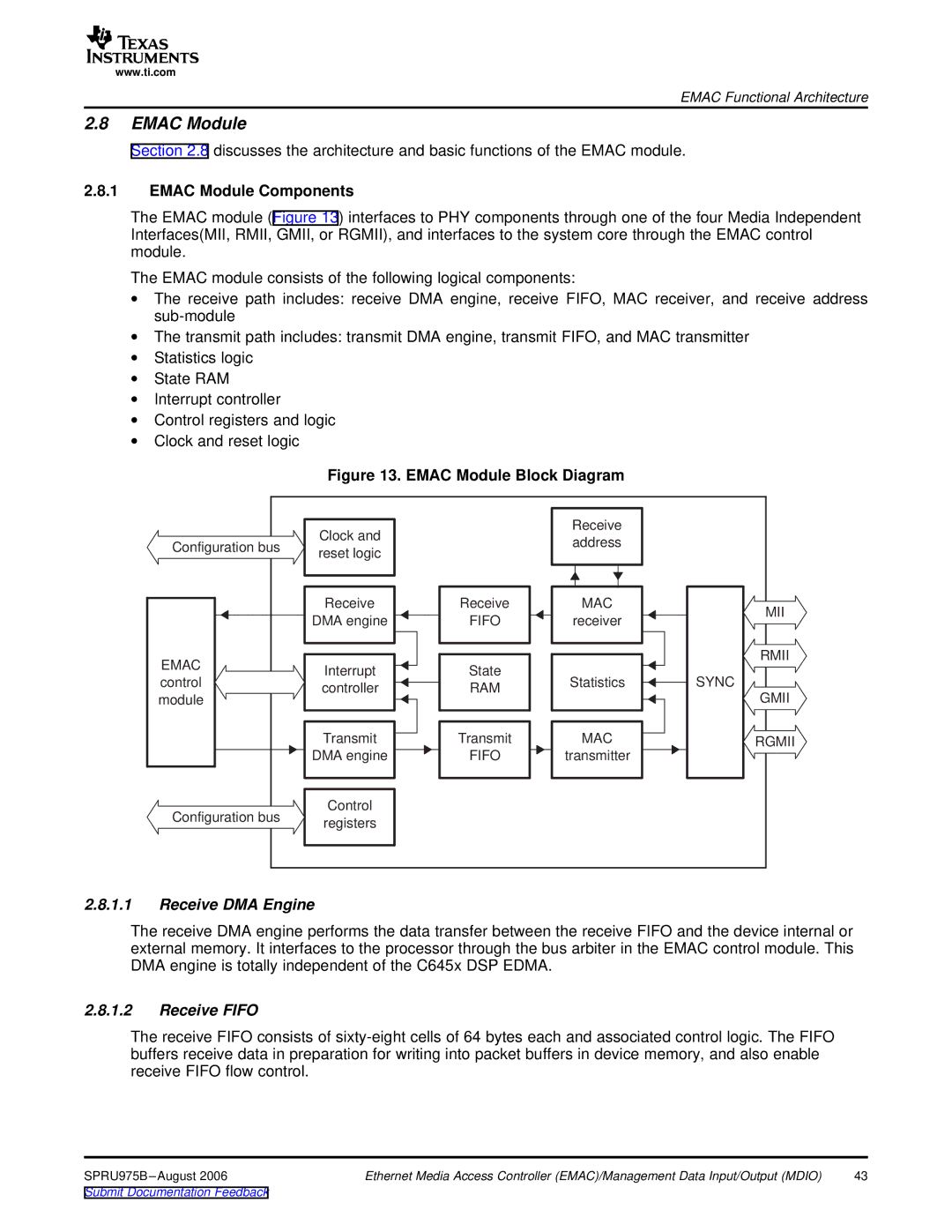
The EMAC module (Figure 13) interfaces to PHY components through one of the four Media Independent Interfaces(MII, RMII, GMII, or RGMII), and interfaces to the system core through the EMAC control module.
The EMAC module consists of the following logical components:
∙The receive path includes: receive DMA engine, receive FIFO, MAC receiver, and receive address
∙The transmit path includes: transmit DMA engine, transmit FIFO, and MAC transmitter
∙Statistics logic
∙State RAM
∙Interrupt controller
∙Control registers and logic
∙Clock and reset logic
Figure 13. EMAC Module Block Diagram
| Clock and |
| Receive |
| |
Configuration bus |
| address |
| ||
reset logic |
|
| |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
| ||
| Receive | Receive | MAC | MII | |
| DMA engine | FIFO | receiver | ||
|
| ||||
EMAC | Interrupt | State |
| RMII | |
|
| ||||
control | Statistics | SYNC | |||
controller | RAM | ||||
module |
| GMII | |||
|
|
| |||
| Transmit | Transmit | MAC | RGMII | |
| DMA engine | FIFO | transmitter |
| |
Configuration bus | Control |
|
|
| |
registers |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
2.8.1.1Receive DMA Engine
The receive DMA engine performs the data transfer between the receive FIFO and the device internal or external memory. It interfaces to the processor through the bus arbiter in the EMAC control module. This DMA engine is totally independent of the C645x DSP EDMA.
2.8.1.2Receive FIFO
The receive FIFO consists of
SPRU975B | Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)/Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) | 43 |