Controller Management
Chapter 3
Controller Management
3.1 Managing the Controller
The controller provides a set of tools that enable administrators to centrally manage the network storage and resources that handle
3.1.1Management Interface
SAN management information for the controller can be accessed locally through a serial interface, or remotely through Telnet.
NOTE : A controller may have only one active login (serial or Telnet) at any given time.
Locally - Serial Interface
Any
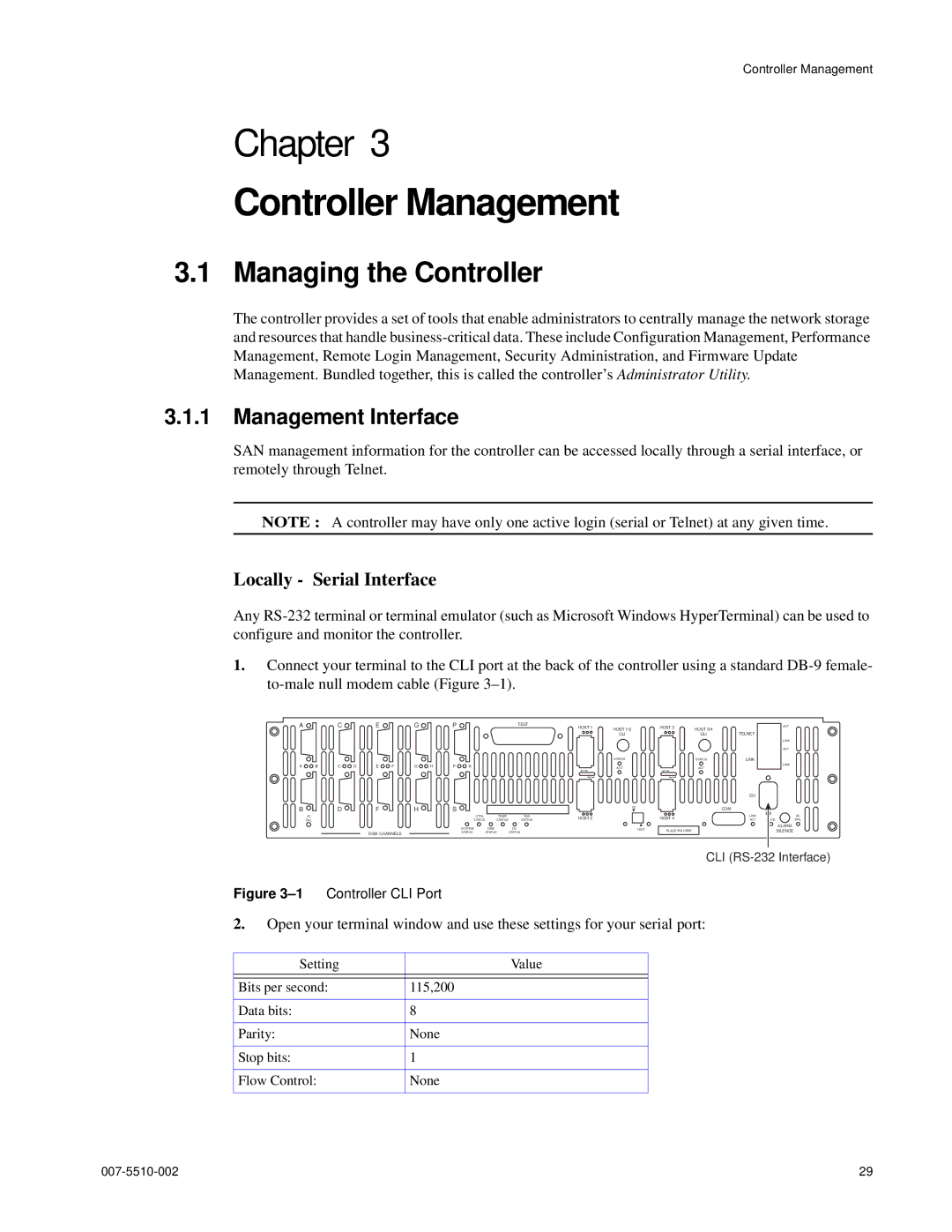
1.Connect your terminal to the CLI port at the back of the controller using a standard
A | C | E | G | P | TEST |
A B | C D | E F | G H | P | S |
B | D | F | H | S |
|
AC |
| CTRL | TEMP | FAN |
FAIL |
| STATUS | STATUS | STATUS |
| SYSTEM |
| DISK | DC |
DISK CHANNELS | STATUS |
| STATUS | STATUS |
HOST 1 | HOST 1/2 |
| CLI |
STATUS
ACT
1
2
1/2
HOST 2
TEST
HOST 3 | HOST 3/4 |
|
| ACT |
|
|
|
| |
| CLI | TELNET |
|
|
|
|
|
| LINK |
|
|
|
| ACT |
| STATUS | LINK |
|
|
|
|
|
| LINK |
3 | ACT |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
| CLI |
|
|
|
| COM |
|
|
HOST 4 |
| LINK |
| AC |
| ACT | MUTE | FAIL | |
|
|
|
| ALARM |
PLACE PIN HERE |
|
|
| SILENCE |
CLI
Figure 3–1 Controller CLI Port
2.Open your terminal window and use these settings for your serial port:
Setting | Value |
Bits per second: | 115,200 |
|
|
Data bits: | 8 |
|
|
Parity: | None |
|
|
Stop bits: | 1 |
|
|
Flow Control: | None |
|
|
29 |