Ow INURFg k D
C C v h
Fo Y b kr
Page
No Changes
Scan
Use the Menu to
Fo Y k Zy y Yh AFD7P HS y Yy y Y y y
Yh R
∙ d
Ks GHPDEc FDe c p
Ks GHPDHc H w p
Ks GHPDGc FDe Ci
Ks GHPDICLc feh p
Ks GHPDOc HDe vg
Ks GHPDMc p p
∙ d BHE8
F7o r8 Fo Delhax 6 8 a Express Exchange
Hs r
Contents
Contents
Contents
Contents
Page
Shift w
Instrument does not turn on properly, see
User’s Guide5 Service Guide5 Quick Reference Guide5
To install the software, see
To Prepare the Instrument for Use
File Run fww xw \setup
Installing HP BenchLink Data Logger Software
Settings Control Panel
Add/Remove Programs Install/Uninstall
0H1
Wzw
To Connect Wiring to a Module
Ml lil l
To Set the Time and Date
Jyw
To Configure a Channel for Scanning
Qw z wz zyw Ww yw Yz yw wy
877
$6772
To Copy a Channel Configuration
Yzz Z3 w wwz yz w yw3 ywz w zw wz Zz yw z w w3 w
To Close a Channel
9AN w 9A8 w
If the Instrument Does Not Turn On
Hq FGPN8a t g
Upt
Zwx 4 y Yy ww
Bench-top viewing positions
To Adjust the Carrying Handle
To Rack Mount the Instrument
Quick Start
Page
Page
X xz Zx x
Front-Panel Menu Reference
Configure system-related instrument parameters
To Monitor a Single Channel
To Set a Scan Interval
1759$/6&$1
To Apply Mx+B Scaling to Measurements
$%/$6/%6
+ ,$/$5021
To Configure Alarm Limits
To Configure Alarm Limits
Ty H
To Read a Digital Input Port
To Write to a Digital Output Port
7 h k
To Read the Totalizer Count
$567
To Output a DC Voltage
+3,%
To Configure the Remote Interface
91,%,76
To Store the Instrument State
+$1*6$9
Page
Computer System
Advantages Disadvantages
Data Acquisition System Overview
HP BenchLink Data Logger
Fo Y k 4yx Wg AFD7O Xx x AFD7O Sdd5 l Xz x x
EFC
STcaLm p
Model Number Module Name Common Uses
Signal Routing
Cable Type Common Uses Comments
System Cabling and Connections starting on
Kxz zx x z Kzx Z3 x z x R3 U3 b5
Relay Cycle Count on
Signal Routing and Switching
D7v
HD8
N7v 2rc3 l
S7v l
X zzx 87 dW X x zx3 Y z z y5
Measurement Input
Sdd’s signal-conditioning
OSR5
Scan Count
GND
HL8
BWa3
Y zx Xx5 p zx x x z x x zx x z5
HH8
Control Output
FB W 2 bWa
ELI
Features and Functions
Features and Functions
Scpi Language Conventions
Scpi Language Conventions
Scanning
Scanning
Scanning
Scanning
Power Fails
Scanning
Fxx xx tz tzx 978 vt Yt z xx
Scan Count
Initiate the scan
Select the interval timer configuration
Set the scan interval to 5 seconds
Sweep the scan list 2 times
∙ Front-Panel Operation
Select the bus once configuration
Group Execute Trigger
Select the external trigger configuration
Ext Trig Connector
See Scan Count on page 86 for more information
On page 86 for more information
Sx wxt vyzz tw z ttxyx Alarm Limits starting on
Fxxv tx
Fxxv x ttvzt
Fxxx vt 9
Ex tt Mt
∙ exx Vxytvx bxt
Sctxt
Scanning
CH Delay Time
Range Channel Delay
Integration Time Channel Delay
AC Filter Channel Delay
∙ Sctxt
Readings
Aux twz x vtx
Twz vtx
Gt zzxw
Ttwz vtx
Single-Channel Monitoring
Single-Channel Monitoring
ROUTMONDATA?
Scanning With External Instruments
Scanning With External Instruments
Scanning With External Instruments
Fxx t
Fxxv t t
Fxvx vtx twvx
Fx t t a xvw
General Measurement Configuration
General Measurement Configuration
Change the range setting
This is the 10 Vdc range, 51⁄2 digits are displayed
101
102
WX c
Integration Time Resolution Digits Bits
104
105
Temperature Measurement Configuration
Temperature Measurement Configuration
Temperature Measurement Configuration
Temperature , Thermocouple
109
To connect an RTD to the module’s screw terminals, see
MoX g
111
∙ Remote Interface Operation You can use the MEASure? or
To connect a thermistor to the module’s screw terminals, see
Mx wv tzx tx
Voltage Measurement Configuration
Voltage Measurement Configuration
XW c
Mx tv tzx tw tv
UW f
Resistance Measurement Configuration
Resistance Measurement Configuration
To connect resistances to the module’s screw terminals, see
Current Measurement Configuration
Current Measurement Configuration
Applies to ac current and ac voltage measurements only
117
Frequency Measurement Configuration
Frequency Measurement Configuration
Sensfreqranglow 3,@203 Select the slow timeout 3 Hz
Mx+B Scaling
Mx+B Scaling
Strain Gage Measurements on
Vy x x tx tux Xtx x
121
Alarm Limits
Alarm Limits
Ux yzx tz x y
Using the Alarm Output Lines on
Then, choose from the following alarm conditions
Alarm queue is cleared when you read the alarms 126
127
Alarms Connector
Oxt tt
Otz x y x x vtx x x vtzx
Oxt y tt
130
131
Or result
Calccompmask command decimal
Result no alarm generated
Pt tw y /wxvt 8=B0
Digital Input Operations
Digital Input Operations
Extw u
Extw
Mww 79 xtw t
Totalizer Operations
Totalizer Operations
136
137
Digital Output Operations
Digital Output Operations
DAC Output Operations
DAC Output Operations
X vxM Xx / PMO vt05
System-Related Operations
System-Related Operations
141
Extw tx x
Vx z
Returns 0 if the self-test is successful or 1 if it fails
Turns on. See the Uc =EC7M fxvx Twx
Xt t z uxx
Exx Vxytvx bxt
144
Fxt Wx 83 8EEC
Fxx
HEWLETT-PACKARD,34901A,0,X.X
System-Related Operations
148
Vtxx fOcV yx ytx5
NWkc f
Remote Interface Configuration
Remote Interface Configuration
BkcV U
151
KDC5
NDC5
Vt xx utw x ytx
Lt vx y vxw y y5
3mnCDC5
154
Calibration Overview
Calibration Overview
156
Hv w vwx
158
159
Factory Reset State
Factory Reset State
Instrument Preset State
Instrument Preset State
Multiplexer Module Default Settings
Multiplexer Module Default Settings
Module Overview
Module Overview
Sx xvyvt xtv 4w3 yx x x xv vt E5
HP 34901A 20-Channel Multiplexer
HP 34901A 20-Channel Multiplexer
Name Function Comments
Slot Number
HP 34902A 16-Channel Multiplexer
HP 34902A 16-Channel Multiplexer
167
HP 34903A 20-Channel Actuator
HP 34903A 20-Channel Actuator
169
HP 34904A 4x8 Matrix Switch
HP 34904A 4x8 Matrix Switch
Name Comments
HP 34905A/6A Dual 4-Channel RF Multiplexers
HP 34905A/6A Dual 4-Channel RF Multiplexers
173
HP 34907A Multifunction Module
HP 34907A Multifunction Module
DAC Output
Slot Number 100 200
Digital Input / Output
Totalizer
HP 34908A 40-Channel Single-Ended Multiplexer
HP 34908A 40-Channel Single-Ended Multiplexer
177
Remote Interface Reference
Remote Interface Reference
Scpi Command Summary
Scpi Command Summary
Eyy
Zz vz 9C
Scpi Command Summary Scan Measurement Commands
Monitor Commands
Zz vz 99B
Scpi Command Summary Scan Configuration Commands
Zz vz 9A
Scpi Command Summary Scan Statistics Commands
Scan Memory Commands
Zz vz
Zz vz 9E
Scpi Command Summary Scanning With an External Instrument
Zz vz 98E
Scpi Command Summary Temperature Configuration Commands
Scpi Command Summary Voltage Configuration Commands
Scpi Command Summary Resistance Configuration Commands
Zz vz Kvy vz 98 vy Ud E78N zz z5
Scpi Command Summary Current Configuration Commands
191
Scpi Command Summary Mx+B Scaling Commands
Scpi Command Summary Alarm Limit Commands
Totalizer Commands
Scpi Command Summary Digital Input Commands
Zz vz 9AB
Zz vz 9AD
Scpi Command Summary Digital Output Commands
DAC Output Commands
Switch Control Commands
Zz vz 9B8
Scpi Command Summary Scan Triggering Commands
State Storage Commands
Zz vz 99D
Zz vz 9B
Scpi Command Summary System-Related Commands
Zz vz 9DB
Scpi Command Summary Interface Configuration Commands
Status System Commands
Zz vz 9BE
Service-Related Commands
Scpi Command Summary Calibration Commands
Zz vz 9E9
Scpi Command Summary Ieee 488.2 Common Commands
Simplified Programming Overview
Simplified Programming Overview
Xy z y zvy
CONFigure zy yvz w
MEASure? v z vz
INITiate xy z vy 5 iz z
Range 41⁄2 Digits
Xv zy zyv w z FETCh? xv3 zxz z Vy vz zy vy z
Gz z READ? xvy z z
205
Xv3 ABORt x Qzxz Pzvzz vz
V v zz vzy z
MEASure? Command Syntax
MEASure? and CONFigure Commands
MEASure? and CONFigure Commands
General Measurement Configuration starting on
MINMAXDEF, @
MEASureTEMPerature? RTDFRTD,8591DEF
Yzz
MEASureVOLTageDC? MEASureVOLTageAC?
MEASureFREQuency? MEASurePERiod?
MEASureRESistance? MEASureFRESistance?
MEASureCURRentDC? MEASureCURRentAC?
Pz vz vz vzy Xv 98 vy Ud E78N zz z5
MEASureDIGitalBYTE? @
MEASureTOTalize? READRRESet ,@
CONFigureTEMPerature TCouple,BEJKNRSTDEF Minmaxdef ,@t
MEASure? and CONFigure Commands CONFigure Command Syntax
CONFigureTEMPerature RTDFRTD,8591DEF
Pzzvzz vz vzy xv 98 vy Ud E78N zz z5
CONFigureVOLTageDC CONFigureVOLTageAC Autominmaxdef
CONFigureRESistance CONFigureFRESistance
CONFigureCURRentDC CONFigureCURRentAC
CONFigure? @x
CONFigureFREQuency CONFigurePERiod Autominmaxdef
CONFigureDIGitalBYTE @
CONFigureTOTalize READRRESet ,@
SENSeFUNCtion
Setting the Function, Range, and Resolution
Setting the Function, Range, and Resolution
See also General Measurement Configuration in starting on
FRESistanceRANGe? @x
SENSe VOLTageDCRANGe? @x
VOLTageACRANGe? @x
RESistanceRANGe? @x
CURRentDCRESolution? @x
SENSe VOLTageDCRESolution? @x
RESistanceRESolution? @x
FRESistanceRESolution? @x
CURRentDCAPERture? @x
SENSe VOLTageDCAPERture? @x
RESistanceAPERture? @x
FRESistanceAPERture? @x
FRESistance
SENSe TEMPerature
VOLTageDC
RESistance
General Temperature Commands
Temperature Configuration Commands
Temperature Configuration Commands Thermocouple Commands
SENSeTEMPeratureRJUNction? @x
Thermistor Commands
Temperature Configuration Commands RTD Commands
SENSe Zeroauto OFFONCEON,@x ZEROAUTO? @x
Voltage Configuration Commands
See also Voltage Measurement Configuration in starting on
INPut IMPedanceAUTO OFFON,@x IMPedanceAUTO? @x
Current Configuration Commands
Resistance Configuration Commands
Frequency Configuration Commands
Frequency Configuration Commands
See also Frequency Measurement Configuration in starting on
Scanning Overview
Scanning Overview
See also Scanning in starting on
Scanning Overview
ROUTeSCANSIZE?
Scanning Overview Scanning Commands
TRIGger SOURce BUSIMMediateEXTernalALARm1234TIMer SOURce?
ROUTe Scan @ SCAN?
TRIGger COUNt x MINMAXINFinity COUNt?
TRIGger TIMer y Minmax TIMer?
ROUTe CHANnelDELay y
CHANnelDELay? @x
ABORt
ROUTe CHANnelDELayAUTO OFFON,@x CHANnelDELayAUTO? @x
INITiate
FORMat READingALARm Offon READingALARm?
Scanning Overview Reading Format Commands
FORMat READingCHANnel Offon READingCHANnel?
Hz vxz
FORMat READingTIME Offon READingTIME?
FORMat READingUNIT Offon READingUNIT?
FORMat READingTIMETYPE ABSoluteRELative READingTIMETYPE?
CALCulateAVERageMAXimum? @x
Scanning Overview Scan Statistics Commands
CALCulateAVERageMINimum? @x
CALCulateAVERageMINimumTIME? @x
CALCulateAVERageCLEar @x
CALCulateAVERageAVERage? @x
CALCulateAVERagePTPeak? @x
CALCulateAVERageCOUNt? @x
DATAPOINts?
Scanning Overview Scan Memory Commands
DATAREMove? t
? tx
See Reading Format Commands on
SYSTemTIMESCAN?
FETCh?
Single-Channel Monitoring Overview
Single-Channel Monitoring Overview
ROUTe MONitorSTATe Offon MONitorSTATe?
ROUTe MONitor @xvz MONitor?
ROUTeMONitorDATA?
Scanning With an External Instrument
TRIGger SOURce BUSIMMediateEXTernalTIMer SOURce?
TRIGger COUNt z MINMAXINFinity COUNt?
Y z v Qaa ywy y Ud EC7N5
INSTrumentDMMINSTalled?
ROUTe CHANnelFWIRe Offon ,@x CHANnelFWIRe? @x
INSTrument
Mx+B Scaling Overview
Mx+B Scaling Overview
See also Mx+B Scaling in starting on
CALCulate SCALeUNIT zyt SCALeUNIT? @x
Mx+B Scaling Overview Mx+B Scaling Commands
CALCulate SCALeGAIN v ,@xt SCALeGAIN? @x
CALCulate SCALeOFFSet ,@xt SCALeOFFSet? @x
CALCulate SCALeSTATe OFFON,@x SCALeSTATe? @x
CALCulateSCALeOFFSetNULL @x
Alarm System Overview
Alarm System Overview
See also Alarm Limits in starting on
Alarm System Overview
Calclimitupper MAX,@101LOWER 9,@101LOWERSTATE on
CALCulate LIMitUPPerSTATe OFFON,@xt LIMitUPPerSTATe? @x
Alarm System Overview Alarm Limit Commands
OUTPut ALARm1234SOURce @xt ALARm1234SOURce?
CALCulate LIMitUPPer z LIMitUPPer? @x
CALCulate LIMitLOWer z LIMitLOWer? @x
SYSTemALARm?
CALCulate LIMitLOWerSTATe OFFON,@xt LIMitLOWerSTATe? @x
Vz xvz z5
Alarm System Overview Alarm Output Commands
OUTPut ALARmMODE LATChTRACk ALARmMODE?
OUTPut ALARmSLOPe NEGativePOSitive ALARmSLOPe?
CALCulate COMPareTYPE EQUalNEQual,@x COMPareTYPE? @x
Alarm System Overview Digital I/O Alarm Commands
CALCulate COMPareDATA yvv ,@xt COMPareDATA? @x
CALCulate COMPareSTATe OFFON,@x COMPareSTATe? @x
CALCulate COMPareMASK COMPareMASK? @x
See also Digital Input Operations in starting on
Digital Input Commands
SENSeDIGitalDATABYTEWORD? @x
SENSe TOTalizeTYPE READRRESet,@x TOTalizeTYPE? @x
Totalizer Commands
See also Totalizer Operations in starting on
SENSeTOTalizeDATA? @x
Commands see Reading Format Commands on
SENSe TOTalizeSLOPe NEGativePOSitive,@x TOTalizeSLOPe? @x
SENSeTOTalizeCLEarIMMediate @x
SOURceDIGitalSTATe? @x
Digital Output Commands
DAC Output Commands
SOURce DIGitalDATABYTEWORD yvv ,@xt DIGitalDATABYTEWORD? @x
ROUTe CLOSe @x CLOSeEXCLusive @x CLOSe? @x
Switch Control Commands
ROUTe Open @x OPEN? @x
Zv z
ROUTe CHANnelFWIRe Offon , @ CHANnelFWIRe? @
ROUTeDONE?
SYSTemCPON 100200300ALL
SAV
State Storage Commands
RCL
MEMorySTATeDELete
MEMorySTATe Name 12345 ,z NAME?
MEMorySTATeVALid?
RECallAUTO?
MEMoryNSTates?
SYSTemTIME 3
System-Related Commands
SYSTemDATE 3 3yy
SYSTemDATE?
Oz v 7
DIAGnostic Pokeslotdata 100200300, zyt PEEKSLOTDATA?
SYSTemCTYPe?
DISPlay Text zyt
DISPlay Offon DISPlay?
DISPlayTEXTCLEar
Gfxz5
SYSTemPRESet
INSTrument DMM Offon
Fxz5
Gzz xv v xz z Ud EC7N z vz5
SYSTemERRor?
SYSTemVERSion?
Interface Configuration Commands
RS-232 Interface Configuration
RS-232 Interface Configuration
Gh6 Sy d
Gh6
Yzv Or xz xvwz
Gh6 Tyyy
Ud EC7N
For more information, see Flow Control Selection on
Modem Communications
Modem Communications
Zz yz
Ny yy gO
Scpi Status System
Ny y S gO
Ny yO
HP 34970A Status System
128
Bit Definitions Status Byte Register
Decimal Bit Number
Definition
Gzv d zzxzy vz hzz3 yxv w gzv d xzv Yxvz vzx Xz5 iz z
Ghgf2 y
Vvzz v xz Xzy wz zzx v gzv d5
S S
Ly QQm2
2048
Bit Definitions Questionable Data Register
512
1024
Scpi Status System
Bit Definitions Standard Event Register
Scpi Status System
Bit Definitions Alarm Register
Bit Definitions Standard Operation Register
Dy g
Gzz z wz vz 9CC z zz wz
Status System Commands
Status Byte Register Commands
Vv xzy xvz C z z Gv g fz5 fzzvz
STATusQUEStionableCONDition?
Status System Commands Questionable Data Register Commands
STATusQUEStionableENABle zv STATusQUEStionableENABle?
Gzz z wz vz 9D7 z zz wz
Gzz z wz vz 9D9 z zz wz
Status System Commands Standard Event Register Commands
ESE zv
STATusALARmENABle zv STATusALARmENABle?
Status System Commands Alarm Register Commands
STATusALARmCONDition?
STATusALARmEVENt?
STATusOPERationCONDition?
Status System Commands Standard Operation Register Commands
STATusOPERationENABle zv STATusOPERationENABle?
Gzz z wz vz 9DA z zz wz
PSC
Miscellaneous Status Register Commands
STATusPRESet
DATAPOINtsEVENtTHReshold t DATAPOINtsEVENtTHReshold?
CALibrationSECureCODE txyz
Calibration Commands
CALibration?
CALibrationCOUNt?
CALibrationVALue z CALibrationVALue?
CALibrationSECureSTATe OFFON,xyz CALibrationSECureSTATe?
CALibrationSTRing zyt
CALibrationSTRing?
DIAGnosticRELayCYCLes? @x
Service-Related Commands
DIAGnosticDMMCYCLes?
DIAGnosticDMMCYCLesCLEar
WAI
Preset state. h xy zz zzxPRESET z fxz5
An Introduction to the Scpi Language
An Introduction to the Scpi Language
Scpi gvyvy Py vw V is an
Syy i byy
Routchandelay 1TRIGSOUR EXT
HSeY Sy
Fy h
Wvvxz
HSeY ey
Channel list parameters specify one or
Using Device Clear
Using Device Clear
Hz ABORt x xyzy v vz v
Page
∙ x o u
Error
105
Execution Errors 101
102
103
124
Execution Errors 114j
121
123
213
Execution Errors 168
178
211
420
Execution Errors 230
310 350
410
203
Instrument Errors 111
201
202
251
Instrument Errors 221
225
226
281
Instrument Errors 261
271
272
307
Instrument Errors 303
305
306
512
Instrument Errors 501
502
511
604
Self-Test Errors
601 602
603
704
Calibration Errors
701
702 703
723
Calibration Errors 710 720
721
722
Error Messages
Page
BA8
Example Programs for Excel
G68
Insert
VISAaddr =
Excel 7.0 Example takeReadings Macro
BAB
BAC
Dim columnIndex As Integer
Excel 7.0 Example ScanChannels Macro
BAF
BAG
Ck qdnT User’s Guide6 o
Example Programs for C and C++
Ck qdnT User’s Guide6
++ Example dacout.c
++ Example statreg.c
BB9
Page
AG=
ABA
AFF
AG8
Uzz
System Cabling and Connections
Lz k
Gz bz 0z
Cable Type Nominal Impedance Capacitance Attenuation
99=
LvLv
3uqyu
Copper-to
Uj m
GxuuB
Gxuyw qs u
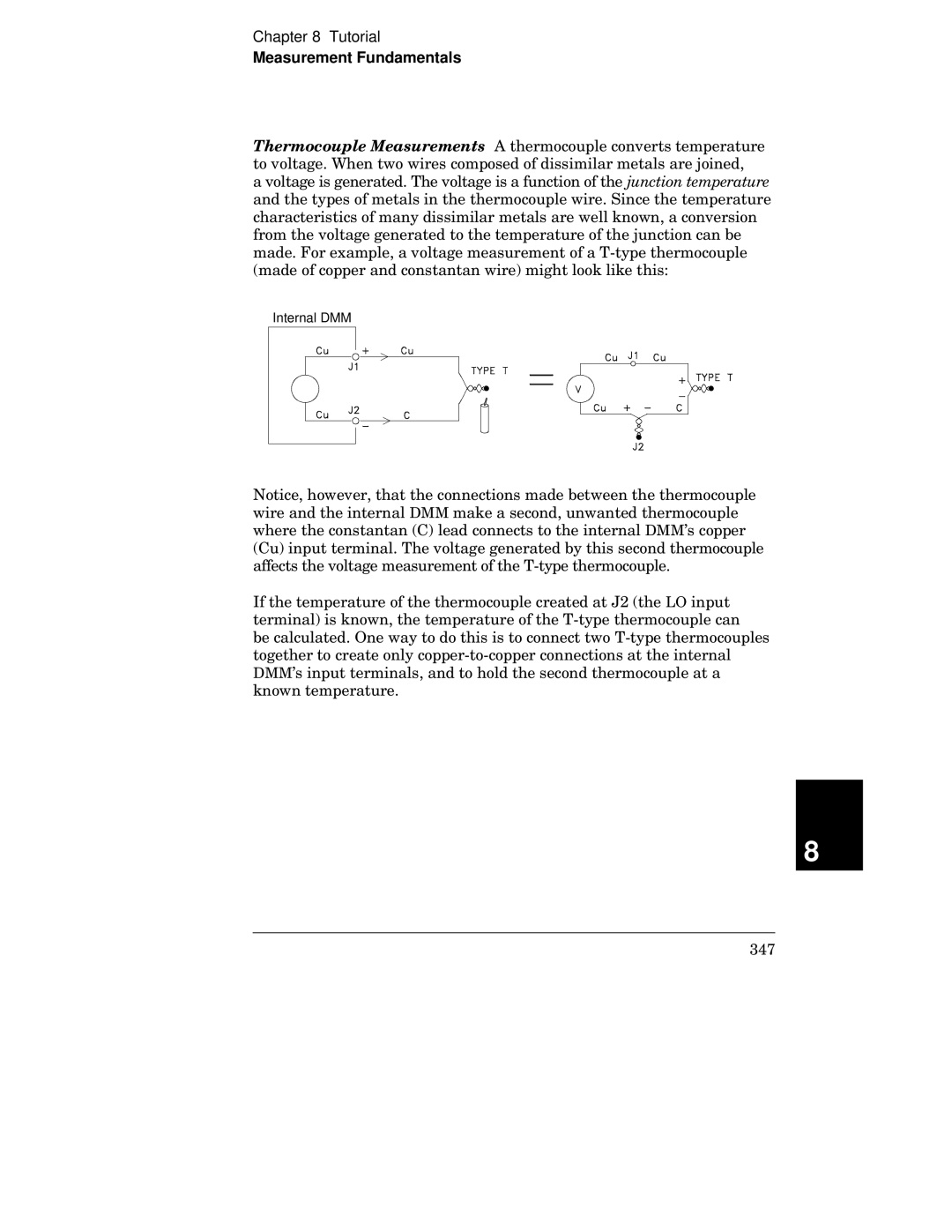
Measurement Fundamentals
Wuq
Z Uff4 Refer to Measurement Input on
Integration Time PLCs
Wsu
Qysq Dxu qsuvqsu ytu qsusyvysq Vq tu4
Bz mz 9GG8
Measurement Fundamentals
Internal DMM
Internal DMM Ice Bath
Ez b
Measurement Fundamentals
Copper Constantan
Temperature Probe Type Pos + Lead Neg Lead
Iron Constantan
Nickel-Chromium Nickel-Aluminum
Z4 z
ABC
MWW2
99A
Nm w
Stuqq
Connection a Connection B
Sl py
Sk p j
HI A1 AC to DC Converter X10 X100
360
361
Km w
Example Calculating Measurement Error
N5zzz z5 z z 0 z AAD16
Hj s
Voltage Measured = ‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾‾√ V 2 + Noise
MWW
On-Card
Km m
Nm m
To Amplifier Analog-to-Digital Converter
HI-Source HI-Sense
Does not sxqu
For more information on channel delay, see
AB8
Offset Compensation on page 115 for more information
Insulating Material Resistance Range Moisture Absorbing
Zz4 z FF
Ai Sz e
HI Source HI Sense LO Sense LO Source
Strain DMM Sensitivity
376
Measurement Fundamentals
V3Vu cyw Wuy q cyxy
Low-Level Signal Multiplexing and Switching
4 AC8
ELo
HI + Source Sense
OUT COM H GND COM L
Zz AE
Module Bank
Module Reference
Actuators and General-Purpose Switching
Rp =
Dxu q u Ytu u qt Dxuuvu2 xu yy b Sq ru t qB
Module Reference
Wqy cyxy
Matrix Switching
Matrix Module
BO cyw
RF Signal Multiplexing
9A7
Multifunction Module
393
= 24 k Ω
GND TTL AC
For more information on cabling noise, see
U55R
EnkmF y
R B8 R URT z16 ∙ d qy s2 u .b Yu tyqwq Qr/ w
Nkm o
Buq Z
Relay Life and Preventative Maintenance
Qsuqsu wuqq
Uu utysuqqy4
AOT
AHe
AHf
AOO
DC Voltage
DC, Resistance, and Temperature Accuracy Specifications
Ki u y
DC Measurement and Operating Characteristics
Gi g
AC Accuracy Specifications
Gi u
AC Measurement and Operating Characteristics
Single Channel Measurement Rates 1 System Characteristics
Measurement Rates and System Characteristics
TagHOr7 TagHPr7 TagHfr7 TagHTr7 TagHar
Module Specifications
TagHcr7 TagHdr
Typical AC Performance Graphs
TagHer
Product and Module Dimensions
Understanding the % of reading Error o
To Calculate Total Measurement Error
× 1,000,000
Understanding the % of range Error o
Interpreting Internal DMM Specifications
Criteria
417
LYR u
BdR u
Vhh 87 b 87 q ∙ p =4 ∙ n ∙ n c 77 =8F
Configuring for Highest Accuracy Measurements
Index
Index
CAB
CAC
CAD
CAE
CAF
CAG
CAH
CB8
CB9
CBA
CBB
Declaration of Conformity
Ajjh