Non-Transparent PCI-to- PCI Bridge
Page
Contents
With SROM, Local, and Host Processors
10.1
Figures
Tables
131
148
108
Page
Brief description of the contents of this manual follows
Preface
Term Words Bytes Bits
Data Units
Numbering
Signal Description Type
Signal Nomenclature
Signal Type Abbreviations
STS
Register Abbreviations
Access Type Description
Register Abbreviations
Introduction
Comparing a 21555 to a Transparent PPB
CPU PCI
Dram PCI ROM
CPU
PPB Feature Comparison
Feature
Registers
Architectural Overview
Data Buffers
Control Logic
Microarchitecture
Primary Bus VGA Support
Special Applications
Programming Notes
Secondary Bus VGA Support
ROM Access
Transaction Forwarding
Page
Group by Signal Pin Description See
Signal Descriptions
Signal Pin Functional Groups
Signal Name Type Description
Primary PCI Bus Interface Signals
Primary PCI Bus Interface Signals Sheet 1
Preql
Primary PCI Bus Interface Signals Sheet 2
Ppar
Pstopl
Pack64l
Primary PCI Bus Interface 64-Bit Extension Signals
Primary PCI Bus Interface 64-Bit Extension Signals Sheet 1
Pad6332
Preq64l
Primary PCI Bus Interface 64-Bit Extension Signals Sheet 2
Ppar64
Pad6332 , pcbel74 , and ppar64 to valid logic levels
Secondary PCI Bus Interface Signals
Secondary PCI Bus Interface Signals Sheet 1
Sstopl
Secondary PCI Bus Interface Signals Sheet 2
Spar
Strdyl
Sad6332
Secondary PCI Bus Interface 64-Bit Extension Signals
Sack64l
Scbel74
Miscellaneous Signals
Miscellaneous Signals
Page
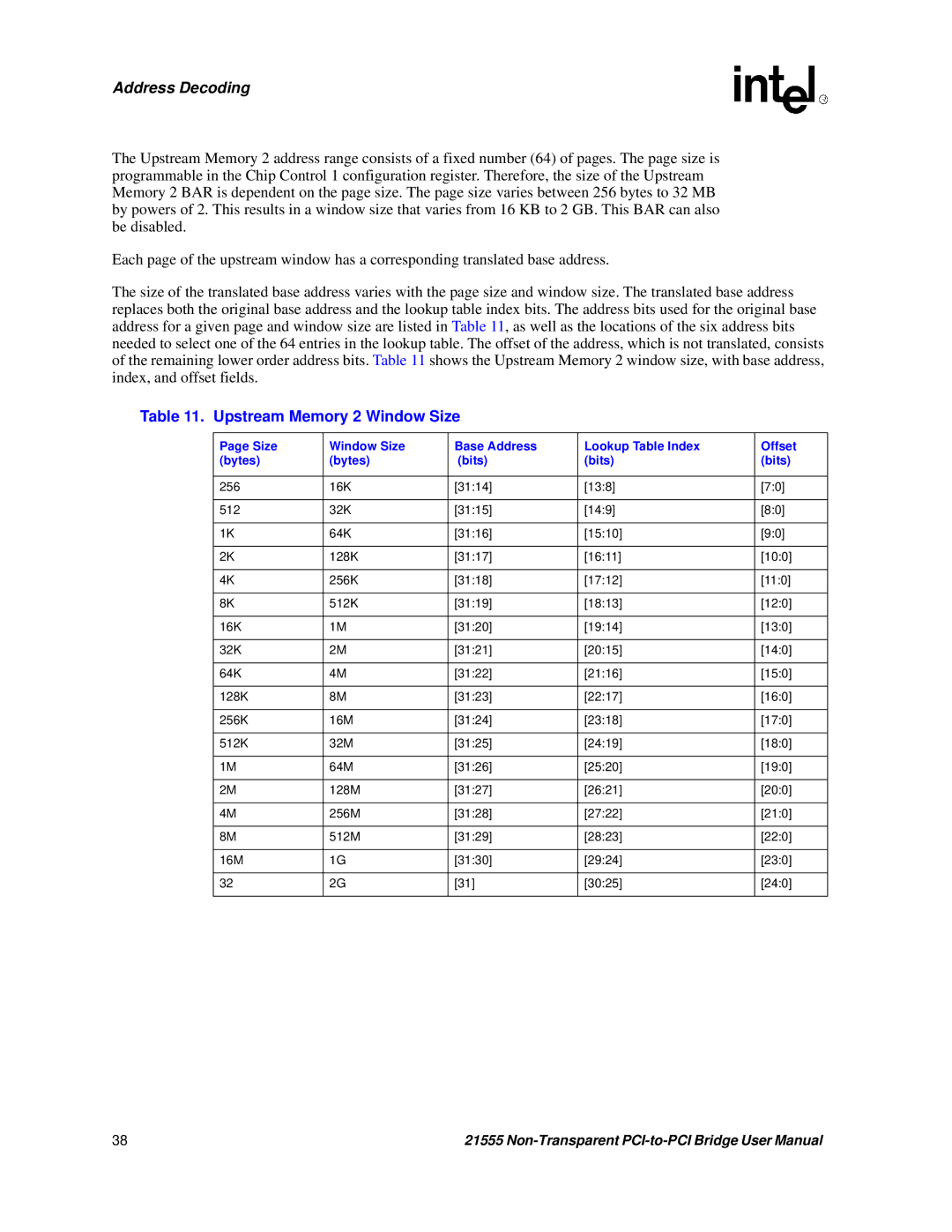
Address Decoding
Memory 0 Transaction Address Decoding
CSR Address Decoding
Expansion ROM Address Mapping Decoding
Using the BAR Setup Registers
BAR Setup Register Example
Direct Address Translation
Address Format
Lookup Table Based Address Translation
Direct Offset Address Translation
Upstream Memory 2 Window Size
Address Translation Using a Lookup Table
Lookup Table Entry Format
Upstream Lookup Table Address Translation
Forwarding of 64-Bit Address Memory Transactions
Lookup Table Entry Format
I/O Transaction Address Decoding
Indirect I/O Transaction Generation
Address Decoding
Subtractive Decoding of I/O Transactions
Configuration Accesses
Type 0 Accesses to 21555 Configuration Space
Initiation of Configuration Transactions by
Address Decoding
Bar Size Address Translation
21555 Bar Summary
Bar Summary
Page
PCI Bus Transactions
Transactions Overview
Posted Write Transactions
Memory Write Transactions
Memory Write and Invalidate Transactions
Write Performance Tuning Options
3 64-bit Extension Posted Write Transaction
Write-Through
Delayed Write Transactions
Target Bus Response Initiator Bus Response
Delayed Read Transactions
Delayed Write Transaction Target Termination Returns
Delayed Read Transaction Target Termination Returns
Nonprefetchable Reads
Prefetchable Reads
Prefetchable Read Transactions Using the 64-bit Extension
Read Performance Features and Tuning Options
Prefetching
Prefetch Boundaries
Read Queue Full Threshold Tuning
64-Bit and 32-Bit Transactions Initiated by
Target Terminations
Target Terminations Returned by
Transaction Termination Errors on the Target Bus
Ordering Rules
Transaction Ordering Rules
PCI Bus Transactions
Page
Initialization Requirements
Power Management, Hot-Swap, and Reset Signals
Power Management, Hot-Swap, and Reset Signals Sheet 1
Spmel
Reset Behavior
Power Management, Hot-Swap, and Reset Signals Sheet 2
Srstinl
Reset Mechanisms
Prstl
Central Function During Reset
21555 Initialization
With SROM, Local, and Host Processors
Without Serial Preload
Without Local Processor and Serial Preload
Power Management Support
Without Local Processor
Without Host Processor
Next Power State Action
Transitions Between Power Management States
Power Management Actions
2 PME# Support
Overview of CompactPCI Controller Hardware Interface
Power Management Data Register
CompactPCI Hot-Swap Functionality
Primary Lstat K Ω
Insertion and Removal Process
Prstl 332 Ω
Initialization Requirements
2a INS ENUM#
W Disconnected
W Connected
4b Insertion
Initialization Requirements
Signal Name Description
Primary and Secondary PCI Bus Clock Signals
Primary and Secondary PCI Bus Clock Signals Sheet 1
Clocking
Sclk
Primary and Secondary PCI Bus Clock Signals Sheet 2
21555 Secondary Clock Outputs
Sclko
66 MHz Support
Page
Interface Signals
Parallel ROM Interface
Prom Interface Signals Sheet 1
Signal Type Description Name
Prom Interface Signals Sheet 2
21555
Prom Read by CSR Access
Parallel and Serial ROM Connection
WE# OE#
Prom Read Timing
Prom Write by CSR Access
Prom Dword Read
Prom Write Timing
Access Time and Strobe Control
Read and Write Strobe Timing
Attaching Additional Devices to the ROM Interface
Attaching Multiple Devices on the ROM Interface
Serial ROM Interface
Srom Interface Signals
Srom Interface Signals
Sromsrom Preload Operation
Srom Configuration Data Preload Format
Srom Operation by CSR Access
Serial ROM Interface
Srom Write All Timing Diagram
Srom Erase Timing Diagram
Page
Primary PCI Bus Arbitration Signals
Primary PCI Bus Arbitration Signals
Secondary PCI Bus Arbitration Signals
Secondary PCI Bus Arbitration Signals
Secondary PCI Bus Arbitration
Secondary Bus Arbitration Using the Internal Arbiter
Primary PCI Bus Arbitration
Secondary Arbiter Example
Bit Name Description
Secondary Bus Arbitration Using an External Arbiter
Arbiter Control Register
Interrupt and Scratchpad Registers
Primary and Secondary PCI Bus Interrupt Signals
Primary and Secondary PCI Bus Interrupt Signals
Interrupt Support
Interrupt and Scratchpad Registers
Doorbell Interrupts
Scratchpad Registers
Page
Primary PCI Bus Error Signals
Error Handling
Error Signals
Primary PCI Bus Error Signals
Secondary PCI Bus Error Signals
Type PER † Action Taken Error Transaction
Parity Errors
Parity Error Responses Sheet 1
Asserts pperrl
Parity Error Responses Sheet 2
Error Transaction
Parity Error Responses Sheet 3
Asserts sperrl
System Error SERR# Reporting
Jtag Test Port
Jtag Signals
Jtag Signals
Test Access Port Controller
Initialization
I2O Support
Inbound Message Passing
I2O Support
Outbound Message Passing
116
117
Page
VPD Support
Reading VPD Information
Writing VPD Information
Register Cross Reference Table
List of Registers
Register Summary
Theory of Operation Chapter Register Reference Information
Byte Reset Value Write Read
Configuration Registers
Configuration Space Address Register Sheet 1
Register Name Preload Hex Access
Configuration Space Address Register Sheet 2
Configuration Space Address Register Sheet 3
Configuration Space Address Register Sheet 4
Control and Status Registers
Configuration Space Address Register Sheet 5
Register Name Reset Value Write Access Read Access
CSR Address Map Sheet 1
CSR Address Map Sheet 2
Ffff W1TC
CSR Address Map Sheet 3
Ffff W1TS
CSR Address Map Sheet 4
CSR Address Map Sheet 5
Address Decoding
Primary and Secondary Address
Primary CSR and Downstream Memory 0 Bara Sheet 1
Primary CSR and Downstream Memory 0 Bara Sheet 2
Secondary CSR Memory BARsa Sheet 1
Offsets Primary CSR I/O BAR Secondary CSR I/O BAR
Secondary CSR Memory BARsa Sheet 2
Primary and Secondary CSR I/O Barsa
Upstream I/O or Memory 0 BAR
Downstream I/O or Memory 1 and Upstream I/O or Memory 0 BAR
Offsets
Downstream Memory 2 and 3 BAR, and Upstream Memory 1 BAR
Upper 32 Bits Downstream Memory 3 Bar
Upstream Memory 2 Bar
Xlatbase
Offsets Downstream I/O or Memory
Translated Base
Downstream Upstream Offsets Memory Translated Base
Upstream I/O or Memory Setup
139
Configuration Transaction Generation Registers
Upper 32 Bits Downstream Memory 3 Setup Register
Downstream and Upstream Configuration Address Registers
Cfgaddr
Configuration Own Bits Register
Cfgdata
Configuration CSR Sheet 1
Offset Downstream I/O Address Upstream I/O Address
Configuration CSR Sheet 2
Downstream I/O Address and Upstream I/O Address Registers
Ioaddr IA
Offsets Downstream I/O Data Upstream I/O Data
Downstream I/O Data and Upstream I/O Data Registers
O Own Bits Registers
Iodata
Lutoffset
O CSR
Lookup Table Offset Register
Lookup Table Data Register
Configuration Registers
PCI Registers
Upstream Memory 2 Lookup Table
Vendor ID Register
Primary Interface Configuration Space Address Map
Secondary Interface Configuration Space Address Map
Device ID Register
Offsets Primary Command Secondary Command
Primary and Secondary Command Registers
Primary and Secondary Command Registers Sheet 1
SERR#
Primary and Secondary Command Registers Sheet 2
Primary and Secondary Status Registers Sheet 1
Offsets Primary Status Secondary Status
Primary and Secondary Status Registers Sheet 2
Revision ID Rev ID Register
Offsets Primary Class Code Secondary Class Code
Primary and Secondary Class Code Registers
Primary and Secondary Cache Line Size Registers
Offsets Primary Cache Line Size Secondary Cache Line Size
Offsets Primary MLT Secondary MLT
Header Type Register
BiST Register
Enhanced Capabilities Pointer Register
Subsystem Vendor ID Register
Subsystem ID Register
Primary and Secondary Interrupt Line Registers
Primary and Secondary Maximum Latency Registers
Primary and Secondary Interrupt Pin Registers
Primary and Secondary Minimum Grant Registers
Chip Control 0 Register Sheet 1
Device-Specific Control and Status Registers
Device-Specific Control and Status Address Map
Chip Control 0 Register Sheet 2
Chip Control 0 Register Sheet 3
Chip Control 0 Register Sheet 4
Chip Control 1 Register Sheet 1
Chip Control 1 Register Sheet 2
I20ENA
Chip Control 1 Register Sheet 3
Chip Status Register
163
Generic Own Bits Register
Rots
I2O Outbound PostList Interrupt Mask
16.6 I2O Registers
I2O Outbound PostList Status
I2O Inbound PostList Status
I2O Outbound Queue
I2O Inbound PostList Interrupt Mask
I2O Inbound Queue
I2OOUT P
I2O Outbound FreeList Tail Pointer
I2O Inbound FreeList Head Pointer
I2O Inbound PostList Tail Pointer
I2O Outbound PostList Head Pointer
Ldipc W1TLS
I2O Inbound PostList Counter
I2O Inbound FreeList Counter
Ldifc W1TLS
Ldopc W1TLS
I2O Outbound PostList Counter
I2O Outbound FreeList Counter
Chip Set IRQ Mask Register
Interrupt Registers
Chip Status CSR
PMD0 W1TC
PAGE0IRQ W1TC
Chip Clear IRQ Mask Register
Upstream Page Boundary IRQ 0 Register
Upstream Page Boundary IRQ Mask 1 Register
Upstream Page Boundary IRQ 1 Register
Upstream Page Boundary IRQ Mask 0 Register
Primary Clear IRQ Secondary Clear IRQ
Primary Clear IRQ and Secondary Clear IRQ Registers
Primary Set IRQ and Secondary Set IRQ Registers
Primary Set IRQ
Primary Clear IRQ Mask Secondary Clear IRQ Mask
Primary Set IRQ Mask and Secondary Set IRQ Mask Registers
Scratchpad 0 Through Scratchpad 7 Registers Sheet 1
Secondary Set IRQ Mask
Primary Expansion ROM BAR
Prom Registers
Scratchpad 0 Through Scratchpad 7 Registers Sheet 2
Primary Expansion ROM Setup Register
Sequence on
Romdata
ROM Setup Register
ROM Data Register
Romaddr
ROM Address Register
ROM Control Register Sheet 1
ROM Control Register Sheet 2
Mode Setting Configuration Register Sheet 1
Srom Registers
Srompoll
Byte Description Offset
Mode Setting Configuration Register Sheet 2
Serial Preload Sequence Sheet 1
Serial Preload Sequence Sheet 2
Serial Preload Sequence Sheet 3
Error Registers
Arbiter Control
Primary SERR# Disable Register
Secondary SERR# Disable Register
PM ECP ID
Power Management ECP ID and Next Pointer Register
Init Registers
DSI
Power Management Capabilities Register
APS
PME
Power Management Control and Status Register
Pmcsr Bridge Support Extensions
Power Management Data Register
Reset Control Register
CompactPCI Hot-Swap Control Register Sheet 1
HS Next Pointer
Jtag Instruction Register Options Sheet 1
Jtag Registers
CompactPCI Hot-Swap Control Register Sheet 2
Boundary-Scan Register
Jtag Instruction Register Options Sheet 2
Bypass Register
Boundary Scan Order
VPD ECP
VPD Registers
Vital Product Data VPD ECP ID and Next Pointer Register
Vital Product Data VPD Address Register
VPD Data Register
Page
Acronyms
Acronyms
Index
CSR
140