Intel® NetStructureTMZT 7102 Chassis Management Module
Hardware Specifications
2.2System Architecture
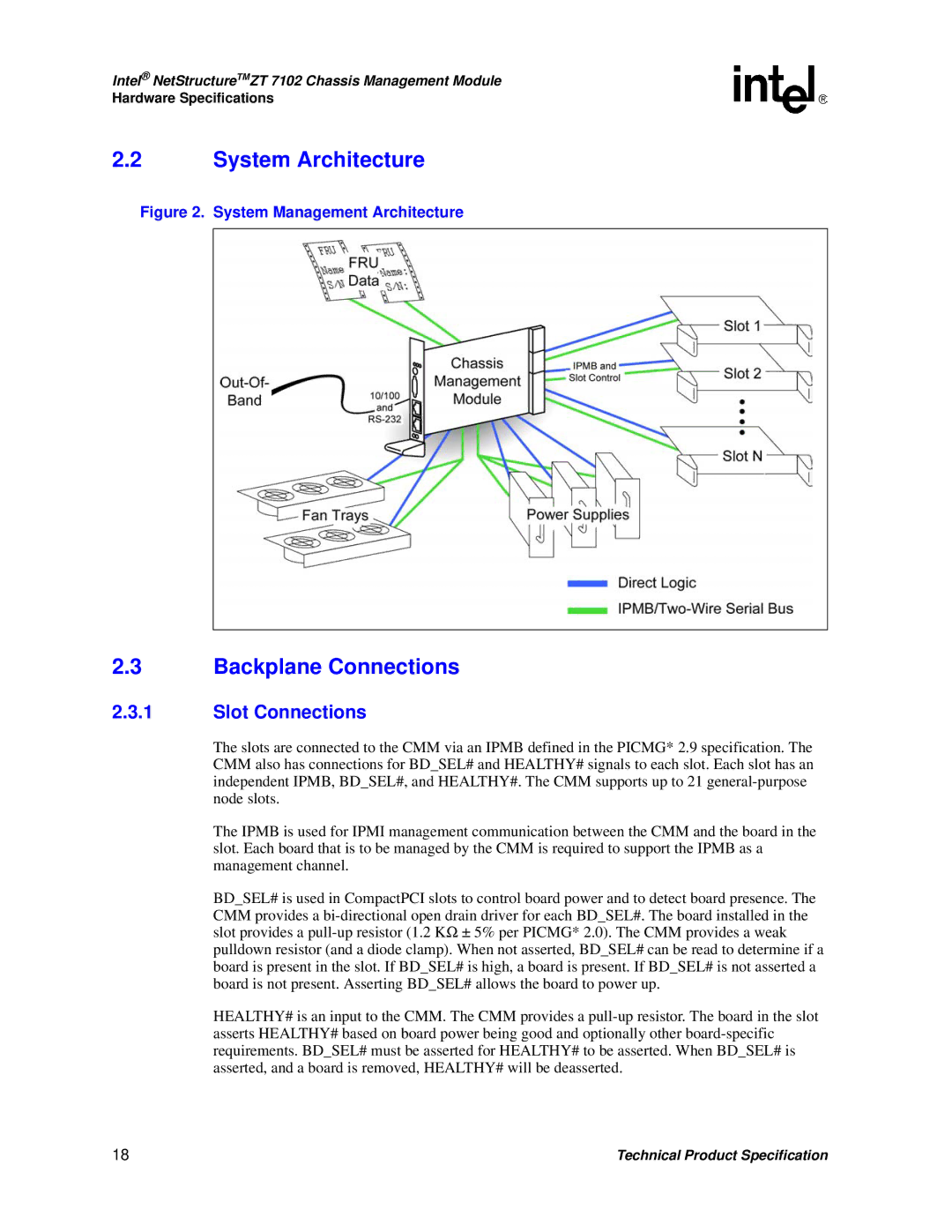
Figure 2. System Management Architecture
2.3Backplane Connections
2.3.1Slot Connections
The slots are connected to the CMM via an IPMB defined in the PICMG* 2.9 specification. The CMM also has connections for BD_SEL# and HEALTHY# signals to each slot. Each slot has an independent IPMB, BD_SEL#, and HEALTHY#. The CMM supports up to 21
The IPMB is used for IPMI management communication between the CMM and the board in the slot. Each board that is to be managed by the CMM is required to support the IPMB as a management channel.
BD_SEL# is used in CompactPCI slots to control board power and to detect board presence. The CMM provides a
HEALTHY# is an input to the CMM. The CMM provides a
18 | Technical Product Specification |