Step 8: Configure Subnet Access
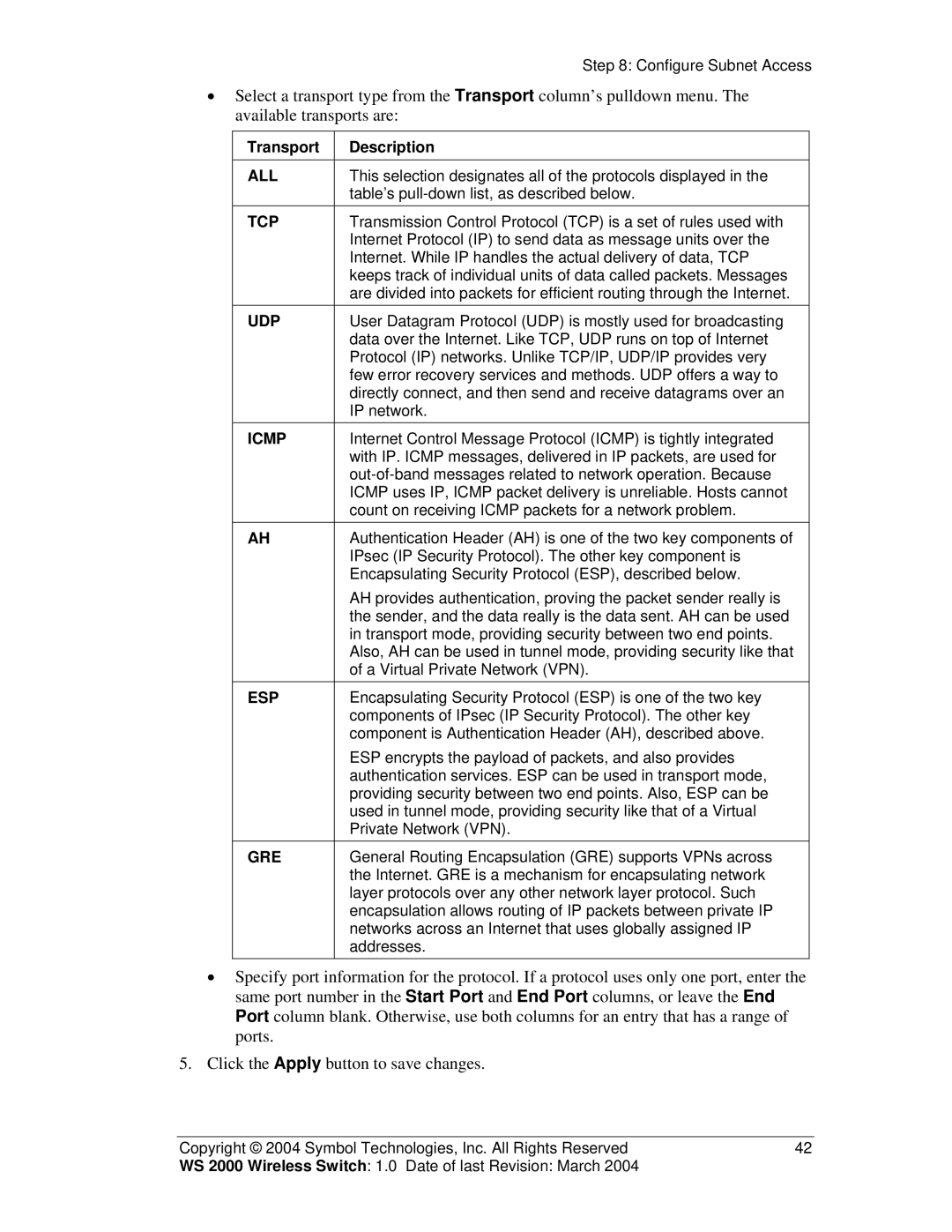
•Select a transport type from the Transport column’s pulldown menu. The available transports are:
Transport | Description |
ALL | This selection designates all of the protocols displayed in the |
| table’s |
TCP | Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a set of rules used with |
| Internet Protocol (IP) to send data as message units over the |
| Internet. While IP handles the actual delivery of data, TCP |
| keeps track of individual units of data called packets. Messages |
| are divided into packets for efficient routing through the Internet. |
UDP | User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is mostly used for broadcasting |
| data over the Internet. Like TCP, UDP runs on top of Internet |
| Protocol (IP) networks. Unlike TCP/IP, UDP/IP provides very |
| few error recovery services and methods. UDP offers a way to |
| directly connect, and then send and receive datagrams over an |
| IP network. |
ICMP | Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is tightly integrated |
| with IP. ICMP messages, delivered in IP packets, are used for |
| |
| ICMP uses IP, ICMP packet delivery is unreliable. Hosts cannot |
| count on receiving ICMP packets for a network problem. |
AH | Authentication Header (AH) is one of the two key components of |
| IPsec (IP Security Protocol). The other key component is |
| Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP), described below. |
| AH provides authentication, proving the packet sender really is |
| the sender, and the data really is the data sent. AH can be used |
| in transport mode, providing security between two end points. |
| Also, AH can be used in tunnel mode, providing security like that |
| of a Virtual Private Network (VPN). |
ESP | Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP) is one of the two key |
| components of IPsec (IP Security Protocol). The other key |
| component is Authentication Header (AH), described above. |
| ESP encrypts the payload of packets, and also provides |
| authentication services. ESP can be used in transport mode, |
| providing security between two end points. Also, ESP can be |
| used in tunnel mode, providing security like that of a Virtual |
| Private Network (VPN). |
GRE | General Routing Encapsulation (GRE) supports VPNs across |
| the Internet. GRE is a mechanism for encapsulating network |
| layer protocols over any other network layer protocol. Such |
| encapsulation allows routing of IP packets between private IP |
| networks across an Internet that uses globally assigned IP |
| addresses. |
•Specify port information for the protocol. If a protocol uses only one port, enter the same port number in the Start Port and End Port columns, or leave the End Port column blank. Otherwise, use both columns for an entry that has a range of ports.
5.Click the Apply button to save changes.
Copyright © 2004 Symbol Technologies, Inc. All Rights Reserved | 42 |
WS 2000 Wireless Switch: 1.0 Date of last Revision: March 2004 |
|