AT-S79 Management Software User’s Guide
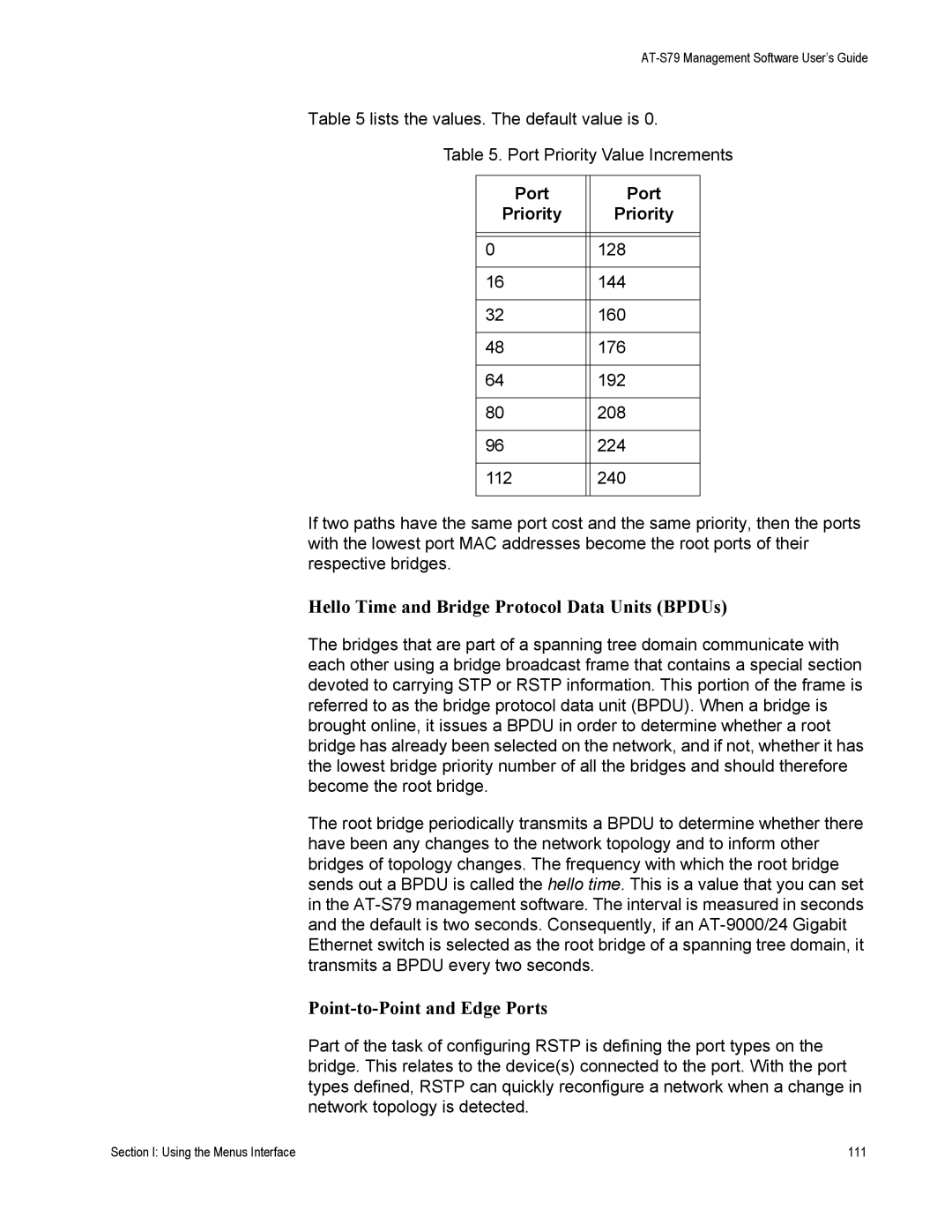
Table 5 lists the values. The default value is 0.
Table 5. Port Priority Value Increments
Port |
| Port |
Priority |
| Priority |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
| 128 |
|
|
|
16 |
| 144 |
|
|
|
32 |
| 160 |
|
|
|
48 |
| 176 |
|
|
|
64 |
| 192 |
|
|
|
80 |
| 208 |
|
|
|
96 |
| 224 |
|
|
|
112 |
| 240 |
|
|
|
If two paths have the same port cost and the same priority, then the ports with the lowest port MAC addresses become the root ports of their respective bridges.
Hello Time and Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)
The bridges that are part of a spanning tree domain communicate with each other using a bridge broadcast frame that contains a special section devoted to carrying STP or RSTP information. This portion of the frame is referred to as the bridge protocol data unit (BPDU). When a bridge is brought online, it issues a BPDU in order to determine whether a root bridge has already been selected on the network, and if not, whether it has the lowest bridge priority number of all the bridges and should therefore become the root bridge.
The root bridge periodically transmits a BPDU to determine whether there have been any changes to the network topology and to inform other bridges of topology changes. The frequency with which the root bridge sends out a BPDU is called the hello time. This is a value that you can set in the
Point-to-Point and Edge Ports
Part of the task of configuring RSTP is defining the port types on the bridge. This relates to the device(s) connected to the port. With the port types defined, RSTP can quickly reconfigure a network when a change in network topology is detected.
Section I: Using the Menus Interface | 111 |