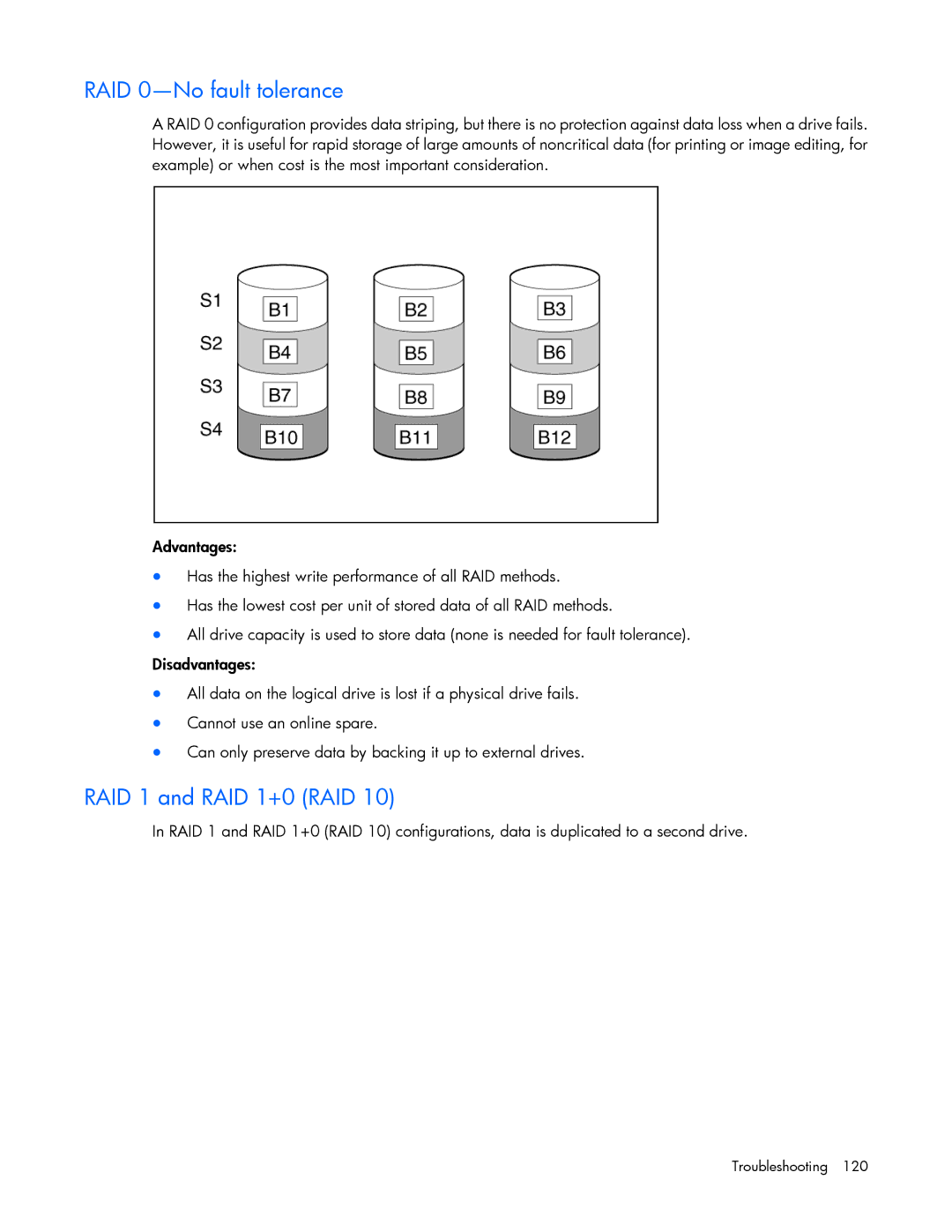
RAID 0—No fault tolerance
A RAID 0 configuration provides data striping, but there is no protection against data loss when a drive fails. However, it is useful for rapid storage of large amounts of noncritical data (for printing or image editing, for example) or when cost is the most important consideration.
Advantages:
•Has the highest write performance of all RAID methods.
•Has the lowest cost per unit of stored data of all RAID methods.
•All drive capacity is used to store data (none is needed for fault tolerance). Disadvantages:
•All data on the logical drive is lost if a physical drive fails.
•Cannot use an online spare.
•Can only preserve data by backing it up to external drives.
RAID 1 and RAID 1+0 (RAID 10)
In RAID 1 and RAID 1+0 (RAID 10) configurations, data is duplicated to a second drive.