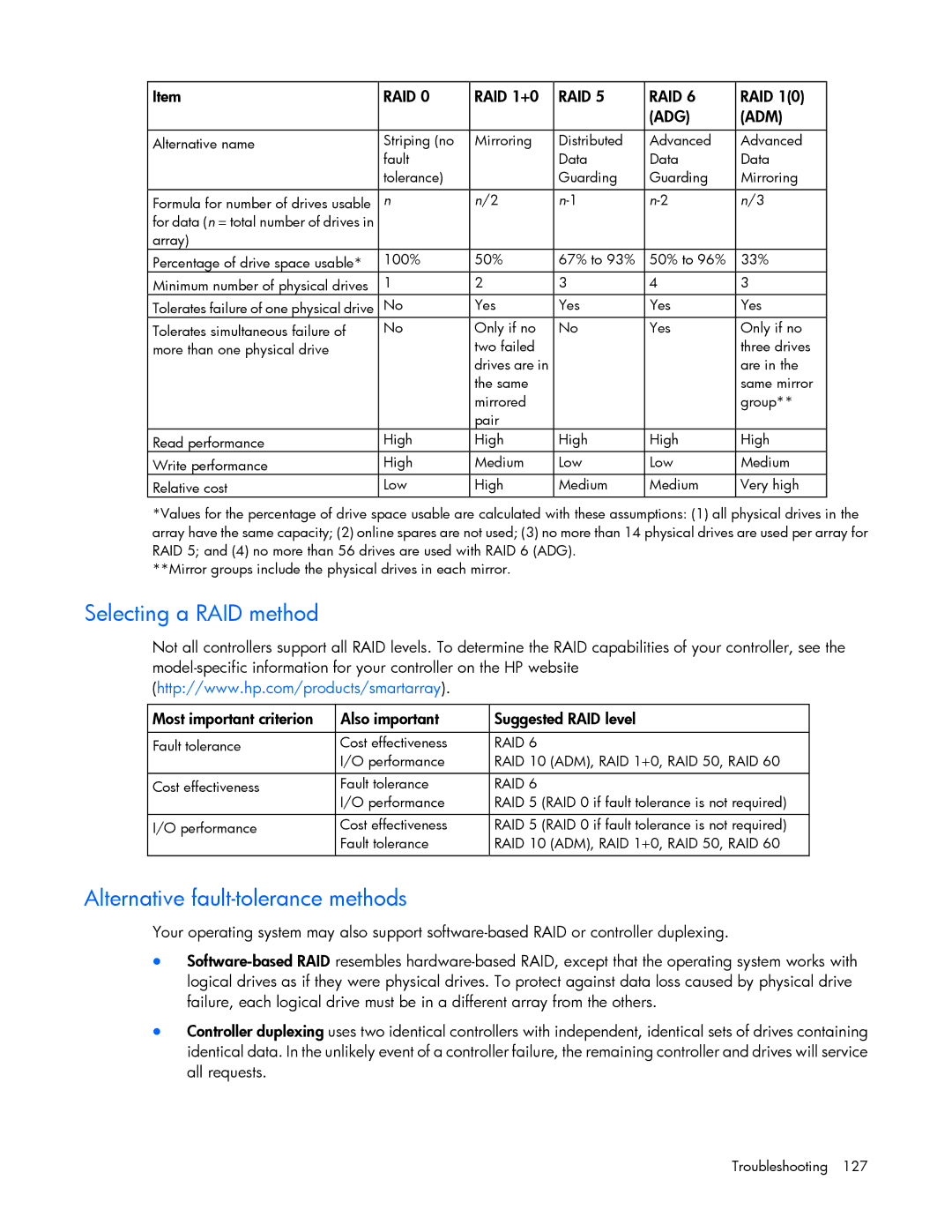
Item | RAID 0 | RAID 1+0 | RAID 5 | RAID 6 | RAID 1(0) |
|
|
|
| (ADG) | (ADM) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alternative name | Striping (no | Mirroring | Distributed | Advanced | Advanced |
| fault |
| Data | Data | Data |
| tolerance) |
| Guarding | Guarding | Mirroring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Formula for number of drives usable | n | n/2 | n/3 | ||
for data (n = total number of drives in |
|
|
|
|
|
array) |
|
|
|
|
|
Percentage of drive space usable* | 100% | 50% | 67% to 93% | 50% to 96% | 33% |
Minimum number of physical drives | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
Tolerates failure of one physical drive | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Tolerates simultaneous failure of | No | Only if no | No | Yes | Only if no |
more than one physical drive |
| two failed |
|
| three drives |
|
| drives are in |
|
| are in the |
|
| the same |
|
| same mirror |
|
| mirrored |
|
| group** |
|
| pair |
|
|
|
Read performance | High | High | High | High | High |
Write performance | High | Medium | Low | Low | Medium |
Relative cost | Low | High | Medium | Medium | Very high |
*Values for the percentage of drive space usable are calculated with these assumptions: (1) all physical drives in the array have the same capacity; (2) online spares are not used; (3) no more than 14 physical drives are used per array for RAID 5; and (4) no more than 56 drives are used with RAID 6 (ADG).
**Mirror groups include the physical drives in each mirror.
Selecting a RAID method
Not all controllers support all RAID levels. To determine the RAID capabilities of your controller, see the
Most important criterion | Also important | Suggested RAID level |
|
|
|
Fault tolerance | Cost effectiveness | RAID 6 |
| I/O performance | RAID 10 (ADM), RAID 1+0, RAID 50, RAID 60 |
Cost effectiveness | Fault tolerance | RAID 6 |
| I/O performance | RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not required) |
I/O performance | Cost effectiveness | RAID 5 (RAID 0 if fault tolerance is not required) |
| Fault tolerance | RAID 10 (ADM), RAID 1+0, RAID 50, RAID 60 |
Alternative fault-tolerance methods
Your operating system may also support
•
•Controller duplexing uses two identical controllers with independent, identical sets of drives containing identical data. In the unlikely event of a controller failure, the remaining controller and drives will service all requests.