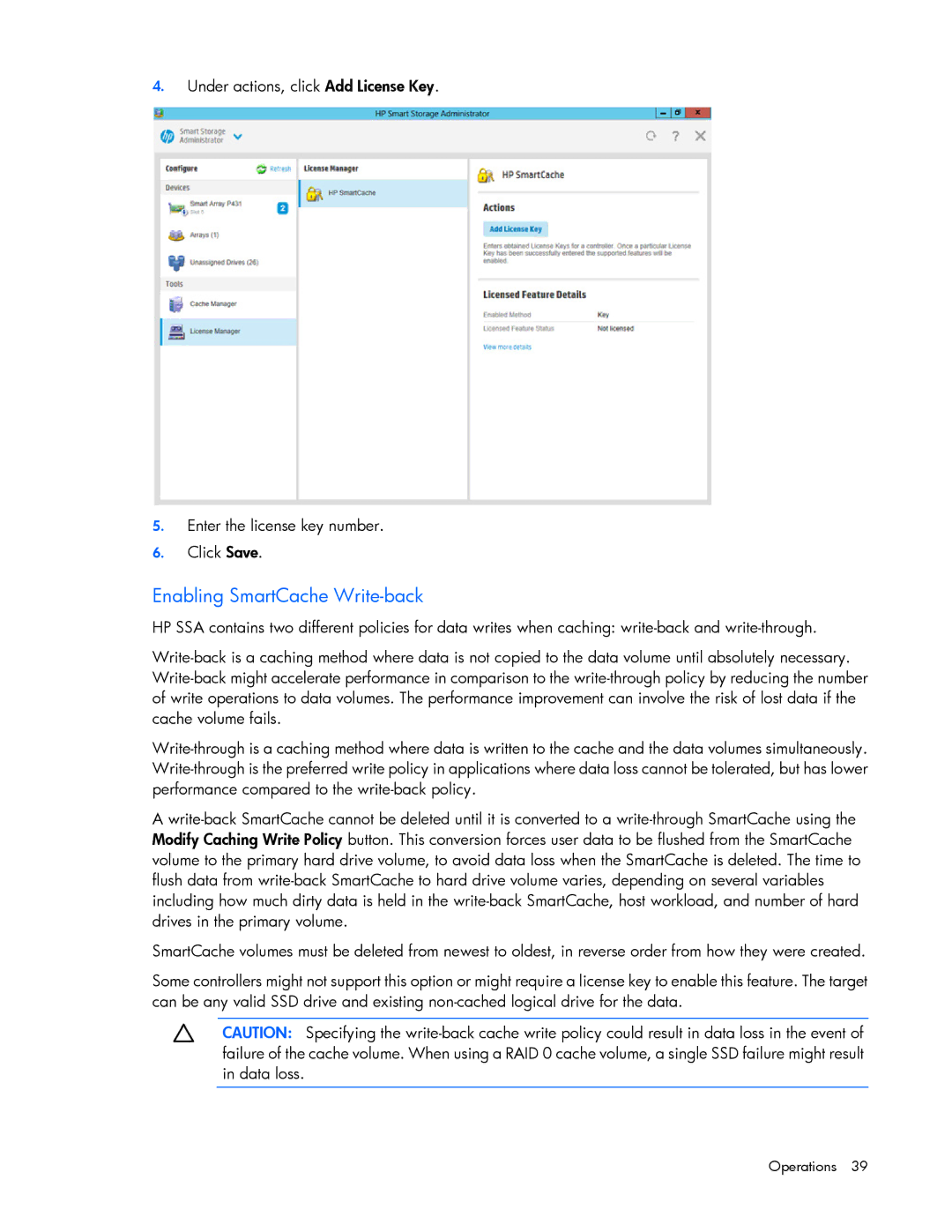
4.Under actions, click Add License Key.
5.Enter the license key number.
6.Click Save.
Enabling SmartCache Write-back
HP SSA contains two different policies for data writes when caching: write-back and write-through.
Write-back is a caching method where data is not copied to the data volume until absolutely necessary. Write-back might accelerate performance in comparison to the write-through policy by reducing the number of write operations to data volumes. The performance improvement can involve the risk of lost data if the cache volume fails.
Write-through is a caching method where data is written to the cache and the data volumes simultaneously. Write-through is the preferred write policy in applications where data loss cannot be tolerated, but has lower performance compared to the write-back policy.
A write-back SmartCache cannot be deleted until it is converted to a write-through SmartCache using the Modify Caching Write Policy button. This conversion forces user data to be flushed from the SmartCache volume to the primary hard drive volume, to avoid data loss when the SmartCache is deleted. The time to flush data from write-back SmartCache to hard drive volume varies, depending on several variables including how much dirty data is held in the write-back SmartCache, host workload, and number of hard drives in the primary volume.
SmartCache volumes must be deleted from newest to oldest, in reverse order from how they were created.
Some controllers might not support this option or might require a license key to enable this feature. The target can be any valid SSD drive and existing non-cached logical drive for the data.
CAUTION: Specifying the write-back cache write policy could result in data loss in the event of failure of the cache volume. When using a RAID 0 cache volume, a single SSD failure might result in data loss.
Operations 39