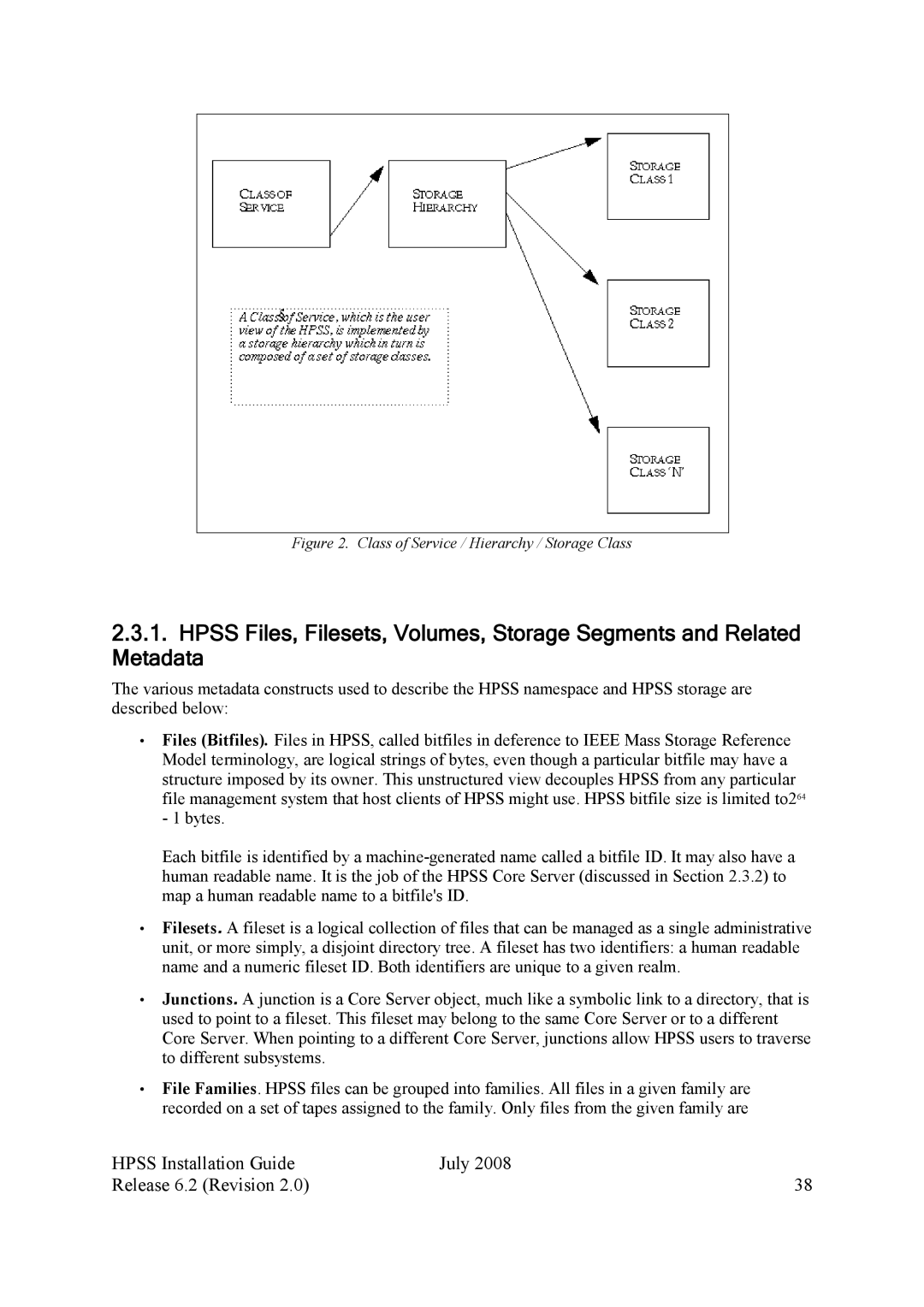
Figure 2. Class of Service / Hierarchy / Storage Class
2.3.1.HPSS Files, Filesets, Volumes, Storage Segments and Related Metadata
The various metadata constructs used to describe the HPSS namespace and HPSS storage are described below:
•Files (Bitfiles). Files in HPSS, called bitfiles in deference to IEEE Mass Storage Reference Model terminology, are logical strings of bytes, even though a particular bitfile may have a structure imposed by its owner. This unstructured view decouples HPSS from any particular file management system that host clients of HPSS might use. HPSS bitfile size is limited to264 - 1 bytes.
Each bitfile is identified by a
•Filesets. A fileset is a logical collection of files that can be managed as a single administrative unit, or more simply, a disjoint directory tree. A fileset has two identifiers: a human readable name and a numeric fileset ID. Both identifiers are unique to a given realm.
•Junctions. A junction is a Core Server object, much like a symbolic link to a directory, that is used to point to a fileset. This fileset may belong to the same Core Server or to a different Core Server. When pointing to a different Core Server, junctions allow HPSS users to traverse to different subsystems.
•File Families. HPSS files can be grouped into families. All files in a given family are recorded on a set of tapes assigned to the family. Only files from the given family are
HPSS Installation Guide | July 2008 |
Release 6.2 (Revision 2.0) | 38 |