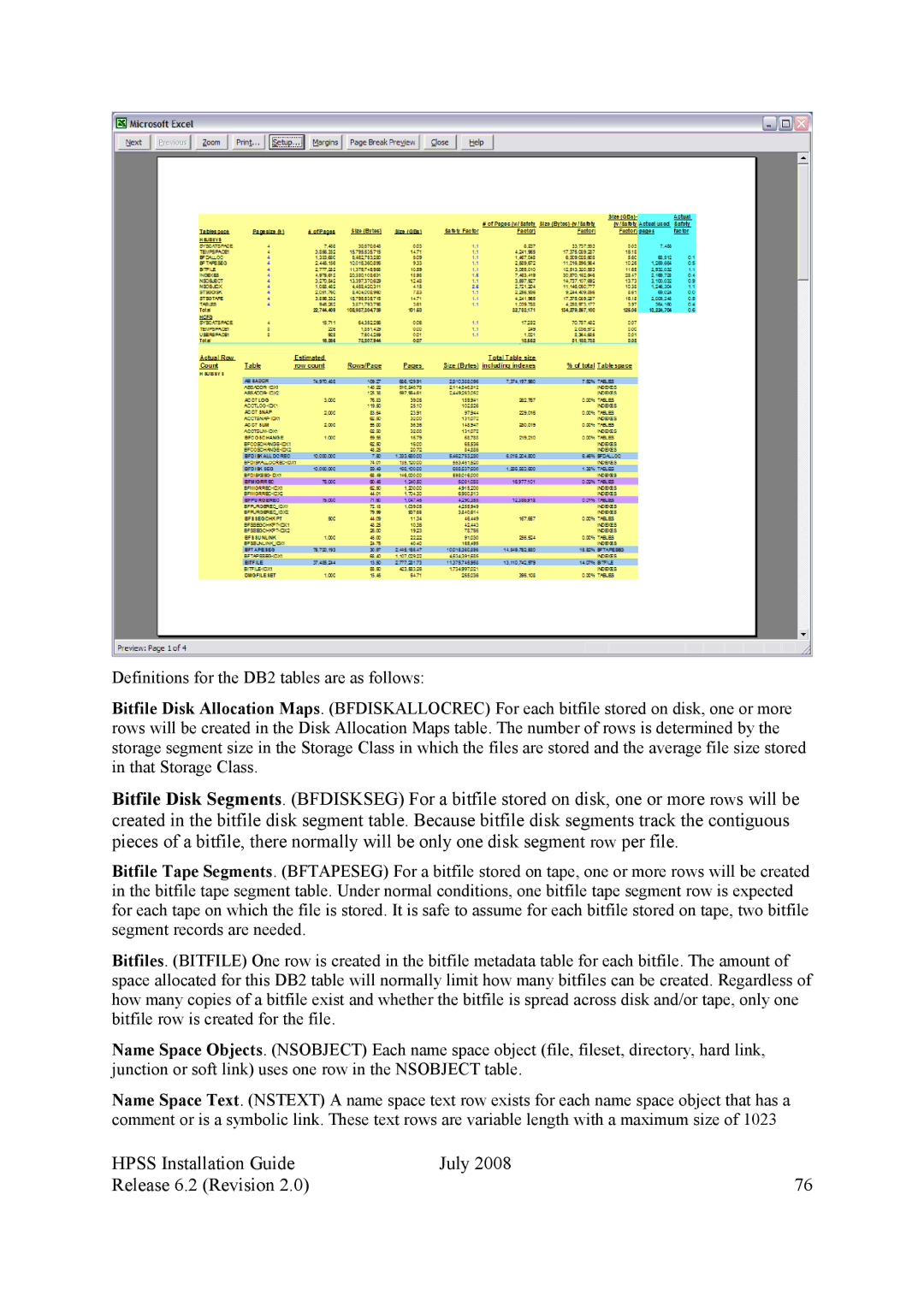
Definitions for the DB2 tables are as follows:
Bitfile Disk Allocation Maps. (BFDISKALLOCREC) For each bitfile stored on disk, one or more rows will be created in the Disk Allocation Maps table. The number of rows is determined by the storage segment size in the Storage Class in which the files are stored and the average file size stored in that Storage Class.
Bitfile Disk Segments. (BFDISKSEG) For a bitfile stored on disk, one or more rows will be created in the bitfile disk segment table. Because bitfile disk segments track the contiguous pieces of a bitfile, there normally will be only one disk segment row per file.
Bitfile Tape Segments. (BFTAPESEG) For a bitfile stored on tape, one or more rows will be created in the bitfile tape segment table. Under normal conditions, one bitfile tape segment row is expected for each tape on which the file is stored. It is safe to assume for each bitfile stored on tape, two bitfile segment records are needed.
Bitfiles. (BITFILE) One row is created in the bitfile metadata table for each bitfile. The amount of space allocated for this DB2 table will normally limit how many bitfiles can be created. Regardless of how many copies of a bitfile exist and whether the bitfile is spread across disk and/or tape, only one bitfile row is created for the file.
Name Space Objects. (NSOBJECT) Each name space object (file, fileset, directory, hard link, junction or soft link) uses one row in the NSOBJECT table.
Name Space Text. (NSTEXT) A name space text row exists for each name space object that has a comment or is a symbolic link. These text rows are variable length with a maximum size of 1023
HPSS Installation Guide | July 2008 |
Release 6.2 (Revision 2.0) | 76 |