Page
Inter
Intel Corporation
Table of Contents
Chapter Architectural Compatibility
Chapter Highlights
Page
32-bit Architecture
High-performance Implementation
Highlights
Configurable Protection
Virtual Memory Support
Extended Debugging Support
Object Code Compatibility
Summary
Application Architecture
Page
Registers
General Registers
Flags and Instruction Pointer
Numeric Coprocessor Registers
Memory and logical Addressing
Segment and Descriptor Registers
Logical Address Translation
Addressing Modes
Data Types and Instructions
Principal Data Types
Numeric Coprocessor Data Types
Other Instructions
Stack Instructions
~.,...I-------.-1 Byte String
LII
Miscellaneous Instructions
Chapter System Architecture
Page
System Registers
Multitasking
Task Switching
Task State Segment
Addressing
Address Translation Overview
Segments
Address Translation Overview
Principal Descriptor Fields
~~~~~.II~~~
Pages
Virtual Memory
Linear to Physical Address Translation
I I I
Protection
Privilege
USing Privilege Levels
Privileged Instructions
Segment Protection
Protection
Interrupts and Exceptions
10. Gates as Protected Entry Points
Interrupt Descriptor Table
Debug Eceptions and Registers
System Architecture
Page
Architectural Compatibility
Page
80286 Compatibility
Real and Virtual 86 Modes
Architectural Compatibility
Trapping Virtual 861\11ode System Calls
Page
Chapter Hardware Implementation
Page
Chapter Hardware Implementation
Hardware Implementation
Clock
Data and Address Buses
Bus Cycle Definition
Bus Cycle Control
Non-pipelined Bus Cycle Timing
Bus Cycles with Pipelined Addresses
Dynamic Bus Sizing
Processor Status and Control
Coprocessor Control
Mixed 16- and 32-bit Accesses
Chapter Data Sheet
Page
80386
Update Notice
Table of Contents
Descriptor Tables Introduction
Interrupt Descriptor Table
Segment Descriptor Cache
Privilege Validation
Functional Data
Package Thermal Specification
3.4
Initiating and Maintaining Pipelined Address
Pipelined Address with Dynamic Data Bus Sizing
Base Architecture Introduction
Register Overview
Register Descriptions
General Purpose Registers
Instruction Pointer
Flags Register
TSS
Segment Registers
Segment Registers Descriptor Registers Loaded Automatically
Other Segment Physical Base Address Segment Limit
Segment Descriptor Registers
Control Registers
Flects the current state of the ET bit
MSW
TS Task Switched, bit
Fault Linear Address Register CR2
System Address Registers
Directory Base Register CR3
Register Accessibility
Debug and Test Registers
Compatibility
Instruction Set Overview
Iopl
Gdtr
Idtr
2 80386 Instructions
2dLogical Instructions
2a Data Transfer
2b Arithmetic Instructions
2e Bit Manipulation Instructions
2f. Program Control Instructions
2g High Level Language Instructions
2h Protection Model
Addressing Modes Overview
Register and Immediate Modes
3 32-Bit Memory Addressing Modes
Addressing Mode Calculations
Differences Between 16 and 32 Bit Addresses
Displacement
Data Types
Base Register BX,BP Index Register SI,DI Scale Factor
None
LilliililillIl
Sign ED rrrrrrrrl
Memory Organization
Introduction
Address Spaces
I/O Space
Segment Register Usage
Interrupts
Interrupts and Ecep~ions
Interrupt Processing
Maskable Interrupt
Non-Maskable Interrupt
Software Interrupts
Interrupt and Exception Priorities
NMI 2.INTR
Reset and Initialization
Double Fault
Instruction Restart
TLB Testing
Testability
Self-Test
Debugging Support
Breakpoint Instruction
Single-Step Trap
Debug Registers
DR1
DR2
DR3
DR4
Encoding Causing Breakpoint
Usage
Real Mode Architecture Real Mode Introduction
Debug Status Register DR6
SET/RESET/COMPLEMENT
Memory Addressing
Xchg
ADD, OR, ADC, SBB
Reserved Locations
Intierrupts
Shutdown and Halt
Protected Mode Addressing
Addressing Mechanism
Segmentation Introduction
Terminology
Descriptor Tables
Descriptor Tables Introduction
Descriptors
Byte
Address
Segment Base 15 Segment Limit 15
Dptm typ , data gm,nt
System Descriptor Formats
Selector
Offset 15
Word
Offset 31
Differences Between 386 and 286 Descriptors
Segment Base 15
Selector Fields
Segment Descriptor Cache
Nil R~L
~~~~~~~EL~~E~ ~A~~ ~I~I! ttl
~!~~~~E L~~E~~~s~ I~I! ~ J
~~?~~~~EL~~E~B~~E ~I~I~ tJ1
Protection Concepts
Rules of Privilege
Privilege Levels
Privilege Level Transfers
GOT/LOT
Call
RET,IRET
CALL, JMP
80386
Task Switching
Call Ga~es
Initialization and Transition to Protected Mode
Infef
Tools for Building Protected
Paging
Systems
Paging Concepts
Paging Organization
Mechanism
Descriptor Base Register
Directory
Level Protection R/W, U/S Bits
Frame Address 31 Reserved
Tables
DIRECTORY/TABLE Entries
Translation Lookaside Buffer
Paging Operation
Paging In Virtual Mode
Access Type
Virtual 8086 Environment
Executing 8086 Programs
Protection and 1/0 Permission Bitmap
24. Virtual 8086 Environment Memory Management
Interrupt Handling
Entering and Leaving Virtual
Task Switches TO/FROM Virtual 8086 Mode
·25.Virtual 8086 Environment Interrupt and Call Handling
For state saving i.e. push all registers in prolog, pop
Introduction
Clock CLK2
Data Bus do through
Address Bus BEO# through BE3#, A2 through A31
Bus Cycle Definition Signals W/R#, D/C#, MIIO#, LOCK#
Bus Control Signals
Introduction
Bus Arbitration Signals
Coprocessor Interface Signals
Interrupt Signals
Signal Summary
Memory and 1/0 Spaces
BEO#
Memory and 110 Organization
Dynamic Data Bus Sizing
Interfacing with 32- and 16-Bit Memories
Cycles 1 and 1a
Operand Alignment
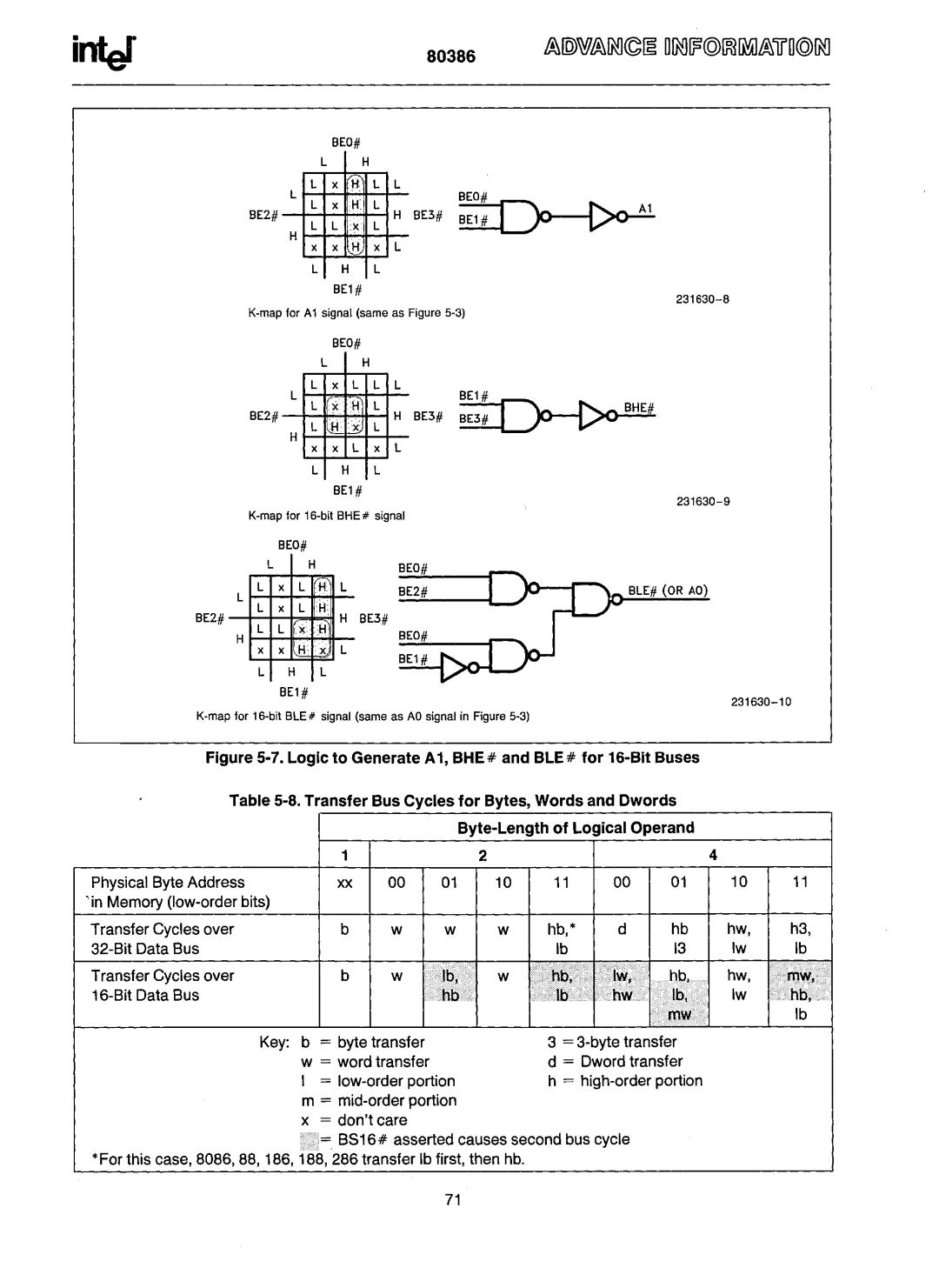
BEO# BHE# BLE# AD
Li,\~~
P1 1.p2 .p1 1.p2 .p1 1.p2 .p1 1.p2 .p1 1.p2 .p1 1.p2 .p1
Address Pipelining
·9.Fastest Read Cycles with Pipelined Address Timing
Address signal A2 selects bank Bit datapath to each bank
TWO-BANK Interleaved Memory
FOUR-BANK Interleaved Memory
Read and Write Cycles
Introduction
NON-PIPELINED Address
Xxxxx Ixxxx
Xxxi Xxxix
Ixxx
13 80386 Bus States not usIng pipelined address
3.3 NON·PIPELINED Address with Dynamic Data BUS Sizing
·14Asserting BS16# zero wait states, non·pipelinedaddress
Xixxxxx Valid
Xixxxx ,XXXXY
~~~~ DOO¥
BSI6# XXX XXx XXX X .. IXXXXwOO~ J, XXX XXX1/ \
B516# ~~..tJ.~~~~~~~
BS16 # 44~~~...l-.lI...l Ready # 44~~.lI...l/l
Bus Sizing with Pipelined Address
~ ,T1-T~-T2PJ ,T1PT2PJ Idle non-pipelined pipelined
Pipelined
Acknowledge
IO#, D/c#
Ffi
20 Complete Bus States including pipelined address
Xxxxy ~j XDONTCAR~X~ x~ ~X~~lKX~ /..XXXX
Xxxxx IXXXXIXXXXI.. /..DXXXIXXX ~ Xxxxiy
Xxixxy ~ /..XIXXY
~ -XXIXXY
Interrupt Acknowledge Inta Cycles
~--cp--- ----- ----- ----- ----- ~
Halt Indication Cycle
23.Halt Indication Cycle
Shutdown Indication Cycle
24. Shutdown Indication Cycle
Reset During Hold Acknowledge
Bus Activity During and Following Reset
Other Functional Descriptions
Entering and Exiting Hold Acknowledge
26. Requesting Hold from Active Bus NA # negated
SELF-TEST Signature
Component and Revision Identifiers
Component Revision
Component Revision Stepping Identifier Name
Software Testing for Coprocessor Presence
CMD1
Mechanical Data Introduction
PIN Assignment
000 0 0 0 000 0 0
Vee Vss
Package Dimensions and Mounting
1654189~1
Package Thermal Specification
Measure PGA Case Temperature
Infef80386
Ill
Power and Grounding
Electrical Data
D.C. Specifications
Maximum Ratings
A.C. Specifications
1 A.C. Spec Definitions
102
2 A.C. Specification Tables
·4 -16 A.C. Characteristics Symbol Parameter 80386-16
Unit Min Max Operating Frequency MHz Half of CLK2
16 A.C. Characteristics Symbol Parameter
Symbol Parameter Min
80386-16 Min Unit Max
3 A.C. Test Loads 4 A.C. Timing Waveforms
80386 ~QW~OOg OOOIP@OOIMl~iiO@OO
106
MAX
Itm
PI~
Instruction SET
80386 Instruction Encoding
8o386Instructlon Set CIock Count Summary
111
·1 Instruction Set Clock Count Summary
112
80386 Instructlon Set CIockCount S ummary Contlnued
RIm
·1 80386 Instruction Set Clock Count Summary
Doubleword
Instruction Set Clock Count Summary
115
Instruction Set Clock Count Summarycontlnued
BIT Manipulation
Instruction Set Clock Count Summar
+ml 7+ml
80386 Ins ruefIon SetCIoek CountSummary ConrInued
Protected
119
120
80386 Instructlon Set CIockCountSummaay Contmued
Interrupt Instructions
O3861nstructlon Set CIockCount Summary Contlnued
Bound
Infef80386
80386 nstructlon Set CIockCount Summary Contlnued
Ns ruetIon StCIe oekCount 5 ummary Contlnued
Madear
Overview
~~~\
2 32-Bit Extensions of the Instruction Set
Encoding of Instruction Fields
Field
Bits
Encoding of Address Mode
Osbx
OSBX+d16
11010
EOI
OS EAX
Scale Factor
Encoding of Operation Direction
NAE
NB/AE
NE/NZ
Domestic Sales Offices
California
United States