Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
| THEORY OF OPERATION | ||||||||
|
|
| |||||||
|
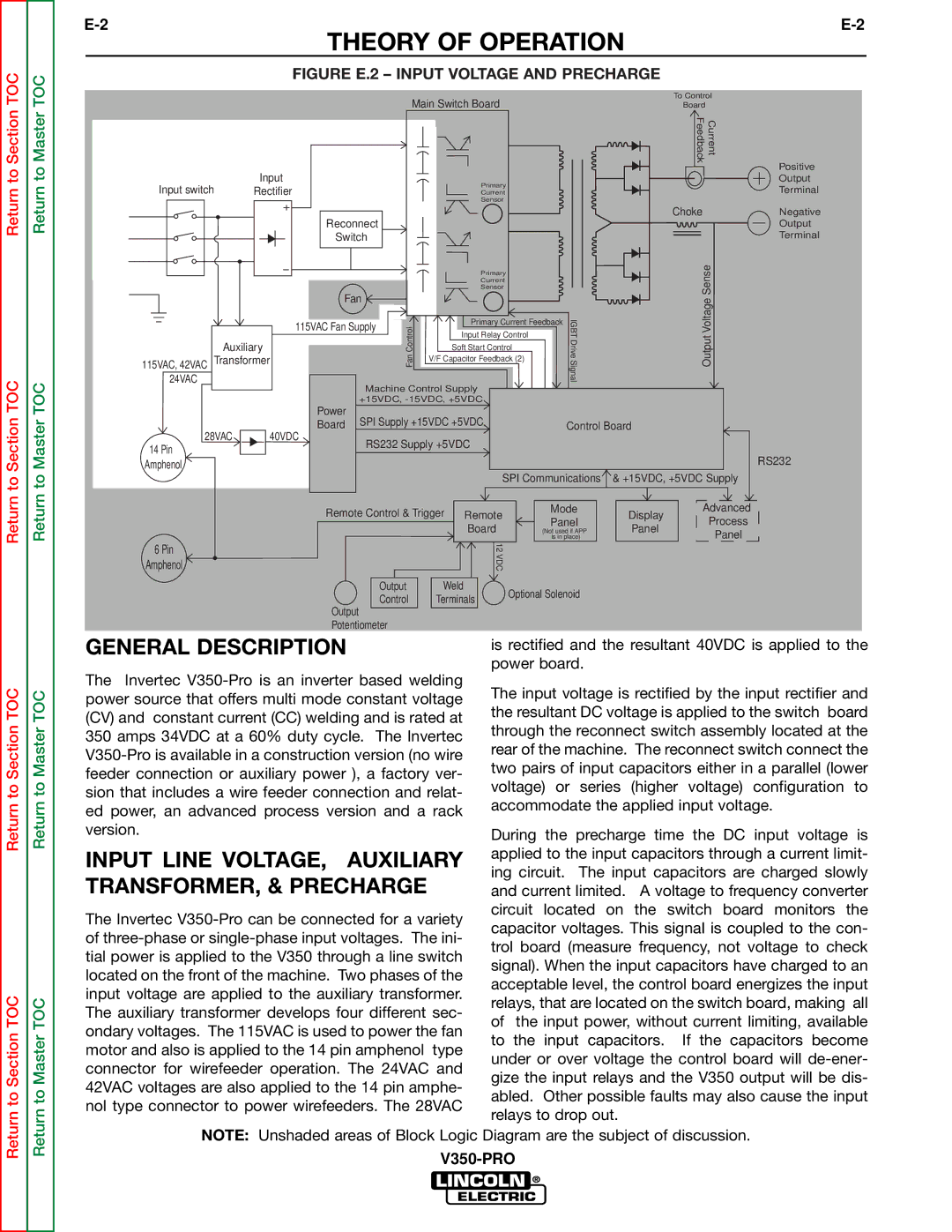
| FIGURE E.2 – INPUT VOLTAGE AND PRECHARGE |
| ||||||
|
|
| Main Switch Board |
|
|
| To Control | ||
|
|
|
|
|
| Board |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Feedback | Current |
| Input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Positive |
Input switch |
|
| Primary |
|
|
|
| Output | |
Rectifier |
|
|
|
|
|
| Terminal | ||
|
| Current |
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
| Sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Reconnect |
|
|
|
|
| Choke | Negative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Output | |
|
| Switch |
|
|
|
|
|
| Terminal |
|
|
|
| Primary |
|
|
| Sense | |
|
|
|
| Current |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| Sensor |
|
|
| ||
|
| Fan |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VoltageOutput | ||
|
| 115VAC Fan Supply | ControlFan | Primary Current Feedback | IGBTDrive Signal | ||||
|
| Input Relay Control |
| ||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||
Auxiliary |
| Soft Start Control |
| ||||||
115VAC, 42VAC Transformer |
| V/F Capacitor Feedback (2) |
| ||||||
|
|
|
| ||||||
24VAC |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
| Machine Control Supply |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| +15VDC, |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28VAC |
| Board SPI Supply +15VDC +5VDC |
|
| Control Board |
| |||
40VDC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
14 Pin |
| RS232 Supply +5VDC |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| RS232 | |
Amphenol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| SPI Communications | & +15VDC, +5VDC Supply | ||||
|
| Remote Control & Trigger Remote |
| Mode | Advanced | ||||
|
|
| Panel | Display | Process | ||||
|
|
|
| Board |
| Panel | |||
|
|
|
|
| (Not used if APP | Panel | |||
|
|
|
|
|
| is in place) |
| ||
6 Pin |
|
|
| 12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VDC |
|
|
|
|
| |
Amphenol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| Output | Weld | Optional Solenoid |
|
| ||
|
|
| Control | Terminals |
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
is rectified and the resultant 40VDC is applied to the power board.
The input voltage is rectified by the input rectifier and the resultant DC voltage is applied to the switch board through the reconnect switch assembly located at the rear of the machine. The reconnect switch connect the two pairs of input capacitors either in a parallel (lower voltage) or series (higher voltage) configuration to accommodate the applied input voltage.
During the precharge time the DC input voltage is applied to the input capacitors through a current limit- ing circuit. The input capacitors are charged slowly and current limited. A voltage to frequency converter circuit located on the switch board monitors the capacitor voltages. This signal is coupled to the con- trol board (measure frequency, not voltage to check signal). When the input capacitors have charged to an acceptable level, the control board energizes the input relays, that are located on the switch board, making all of the input power, without current limiting, available to the input capacitors. If the capacitors become under or over voltage the control board will
NOTE: Unshaded areas of Block Logic Diagram are the subject of discussion.