Data Manual
Data Manual
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
Recommended Operating Conditions
C64x+ Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
Enhanced Turbo Decoder Coprocessor TCP2
Features
Description
ZTZ/GTZ BGA Package Bottom View
ZTZ/GTZ 697-PIN Ball Grid Array BGA Package Bottom View
Submit Documentation Feedback
Functional Block Diagram
Functional Block Diagram
Characteristics of the C6455 Processor
Device Characteristics
Hardware Features
C6455
CPU DSP Core Description
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
C64x+ CPU DSP Core Data Paths
C6455 Memory Map Summary
Memory Map Summary
Memory Block Description Block Size Bytes HEX Address Range
02DF Ffff
02CF Ffff
03FF Ffff
0FFF Ffff
Boot Modes Supported
Boot Sequence
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
2 2nd-Level Bootloaders
Pin Map
Pin Assignments
C6455 Pin Map Bottom View Quadrant B
C6455 Pin Map Bottom View Quadrant C
C6455 Pin Map Bottom View Quadrant D
Signal Groups Description
TINPL0
TINPL1 TOUTL1
Gpio
URADDR4/PCBE0/GP2C SYSCLK4/GP1A
ACE3A
ACE5A ACE4A
ACE2A
ABE7 ABE6 ABE5 ABE4
Hpia
HCNTL0/PSTOP HCNTL1/PDEVSEL HHWIL/PCLK HPI16 only
CLKR1/GP0
Clks Shared
Rgmdio
UXADDR3/MDIO
UXADDR4/MDCLK
URSOC/MRXER/RMRXER
URDATA3/MRXD3 UXDATA3/MTXD3 URDATA2/MRXD2 UXDATA2/MTXD2
UXDATA4/MTXD4
UXDATA1/MTXD1/RMTXD1
UXDATA0/MTXD0/RMTXD0
IPD/IPU Description Name CLOCK/PLL Configurations
Signal
Terminal Functions
Terminal Functions
Signal Name
Type 1 IPD/IPU
Emifa 64 BIT BUS Arbitration
Emifa 64 BIT Control Signals Common to ALL Types of Memory
Emifa 64 BIT ASYNCHRONOUS/SYNCHRONOUS Memory Control
IPD/IPU2 Description Emifa 64 BIT Address
Signal TYPE1 Name
AEA1916
AEA15
AEA6
IPD/IPU Description Name
AEA5
AEA4
Signal TYPE1 IPD/IPU2 Description Name Emifa 64 BIT Data
AED20
AED21
AED19
AED18
DDR2 Memory Controller 32 BIT Address
IPD/IPU2 Description
IPD/IPU Description Name DDR2 Memory Controller 32 BIT Data
Timer
INTER-INTEGRATED Circuit I2C
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port 1 McBSP1
Signal TYPE1 IPD/IPU2 Description Name
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port 0 McBSP0
Utopia Slave ATM Controller Transmit Interface
TYPE1 IPD/IPU2 Description
URADDR2/PINTA1/ GP14 URADDR1/PRST
Utopia Slave ATM Controller Receive Interface
Management Data INPUT/OUTPUT Mdio for MII/RMII/GMII
Signal TYPE1 IPD/IPU2 Description Name Rapidio Serial Port
Management Data INPUT/OUTPUT Mdio for Rgmii
Device Configuration
RSV05
Rgrefclk
RSV07 RSV09
Reserved for Test
RSV14
RSV13
RSV15
RSV16
IPD/IPU2 Description Supply Voltage Monitor Pins
Signal TYPE1 Name no
Supply Voltage Pins
U16
AB7
AA1 AA6
AC6 AC9
AE6 AE8
AD5 AD7
AF1
CV DD
Cvdd
Ground Pins
GND
F20 F22 F24 G11 G13 G15 G17 G19 G21 G23
M16 M18 M24 M26 M29 N13 N15 N17 N19 N23 P12 P14 P16 P18
AB6
AA2 AA7
AC7 AC8
AE4 AE7
AD6
GND AF2
AH1
Development Support
Development
Device Support
Device and Development-Support Tool Nomenclature
SM=Qualifieddevice
C6000 DSP platforms
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
C6455 Device Configuration Pins AEA190, ABA10, and Pcien
Device Configuration at Device Reset
Configuration IPD PIN
IPU1
AEA13
AEA14
AEA12
AEA11
Configuration IPD Functional Description PIN
Peripheral Configuration at Device Reset
IPU
ABA0
UTOPIAEN, and MACSEL10 Peripheral Selection Utopia and Emac
Configuration PIN Setting Utopiaen Pcien PIN
Lower Upper
AUTO-INIT
Peripheral States
Peripheral Selection After Device Reset
State
Peripherals That can be This State
Unlock the PERCFG0 register by Using the Perlock register
Static Powerdown Reset Enable Progress Disabled Enabled
Device State Control Registers
Device State Control Registers
HEX Address Range Acronym Register Name
Lockval
Peripheral Lock Register Description
Bit Field Value Description 310
Lockval
Bit Field Value Description
Peripheral Configuration Register 0 Description
Bit Field
DDR2CTL Emifactl
Peripheral Configuration Register 1 Description
DDR2CTL
Hpistat
Peripheral Status Registers Description
I2CSTAT
1715
Utopiastat Pcistat
SM320C6455-EP
Utopiastat
Rmiirst
Emac Configuration Register Emaccfg Description
Emuctl
Emulator Buffer Powerdown Register Emubufpd Description
Emifaen DDR2EN Pcien CFGGP2 CFGGP1 CFGGP0
Device Status Register Description
Sysclkout MCBSP1EN PCI66
Pcieeai MACSEL1 MACSEL0
MACSEL10
Pcieeai
Utopiaen
Jtag ID Jtagid Register Description
BOOTMODE30
Variant Part Number Manufacturer LSB
Variant
Pullup/Pulldown Resistors
Configuration Examples
HPI VCP2 HRDY,HINT
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
System Interconnect
Internal Buses, Bridges, and Switch Fabrics
Data Switch Fabric Connections
Switched Central Resource Block Diagram
SCR Connection Matrix
Configuration Switch Fabric
C64x+ Megamodule SCR Connection
BUS Master Default Priority Control Priority Level
C6455 Default Bus Master Priorities
Bus Priorities
Memory Architecture
X+ Megamodule Block Diagram
C6455 L1P Memory Configurations
C6455 L2 Memory Configurations
Bandwidth Management
Memory Protection
Available Memory Page Protection Schemes
AID0 Bit
Megamodule Resets
Power-Down Control
Megamodule Reset Global or Local
Reset Type Megamodule
Version Revision a
Megamodule Revision
Version
Revision
Megamodule Interrupt Registers
C64x+ Megamodule Register Descriptions
Megamodule Revision Register
Megamodule Powerdown Control Registers
Megamodule Idma Registers
Megamodule Cache Configuration Registers
MAR168 Controls Emifa CE2 Range A800 0000 A8FF Ffff
Megamodule L1/L2 Memory Protection Registers
L2MPPA5
L2MPPA4
L2MPPA6
L2MPPA7
L1PMPPA19
L1PMPPA18
L1PMPPA20
L1PMPPA21
10. CPU Megamodule Bandwidth Management Registers
11. Device Configuration Registers Chip-Level Registers
HEX Address Range Acronym Register Name Comments
DV DD12, DV DDRM, AV DDT, AV DDA
Recommended Operating Conditions
MIN NOM MAX Unit
AV DDA
VSS VIH VIL
Recommended Operating Conditions
VOS
VOH VOL
Parameter Test CONDITIONS1 MIN TYP MAX Unit
TDO DVDD33 = MIN IOH = MAX
DVDD33 = MIN IOL = MAX
Current DC
2 3.3-V Signal Transition Rates
1 3.3-V Signal Transition Levels
Parameter Information
Timing Parameters and Board Routing Analysis
Power Supplies
Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
Power-Supply Sequencing
Power-Supply Decoupling
108
Enhanced Direct Memory Access EDMA3 Controller
EDMA3 Channel Synchronization Events
EDMA3 Device-Specific Information
C6455 EDMA3 Channel Synchronization Events1
Edma Binary Event Name Event Description Channel
C6455 EDMA3 Channel Synchronization Events
EDMA3 Peripheral Register Descriptions
EDMA3 Channel Controller Registers
DCHMAP9
DCHMAP8
DCHMAP10
DCHMAP11
DCHMAP56
DCHMAP55
DCHMAP57
DCHMAP58
DRAEH5
DRAE5
DRAE6
DRAEH6
QSTAT1
QSTAT0
QSTAT2
QSTAT3
Shadow Region 0 Channel Registers
Interrupt Enable Register High
EDMA3 Transfer Controller 0 Registers
EDMA3 Parameter RAM1
EDMA3 Transfer Controller 1 Registers
EDMA3 Transfer Controller 2 Registers
121
EDMA3 Transfer Controller 3 Registers
123
Interrupt Sources and Interrupt Controller
Interrupts
10. C6455 System Event Mapping
Event Number Interrupt Event Description
RINT1
XINT0
XINT1
TINTLO0
Pdcint
L1PED1
L1PCMPA
L1PDMPA
11. Timing Requirements for External Interrupts1 see Figure
External Interrupts Electrical Data/Timing
NMI
Power-on Reset POR Pin
Reset Controller
12. Reset Types
Type Initiator
Warm Reset Reset Pin
System Reset
Max Reset
CPU Reset
Reset Priority
Reset Type Status Register Description
Reset Controller Register
Srst Mrst Wrst POR
Srst
14. Timing Requirements for Reset12 3see -8and Figure
Reset Electrical Data/Timing
720 1000/-1000 Unit
Parameter
Power-Up Timing
CLKIN1 CLKIN2 POR
Resetstat
PLL1 and PLL1 Controller
Internal Clocks and Maximum Operating Frequencies
1 PLL1 Controller Device-Specific Information
Clock Signal MIN MAX Unit
1.3 PLL1 Stabilization, Lock, and Reset Times
16. PLL1 Clock Frequency Ranges
1.2 PLL1 Controller Operating Modes
18. PLL1 Controller Registers Including Reset Controller
17. PLL1 Stabilization, Lock, and Reset Times
2 PLL1 Controller Memory Map
MIN TYP
3.1 PLL1 Control Register
3 PLL1 Controller Register Descriptions
Pllrst
Pllpwrdn
20. PLL Multiplier Control Register Pllm Field Descriptions
PLL Multiplier Control Register
Preden
PLL Pre-Divider Control Register
Ratio
D4EN
PLL Controller Divider 4 Register
D5EN
PLL Controller Divider 5 Register
Goset
PLL Controller Command Register
Gostat
PLL Controller Status Register
PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register
SYS5 SYS4
Plldiv Ratio Change Status Register
SYS5
SYS5ON SYS4ON SYS3ON SYS2ON
Sysclk Status Register
PLL Modes
29. Timing Requirements for CLKIN1 Devices123 see Figure
SYSCLK4
PLL2 and PLL2 Controller
23. PLL2 Block Diagram
31. PLL2 Clock Frequency Ranges
1 PLL2 Controller Device-Specific Information
1.2 PLL2 Controller Operating Modes
Pllref Pllen =
3 PLL2 Controller Register Descriptions
2 PLL2 Controller Memory Map
32. PLL2 Controller Registers
HEX Address Range Acronym Description
D1EN
PLL Controller Divider 1 Register
155
ALN1
SYS1
SYS1ON
39. Timing Requirements for CLKIN2123 see Figure
4 PLL2 Controller Input Clock Electrical Data/Timing
1 DDR2 Memory Controller Device-Specific Information
DDR2 Memory Controller
3 DDR2 Memory Controller Electrical Data/Timing
2 DDR2 Memory Controller Peripheral Register Descriptions
40. DDR2 Memory Controller Registers
Emifa Device-Specific Information
External Memory Interface a Emifa
41. Emifa Registers
Emifa Peripheral Register Descriptions
42. Timing Requirements for Aeclkin for EMIFA12 see Figure
Emifa Electrical Data/Timing
Aeclkin
Aeclkin AECLKOUT1
See -33and Figure
ACEx ABE70
Setup = Hold =
ABA10 AED630 Read Data
AAOE/ASOE a AAWE/ASWE a AR/W Aardy B Deasserted
ABA10 AED630
Strobe Setup = Extended Strobe
Aeclkout Aardya Asserted Deasserted
Setup time, read AEDx valid before Aeclkout high
BE1 BE2 BE3 BE4
SM320C6455-EP
EA1 EA2 EA3 EA4
ASADS/ASRE B AAOE/ASOE B AAWE/ASWEB
Write Latency =
HHOLDAL-HOLDL Hold time, Hold low after Holda low
HOLD/HOLDA Timing
DSP Owns Bus
Hold Holda
Busreq Timing
Delay time, Aeclkout high to Abusreq valid AECLKOUTx
11.1 I2C Device-Specific Information
11 I2C Peripheral
I2CCLKH I2CSAR
I2COAR
I2CXSR
I2CEMDR
51. I2C Registers
11.2 I2C Peripheral Register Descriptions
11.3 I2C Electrical Data/Timing
Standard Mode Fast Mode MIN MAX
Stop Start
SDA SCL
Start Stop
Stop Start Repeated
43. I2C Transmit Timings
HPI Device-Specific Information
Host-Port Interface HPI Peripheral
HPI Peripheral Register Descriptions
54. HPI Control Registers
HPI Electrical Data/Timing
NO.PARAMETER
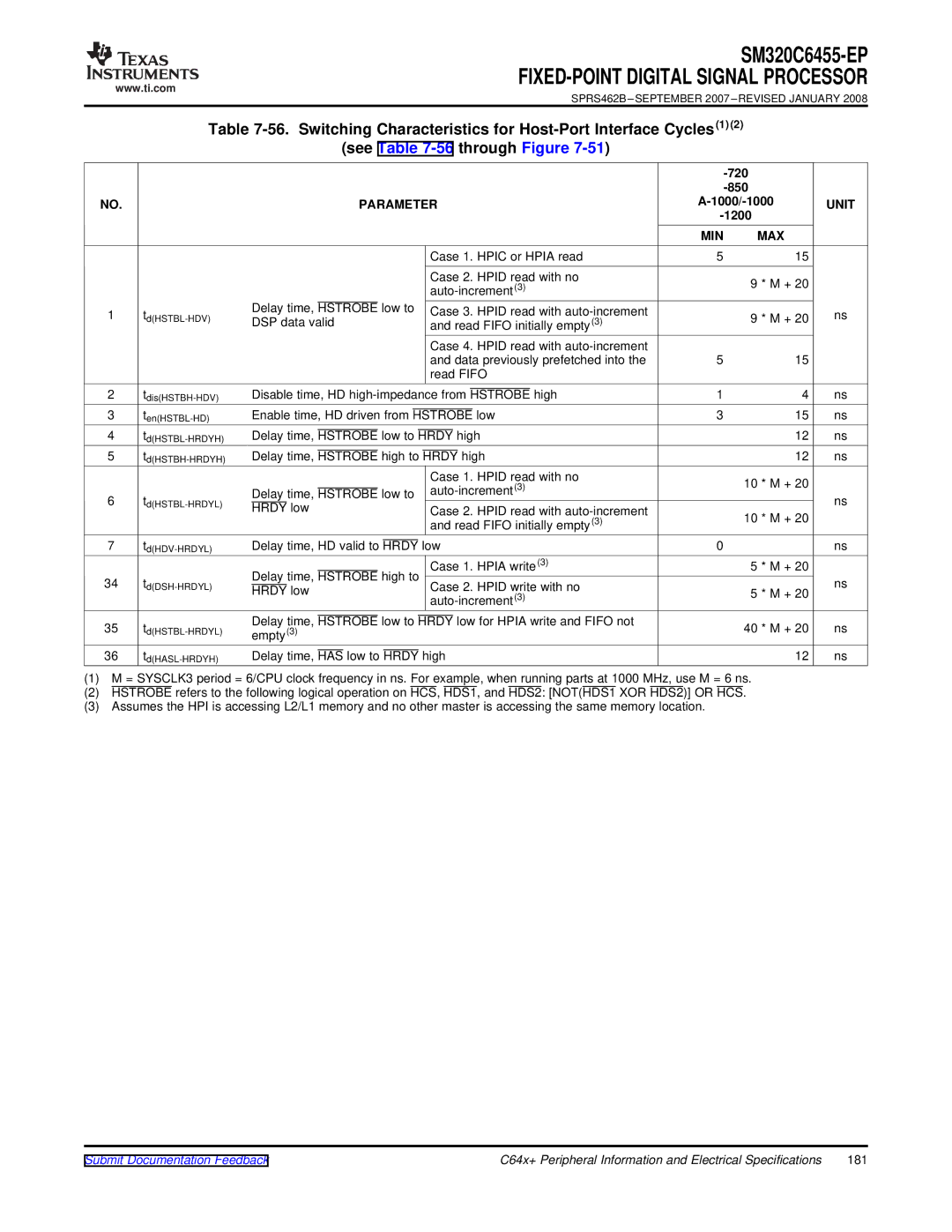
See -56through Figure
HCNTL10
HCS Has
HR/W Hhwil Hstrobea
HD150
Hrdyb
HR/W Hhwil Hstrobe a
46. HPI16 Write Timing has Not Used, Tied High
47. HPI16 Write Timing has Used
48. HPI32 Read Timing has Not Used, Tied High
49. HPI32 Read Timing has Used
Input HCS input
Has input HCNTL10 Input HR/W input
Input HCS input HD310 input
51. HPI32 Write Timing has Used
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port McBSP
McBSP Device-Specific Information
58. McBSP 1 Registers
720 850 1000/-1000
McBSP Electrical Data/Timing
FIXED-POINT Digital Signal Processor
Clkx
Clks Clkr
Clks
MASTER3 Slave MIN MAX
Master Slave MIN MAX
Clkx FSX
Bit Bitn-1
Master Slave MIN
Setup time, DR valid before Clkx high 18P
Hold time, DR valid after Clkx high + 36P
198
199
Ethernet Bus
Ethernet MAC Emac
Interface Modes
Emac Device-Specific Information
Ball Number Device PIN Name
70. EMAC/MDIO Multiplexed Pins MII, RMII, and Gmii Modes
Rmii
Interface Mode Clocking
71. Ethernet MAC Emac Control Registers
Emac Peripheral Register Descriptions
Softreset
Macconfig
RX6FREEBUFFER
RX7FREEBUFFER
HEX Address Range Acronym
72. Emac Statistics Registers
74. Emac Descriptor Memory
73. Emac Control Module Registers
02C8 2000 02C8 3FFF Emac Descriptor Memory
Mbps Gmii Only
Emac Electrical Data/Timing
Mrclk Input
Mtclk
Output
Gmtclk
Mrclk Input MRXD7−MRXD4GMII only
MRXD3−MRXD0
MTXD3−MTXD0
Mtclk Input MTXD7−MTXD4GMII only
Mtxen Outputs
Gmtclk Output
Rmrefclk Input
Emac Rmii Electrical Data/Timing
Mrxer Inputs 720 1000/-1000 Unit
MRXD1-MRXD0 Mcrsdv
Emac Rgmii Electrical Data/Timing
Cycle time, TXC Mbps 40*t cTXC 60*t cTXC
70. Emac Transmit Interface Timing Rgmii OperationAB
Mdio Device-Specific Information
Management Data Input/Output Mdio
Mdio Peripheral Register Descriptions 89. Mdio Registers
Mdclk
Delay time, Mdclk low to Mdio data output valid 100
Mdio input
Mdio output
Timers Device-Specific Information
Timers
Timers Peripheral Register Descriptions
92. Timer 0 Registers
94. Timing Requirements for Timer Inputs1 see Figure
Timers Electrical Data/Timing
TINPLx TOUTLx
16.1 VCP2 Device-Specific Information
Enhanced Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor VCP2
16.2 VCP2 Peripheral Register Descriptions
96. VCP2 Registers
17.1 TCP2 Device-Specific Information
Enhanced Turbo Decoder Coprocessor TCP2
Tbhd
Tbsd
97. TCP2 Registers
17.2 TCP2 Peripheral Register Descriptions
Register Default Value
98. Default Values for PCI Configuration Registers
Peripheral Component Interconnect PCI
PCI Device-Specific Information
PCI Peripheral Register Descriptions
99. PCI Configuration Registers
100. PCI Back End Configuration Registers
101. DSP-toPCI Address Translation Registers
103. PCI External Memory Space
102. PCI Hook Configuration Registers
HEX Address Offset Acronym Register Name
49FF Ffff
48FF Ffff
4A7F Ffff
4AFF Ffff
PCI Electrical Data/Timing
Utopia Peripheral Register Descriptions
Utopia Device-Specific Information
104. Utopia Registers
105. Utopia Data Queues Receive and Transmit Registers
106. Timing Requirements for UXCLK1 see Figure
Utopia Electrical Data/Timing
Uxclk
Urclk
UXADDR40
Uxclk UXDATA70
Uxclav Uxenb Uxsoc
P48 0x1F
Urclk URDATA70 URADDR40 N Urclav Urenb Ursoc
Serial RapidIO Device-Specific Information
Serial RapidIO Srio Port
Serial RapidIO Peripheral Register Descriptions
112. RapidIO Control Registers
RIOBLK2ENSTAT
RIOBLK2EN
RIOBLK3EN
RIOBLK3ENSTAT
RIODOORBELL2ICCR
RIODOORBELL2ICSR
RIODOORBELL3ICSR
RIODOORBELL3ICCR
RIOERRRSTEVNTICRR2
Rioerrrstevnticrr
RIOERRRSTEVNTICRR3
RIOINTDST0DECODE
RIOLSU4REG1
RIOLSU4REG0
RIOLSU4REG2
RIOLSU4REG3
RIOQUEUE5RXDMAHDP
RIOQUEUE4RXDMAHDP
RIOQUEUE6RXDMAHDP
RIOQUEUE7RXDMAHDP
RIORXUMAPH0
RIORXUMAPL0
RIORXUMAPL1
RIORXUMAPH1
RapidIO Peripheral-Specific Registers
Riolclcfgbar
Riolclcfghbar
Riobaseid
Riohostbaseidlock
Riopwtgtid
Rioctrlcapt
RIOSP0ERRDET
RIOSP0RATEEN
Serial RapidIO Electrical Data/Timing
245
Gpio Device-Specific Information
General-Purpose Input/Output Gpio
Gpio Peripheral Register Descriptions
113. Gpio Registers
114. Timing Requirements for Gpio Inputs12 see Figure
Gpio Electrical Data/Timing
Pulse duration, GPOx high 36P 8
Pulse duration, GPOx low 36P 8
Advanced Event Triggering AET
Emulation Features and Capability
Trace
Ieee 1149.1 Jtag
Delay time, TCK low to TDO valid
Jtag Device-Specific Information
116. Timing Requirements for Jtag Test Port see Figure
C6455 Revision History
Revision History
See ADDITIONS/MODIFICATIONS/DELETIONS
Added 0.83 ns C6455-1200 1.2-GHz CPU Cycle Time
Thermal Data
Thermal Resistance Characteristics S-PBGA Package ZTZ/GTZ
Packaging Information
AIR Flow
MSL Peak Temp
Orderable Device Status Package Pins Package Eco Plan
Qty
Page
DSP
Products Applications
Rfid

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()