Part number Document version
HP V1910 Switch Series
Warranty
Contents
Page
Page
STP177
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
Overview
Logging in to the web interface
Configuration through the web interface
Default login information
Web-based network management operating environment
Example
Login page of the web interface
Navigation tree Body area Title area
Web-based configuration interface
Logging out of the web interface
Introduction to the web interface
Function menu Description User level
Web user level
Introduction to the web-based NM functions
Description of Web-based NM functions
Used at the next startup from the host of the current
Snmp
VCT
Rmon
Mstp
Vlan
MAC
Igmp
Lacp
Their partner ports
Lldp
AAA
ARP
CRL
Radius
PKI
Class
Commonly used buttons and icons
Introduction to the common items on the web pages
Buttons and icons
Display
Advanced search
Content display by pages
Search function
Sorting function
Sort display based on MAC address in the ascending order
Configuration guidelines
Console cable
Configuration at the CLI
Setting up the configuration environment
Getting started with the CLI
Network diagram for configuration environment setup
Setting terminal parameters
Set the serial port used by the HyperTerminal connection
Connection description of the HyperTerminal
HyperTerminal window
Set the serial port parameters
Select File Properties in the HyperTerminal window
Enter your username at the Username prompt
Set terminal emulation in Switch Properties dialog box
Press Enter. The Password prompt display
Logging in to the CLI
Initialize
CLI commands
Ipsetup
# Modify the login password of user admin
Password
Password
Quit
Ping
Summary
Reboot
# Display summary information of the device
Upgrade
Network requirements
Configuration procedure
# Reboot the switch
Configuring system parameters
Configuration wizard
Basic service setup
Entering the configuration wizard homepage
Configuring management IP address
Select a Vlan interface
Admin Status
Configure IPv4
Configure how the Vlan interface obtains an IPv4 address
Manual Important
Finishing configuration wizard
Configuration finishes
ItemDescription
Stack management configuration task list
Configuring stack management
Stack management configuration task list
Network diagram for stack management
Configuring global parameters of a stack
Setup Configuration items of global parameters
Topology summary Fields of topology summary
Configuring stack ports
Return to Stack management configuration task list
Displaying topology summary of a stack
Displaying device summary of a stack
Stack configuration example
Logging into a member switch from the master switch
Stack
Configure global parameters for the stack on Switch a
Configure a stack port on Switch a
Configure stack ports on Switch B
Configure a stack port on Switch C
Configuration guidelines
System information
Summary
Displaying device summary
Displaying system information
Recent system operation logs
Displaying device information
Basic system information
System resource state
Device information
Configuring idle timeout period
Device basic information configuration
Configuring device basic information
Configuring system name
Idle timeout Set the idle timeout period for logged-in users
System time configuration
System time configuration
Configuring system time
NTP
System time configuration example
System time configuration items
Network diagram for configuring system time
Configure Device a as the NTP server of Switch B
Configure Device a
Configuration guidelines
Setting syslog related parameters
Log management configuration
Configuring log management
Configuration task list
Displaying syslog
Return to Log management configuration task list
See
Display syslog Syslog display items
System logs severity level
Severity level Description Value
IP address of the loghost
Setting loghost
Set loghost Loghost configuration item
Backup configuration
Configuration management
Back up configuration
Restore configuration
Save configuration confirmation
Save configuration
Configuration restore
Initialize confirmation dialog box
Initialize
Filename
Device maintenance
Software upgrade
Extension .bin
Already exists, overwrite
Device reboot
Device reboot
Specifies the type of the startup configuration file
Electronic label
Diagnostic information
Diagnostic information
Electronic label
Diagnostic information file is created
File management
File management configuration
File management
Displaying file list
Removing a file
Downloading a file
Uploading a file
Setup tab
Port management configuration
Configuring a port
Setting operation parameters for a port
Pvid
Port configuration items
MDI
Multicast Suppression Input a number in the box below
Percentage or by PPS as follows
Input a percentage in the box below
Constrain
Viewing the operation parameters of a port
Details tab
Port management configuration example
Network diagram for port rate configuration
Configure the rate of GigabitEthernet 1/0/4
Batch configure port rate
Display the rate settings of ports
Local port mirroring
Port mirroring configuration
Introduction to port mirroring
Implementing port mirroring
Creating a mirroring group
Configuring local port mirroring
Configuring local port mirroring
Local port mirroring configuration task list
Return to Local port mirroring configuration task list
Configuring ports for a mirroring group
Mirroring ports of a port mirroring group
Local port mirroring configuration example
Configuration examples
Create a local mirroring group
Configuration progress dialog box
Configure the mirroring ports
Configure the monitor port
Adding a local user
Add a user Local user configuration items
User management
Managing users
Super password
Setting the super password
Input are not consistent when you apply the configuration
Switching to the management level
Super password configuration items
Switch to the management level
Loopback operation
Loopback test configuration
Loopback test result
Test the status of the cable connected to an Ethernet port
Testing cable status
Failure
Description on the cable test result
Status and length of the cable
Viewing port traffic statistics
Flow interval configuration
Setting the traffic statistics generating interval
Monitoring port traffic statistics
Port traffic statistics
Configuring storm constrain
Storm constrain configuration
Storm Constrain tab
Configuring storm constrain
Thresholds for at least a type of traffic
Upper threshold. Available options include
∙ None-Performs no action
Upper threshold
After that
Crossed after that
Working mechanism
Rmon configuration
History group
Alarm group
Rmon groups
Ethernet statistics group
Event group
Configuring Rmon
Configuring the Rmon statistics function
Rising and falling alarm events
TaskRemarks
Configuring the Rmon alarm function
Rmon statistics group configuration task list
Rmon history group configuration task list
Display Rmon running status
Configuring a statistics entry
Rmon alarm configuration task list
Displaying Rmon running status
100
Configuring a history entry
Return to Rmon statistics group configuration task list
101
Configuring an event entry
Return to Rmon history group configuration task list
Buckets Granted
102
Configuring an alarm entry
Return to Rmon alarm configuration task list
None of them is selected, the system will take no action
Statics Item
104
Displaying Rmon statistics information
Log-and-trap
Rmon statistics information Fields of Rmon statistics
Return to Display Rmon running status
Displaying Rmon history sampling information
Node etherHistoryOctets
CRCAlignErrors
Corresponding to the MIB node etherHistoryCRCAlignErrors
Number of the entry in the system buffer
Log Return to Display Rmon running status
Rmon configuration example
Network diagram for Rmon
Displaying Rmon event logs
109
110
Display Rmon statistics
111
Configure an event group
Display the index of a event entry
112
Configure an alarm group
PoE Disabled Disable PoE on the port 113
Energy saving configuration
Configuring energy saving on a port
ItemDescription
MIB tree
Snmp configuration
Snmp mechanism
Relationship between an NMS, agent and MIB
SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c configuration task list
Snmp configuration
Configuring SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c
Perform the tasks in 1 to configure SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c
Configuring Snmp trap
Configuring SNMPv3
Perform the tasks in 1 to configure SNMPv3
SNMPv3 configuration task list
Local Engine ID
Set up Configuration items for enabling Snmp
Specify to enable or disable Snmp
Configure the local engine ID
Create an Snmp view
Configuring an Snmp view
Creating an Snmp view
View
Set the subtree mask
Configuration items for creating an Snmp view
Adding rules to an Snmp view
Identify a MIB subtree
121
Configuring an Snmp community
Configure an Snmp community Create an Snmp Community
Add rules to an Snmp view
Snmp group
Configuring an Snmp group
Configuration items for configuring an Snmp community
Return to SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c configuration task list
Agent
Configuring an Snmp user
Return to SNMPv3 configuration task list
Objects on the device
Description
Configuring Snmp trap function
Address in the text box according to the IP address type
Set the destination IP address
Destination IP Address
NMS
Snmp configuration example
Network diagram for Snmp configuration
128
Enable Snmp
129
130
Create an Snmp group
131
Enable the agent to send Snmp traps
Add target hosts of Snmp traps
132
Configuration verification
Displaying interface statistics
Interface statistics
Field Description
Vlan fundamentals
Vlan configuration
Vlan diagram
Introduction to Vlan
136
Vlan types
Traditional Ethernet frame format
Position and format of Vlan tag
Frame
Tag removed or intact depending on your configuration 137
Introduction to port-based Vlan
Port link type
Creating VLANs
Configuring a Vlan
Vlan configuration task list approach
139
Create tab Configuration items of creating VLANs
Return to Vlan configuration task list approach
Selecting VLANs
140
Select Vlan tab Configuration items of selecting VLANs
Modifying a Vlan
141
Modify Vlan tab Configuration items of modifying a Vlan
Assigned to this Vlan
Aggregate interfaces from this list
Untagged
Modify Port tab Configuration items of modifying ports
Modifying ports
Select the ports to be modified
Network diagram for Vlan configuration
Vlan configuration example
144
145
Create Vlan 2, Vlan 6 through Vlan 50, and Vlan
146
Set a Vlan range
147
148
Vlan interface configuration task list
Vlan interface configuration
Configuring Vlan interfaces
Perform the tasks in 1 to configure a Vlan interface
Modifying a Vlan interface
Create tab Configuration items of creating a Vlan interface
Return to Vlan interface configuration task list
Bootp
Select the Vlan interface to be configured
Modify tab Configuration items of modifying a Vlan interface
152
Selected Vlan interface
Is up if one or more Ethernet ports in the Vlan are up
Voice Vlan assignment modes
Voice Vlan configuration
Default OUI addresses of different vendors
OUI addresses
154
Co-relation
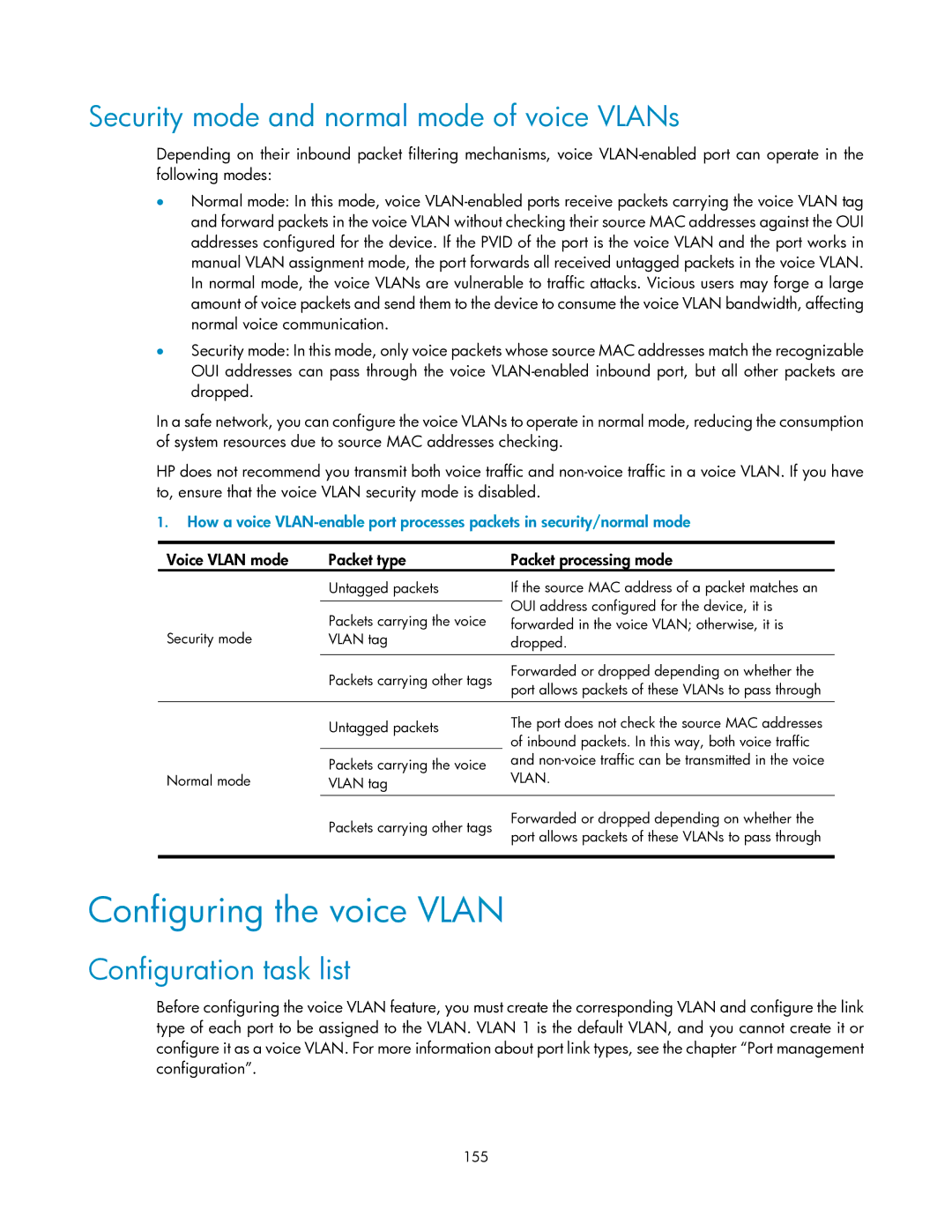
Voice Vlan mode Packet type Packet processing mode
Configuring the voice Vlan
Security mode and normal mode of voice VLANs
Adding OUI addresses to the OUI list
Configuring voice Vlan globally
Configuring voice Vlan on a port
Timer expires, the port is removed from the voice Vlan
Configuring voice Vlan globally
Configuring voice Vlan on a port
Configure voice Vlan Global voice Vlan configuration items
Set the voice Vlan ID
Set the voice Vlan assignment mode of a port
Be configured as the voice Vlan
Voice Vlan function on the port
159
Adding OUI addresses to the OUI list
160
Voice Vlan configuration examples
161
Create Vlan
162
Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a hybrid port
163
Configure the voice Vlan function globally
164
Verify the configuration
Add OUI addresses to the OUI list
Current OUI list of the device
165
Current voice Vlan information
166
167
168
Assign GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to Vlan 2 as an untagged member
169
Configure voice Vlan on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
170
171
172
MAC address configuration
173
Configuring MAC addresses
Configuring a MAC address entry
MAC address table of the device
174
MAC tab
Click Add in the bottom to enter the page as shown in b
Create a MAC address entry
Port Set the port to which the MAC address belongs
Setting the aging time of MAC address entries
Configuration items of creating a MAC address entry
Set the ID of the Vlan to which the MAC address belongs
176
MAC address configuration example
Create a static MAC address entry
Root bridge
Mstp configuration
STP protocol packets
Basic concepts in STP
Description of designated bridges and designated ports
How STP works
Designated bridge and designated port
Path cost
Step Actions
Selection of the optimum configuration Bpdu
Calculation process of the STP algorithm
180
Selection of the root port and designated ports
Step Description
∙ Comparison process and result on each device
Network diagram for the STP algorithm
Initial state of each device
Device Port name Bpdu of port
CP2 1, 0, 1, BP2
BP2 with the configuration Bpdu of BP2. If the calculated
0, 1, BP2 before the configuration Bpdu is updated
Bpdu
183
Configuration Bpdu forwarding mechanism in STP
Final calculated spanning tree
Blocked port CP2 0, 0, 0, AP2 Root port CP2 0, 5, 1, BP2
184
STP timers
185
Mstp features
STP and Rstp limitations
Mstp basic concepts
186
MST region
VLAN-to-MSTI mapping table
Basic concepts in Mstp
Port roles
Regional root
Common root bridge
Boundary port
188
Port states
Port roles
Msti calculation
How Mstp works
Implementation of Mstp on devices
Cist calculation
Mstp configuration task list
Configuring Mstp
Configuring an MST region
Perform the tasks described in 1 to configure Mstp
Vlan ID
Return to Mstp configuration task list
MST region
Click Modify to enter the page shown in b
Configuring Mstp globally
Bridge Diameter
Set the STP working mode
∙ STP-Each port on a device sends out STP BPDUs
Number of devices on the path composed of the most devices
STP
Configuring Mstp on a port
Recommends you to use the default value
Set the type of protection to be enabled on the port
Manually configure path cost for ports
Configuration may cause a temporary loop
Protection type Description
Displaying Mstp information of a port
Protection types
Discarding
Port Summary tab
Forwarding
Learning
Whether or not the port is an edge port
199
Mstp configuration example
Network diagram for Mstp configuration
200
Configure an MST region
Region tab
∙ Click Modify to enter the page shown in c
201
Configure Mstp globally on Switch a
202
203
Configure Mstp globally on Switch D
When configuring MSTP, follow these guidelines
Page
Aggregation group
Link aggregation and Lacp configuration
Basic concepts
Aggregate interface
Link aggregation modes
Class-two configurations
Static aggregation mode
Class-two configurations
207
Dynamic aggregation mode
Configuring a dynamic aggregation group
Configuring link aggregation and Lacp
Load sharing mode of an aggregation group
Configuring a static aggregation group
Creating a link aggregation group
Dynamic aggregation group configuration task list
Setting Lacp priority
Displaying information of LACP-enabled ports
210
Assign an ID to the link aggregation group to be created
Displaying information of an aggregate interface
Setting Lacp priority
System Priority Set the Lacp priority of the local system
Displaying information of LACP-enabled ports
Lacp priority configuration items
Also on LACP-disabled ports
Field/button Description
Display information about LACP-enabled ports
Fields in the LACP-enabled port summary table
Fields in the Partner Port Details table
Link aggregation and Lacp configuration example
Describes the fields in the Partner Port Details table
215
Network diagram for static link aggregation configuration
Create static link aggregation group
∙ Set the link aggregation interface ID to
216
Create dynamic link aggregation group
217
Lldpdu
Lldp configuration
Background
LLDPDUs
FCS
TLVs
SNAP-encapsulated Lldpdu format
Lldpdu encapsulation format
Ieee 802.1 organizationally specific TLVs
Basic Lldp TLVs
Type Description Remarks
Ieee 802.1 organizationally specific TLVs
LLDP-MED TLVs
LLDP-MED TLVs
Ieee 802.3 organizationally specific TLVs
Ieee 802.3 organizationally specific TLVs
Compatibility of Lldp with CDP
How Lldp works
Lldp configuration task list
Configuring Lldp
Lldp configuration task list
Perform the tasks in 1 to configure Lldp
224
Enabling Lldp on ports
Task Remarks
225
Configuring Lldp settings on ports
Port Setup tab Return to Lldp configuration task list
226
For modifying Lldp settings on a port
Is Ethernet
Enable Lldp polling and set the polling interval
∙ Disable-Neither sends nor receives CDPDUs
CDP Operating Mode
CDP operating mode on the port to TxRx
DOT3 TLV MAC/PHY
Configuring global Lldp setup
Global Setup tab Global Lldp setup configuration items
Displaying Lldp information for a port
Port component
Port ID type
Interface alias
233
Type of PSE power source advertised by the local device
Chassis ID type
Chassis component
234
Link aggregation group
Endpoint devices
III endpoint devices are used directly by end users
Unknown
236
Displaying global Lldp information
Global Summary tab Global Lldp information
Displaying Lldp information received from Lldp neighbors
Lldp configuration examples
Basic Lldp configuration example
Neighbor Summary tab Return to Lldp configuration task list
239
Network diagram for basic Lldp configuration
240
Port Setup tab
241
For setting Lldp on multiple ports
242
Global Setup tab
243
For configuring Lldp on the selected port
244
CDP-compatible Lldp configuration example
245
Network diagram for CDP-compatible Lldp configuration
For creating VLANs
246
For configuring ports
247
For configuring the voice Vlan function on ports
248
249
For modifying Lldp settings on ports
250
Multicast forwarding before and after Igmp snooping runs
Igmp snooping configuration
Principle of Igmp snooping
Igmp snooping related ports
252
When receiving a general query
Work mechanism of Igmp snooping
Igmp snooping related ports
253
When receiving a membership report
When receiving a leave group message
254
Configuring Igmp snooping
Igmp snooping querier
Enabling Igmp snooping globally
Basic Igmp snooping configurations
Return to Configuration task list
Configuring Igmp snooping in a Vlan
Igmp snooping configuration items
Advanced configuration
Configuring Igmp snooping port functions
Group Limit
Configuration items for advanced Igmp snooping features
Display Igmp snooping multicast entry information
259
Igmp snooping configuration example
ID of the Vlan to which the entry belongs
260
Network diagram for Igmp snooping configuration
261
262
Add a port to the Vlan
263
Enable Igmp snooping globally
Configure Igmp snooping in the Vlan
264
Configure Igmp snooping on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
Igmp snooping multicast entry information displaying
265
Details about an Igmp snooping multicast entry
266
Routing configuration
Routing table
Static route
Address will be forwarded out the interface
Configuring IPv4 routing
Default route
Displaying the IPv4 active route table
Specify the mask of the destination IP address
Preferences enables route backup
Creating an IPv4 static route
Select the output interface
Static route configuration example
Configuration outlines
Network diagram for IPv4 static route configuration
270
Configure a default route
271
Configure a static route
272
273
Precautions
Allocation mechanisms
Dhcp overview
Introduction to Dhcp
Dhcp address allocation
275
Dynamic IP address allocation process
IP address lease extension
Dynamic IP address allocation process
276
Dhcp message format
Dhcp message format
Introduction to Option
Dhcp options
Dhcp options overview
Introduction to Dhcp options
278
Protocols and standards
Sub-option 1 in normal padding format
Sub-option 2 in normal padding format
Fundamentals
Dhcp relay agent configuration
Introduction to Dhcp relay agent
Application environment
Dhcp relay agent work process
Dhcp relay agent configuration task list
281
Dhcp relay agent configuration
Configuring and displaying clients IP-to-MAC bindings
Create a server group
Return to Dhcp relay agent configuration task list
Creating a Dhcp server group
283
Dhcp server group configuration items
Enabling the Dhcp relay agent on an interface
284
Configuring and displaying clients IP-to-MAC bindings
285
Dhcp relay agent configuration example
Network diagram for Dhcp relay agent configuration
286
Enable Dhcp
287
Recording IP-to-MAC mappings of Dhcp clients
Dhcp snooping configuration
Dhcp snooping overview
Functions of Dhcp snooping
Configure trusted ports in a cascaded network
Configuring a trusted port connected to a Dhcp server
Configuring trusted ports in a cascaded network
Configure trusted and untrusted ports
Roles of ports
Dhcp snooping configuration task list
Dhcp snooping support for Option
Describes roles of the ports shown in a
Displaying clients IP-to-MAC
Configuring Dhcp snooping
Enabling Dhcp snooping
Functions on an interface
292
Dhcp snooping configuration
Return to Dhcp snooping configuration task list
Option 82 padded in normal format
Configuring Dhcp snooping functions on an interface
Displaying clients IP-to-MAC bindings
Include
294
Dhcp snooping configuration example
This field displays the Vlan to which the device belongs
295
Network diagram for Dhcp snooping configuration
296
Enable Dhcp snooping
297
Configure Dhcp snooping functions on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
Configure Dhcp snooping functions on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2
298
Configure Dhcp snooping functions on GigabitEthernet 1/0/3
Service management configuration
Service management Service management configuration items
Configuring service management
Https
302
Diagnostic tools
Trace route diagram
Trace route
303
Diagnostic tool operations
Ping configuration
Ping operation
304
Trace route configuration
Trace route operation
Ping operation result
305
Trace route operation result
ARP message format
ARP management
ARP overview
ARP function
307
ARP address resolution process
ARP operation
ARP table
Dynamic ARP entry
ARP Table configuration
Managing ARP entries
Displaying ARP entries
Creating a static ARP entry
Static ARP configuration example
Describes the static ARP entry configuration items
Static ARP entry configuration items
310
Network diagram for configuring static ARP entries
311
∙ After the configuration process is complete, click Close
Add GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to Vlan
312
Create VLAN-interface
Create a static ARP entry
Configuring gratuitous ARP
Gratuitous ARP
Introduction to gratuitous ARP
Period
Enabled by default
Packets
Learning function
Man-in-the-middle attack
ARP attack defense configuration
ARP detection
Introduction to ARP detection
316
ARP detection mechanism
Man-in-the-middle attack
317
Configuring ARP detection
ItemDescription
Creating a static binding entry
Configuration, see Creating a static binding entry
Architecture
Controlled/uncontrolled port and port authorization status
802.1X fundamentals
Architecture
Authorized/unauthorized state of a controlled port
802.1X-related protocols
Packet formats
EAP packet format
Types of Eapol packets
Eapol frame format
EAP packet format
Eapol frame format
802.1X client as the initiator
Initiating 802.1X authentication
Access device as the initiator
EAP over Radius
EAP termination
802.1X authentication procedures
Comparison of EAP relay and EAP termination
EAP relay
EAP termination Works with any Radius server that
802.1X authentication procedure in EAP relay mode
EAP relay
Packet exchange method Benefits Limitations
326
327
802.1X authentication procedure in EAP termination mode
EAP termination
HP implementation
802.1X configuration
Access control methods
Using 802.1X authentication with other features
ACL assignment
Configuring
Configuration prerequisites
Guest Vlan
802.1X configuration Basic 802.1X configuration items
802.1X configuration task list
Configuring 802.1X globally
802.1X configuration task list
Authentication on the user
Authentication Method
Authentication procedures
Specify whether to enable the quiet timer
Return to 802.1X configuration task list
Configuring 802.1X on a port
Access requests from users on the port
Select the port authorization state for
Port Authorization
Port to access the network without authentication
Configuring an 802.1X guest Vlan
802.1X configuration example
Configuring an 802.1X guest Vlan
335
Network diagram for 802.1X configuration
336
Global 802.1X configuration
337
Radius authentication server configuration
338
Radius parameter configuration
339
Configure the AAA authentication method for the ISP domain
Create an ISP domain
∙ Select the domain name test
340
Configure the AAA authorization method for the ISP domain
341
ACL assignment configuration example
Configure the AAA accounting method for the ISP domain
Network diagram for ACL assignment
342
343
344
345
346
Create ACL
347
ACL rule configuration
348
349
802.1X configuration of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
350
Ping operation summary
351
AAA configuration
Network diagram for AAA
Introduction to AAA
Determine the ISP domain of a user by the username
Configuring AAA
Configuring an ISP domain
Domain-based user management
Domain Setup
Configuring an ISP domain
ISP domain configuration items
Configuring authentication methods for the ISP domain
355
Configuring authorization methods for the ISP domain
Authorization method configuration
Authorization method configuration items
Configuring accounting methods for the ISP domain
Real-time accounting updates for the users
∙ None -Performs no accounting
AAA configuration example
Network diagram for AAA configuration example
Method Used Not Set -Uses the default accounting methods
359
Configure a local user
360
Configure ISP domain test
Configure the ISP domain to use local authentication
361
Configure the ISP domain to use local authorization
362
Configure the ISP domain to use local accounting
Client/server model
Radius configuration
Security and authentication mechanisms
Introduction to Radius
Basic message exchange process of Radius
Basic message exchange process of Radius
Code Packet type Description
Radius packet format
Radius packet format
Main values of the Code field
Attribute
Radius attributes
Extended Radius attributes
TaskDescription
Configuring Radius
Radius configuration task list
Segment of a Radius packet containing an extended attribute
Parameters
Configuring Radius servers
Radius server configuration
Configuring Radius
Return to Radius configuration task list
Configuring Radius parameters
NAS-IP
Radius parameter configuration Radius parameters
Is an integer
Timeout Retransmission Times
Set the maximum number of transmission attempts
Attempts cannot exceed
Can be
Radius configuration example
Network diagram for Radius server configuration
Number of users Real-time accounting interval in minutes
Configure the Radius authentication server
Configure Radius parameters
Create an ISP domain
Configuration progress dialog box
Configuration guidelines
Local user
Configuring users
Configuring a local user
Users
User cannot pass authentication and therefore cannot log
Local user configuration Local user configuration items
Username Specify a name for the local user Password
381
Configuring a user group
User group list User group configuration
Vlan ACL
Specify the user profile for the user group
User group configuration items
User group after the users pass authentication
Architecture of PKI
PKI configuration
PKI overview
PKI terms
PKI architecture
Applications of PKI
Entity
PKI repository
Web security
Configuring PKI
Operation of PKI
Secure email
Generating an RSA
Creating a PKI entity
Creating a PKI
Domain
Requesting a Certificate Automatically
388
PKI entity list PKI entity configuration
Creating a PKI entity
Fqdn
PKI entity configuration items
Creating a PKI domain
PKI domain list
Select the local PKI entity
PKI domain configuration PKI domain configuration items
CRL URL
Ldap IP
Key Length Type the length of the RSA keys
Generating an RSA key pair
Destroying the RSA key pair
Retrieving a certificate
394
Get File From PC Specify the path of the file on the device
395
Requesting a local certificate
CRL
Retrieving and displaying a CRL
Configuring a PKI entity to request a certificate from a CA
PKI configuration example
398
PKI entity list Configure a PKI entity
399
PKI domain list Configure a PKI domain
400
Certificate list Generate an RSA key pair
401
Certificate list Retrieve the CA certificate
Certificate list
402
Request a local certificate
403
Port isolation group configuration
Configuring a port isolation group
Configure a port isolation group
404
Port isolation group configuration example
Port isolation group configuration items
Networking diagram for port isolation group configuration
405
Configure isolated ports for an isolation group
Web IPv4 ACL Associate the Http service with an IPv4 ACL
Authorized IP configuration
Configuring authorized IP
IPv4 ACL Associate the Telnet service with an IPv4 ACL
Create an ACL
Authorized IP configuration example
Authorized IP configuration example
Network diagram for authorized IP
408
Configure an ACL rule to permit Host B
409
Configure authorized IP
IPv4 ACL classification
ACL configuration
ACL overview
Introduction to IPv4 ACL
Depth-first match for IPv4 ACLs
IPv4 ACL category Depth-first match procedure
Effective period of an ACL
Fragments filtering with IPv4 ACLs
ACL step
Configuring an ACL
Benefits of using the step
Configuring an IPv4 ACL
For creating a time range
Configuring a time range
Describes the configuration items for creating a time range
Time range configuration items
Creating an IPv4 ACL
Configuring a rule for a basic IPv4 ACL
Return to IPv4 ACL configuration task list
IPv4 ACL configuration items
415
For configuring an basic IPv4 ACL
Configuration items for a basic IPv4 ACL rule
416
Configuring a rule for an advanced IPv4 ACL
417
For configuring an advanced IPv4 ACL
Configuration items for an advanced IPv4 ACL rule
TOS
Configuring a rule for an Ethernet frame header ACL
Dscp
Source Mask
For configuring a rule for an Ethernet frame header ACL
421
Encapsulation by configuring the following items
∙ Lsap Type-Indicates the frame encapsulation format
QoS requirements of new applications
QoS configuration
Networks without QoS guarantee
Introduction to QoS
423
Impacts
Countermeasures
Traffic congestion causes
End-to-end QoS model
End-to-end QoS
Traffic classification
IP Precedence decimal IP Precedence binary Description
Packet precedences
DS field and ToS bytes
Description on IP Precedence
426
Description on Dscp values
Dscp value decimal Dscp value binary Description
An Ethernet frame with an 802.1Q tag header
Description on 802.1p precedence
Queue scheduling
SP queuing
802.1Q tag header
428
Schematic diagram for SP queuing
Schematic diagram for WRR queuing
WRR queuing
429
Line rate
Traffic evaluation and token bucket
Evaluate traffic with the token bucket
Line rate implementation
What is priority mapping
Priority mapping
How line rate works
Input CoS value Local precedence Queue
Default CoS to DSCP/CoS to Queue mapping table
Introduction to priority mapping tables
Priority mapping process
Default Dscp to CoS/DSCP to Queue mapping table
QoS configuration
Configuration task lists
Configuring a QoS policy
Perform the task in 1 to configure queue scheduling
Configuring queue scheduling
Configuring line rate
Configuring the priority mapping tables
Creating a class
Configuring priority trust mode
Shows the configuration items of configuring match criteria
Configuring match criteria
Return to QoS policy configuration task list
For configuring match criteria
Values are automatically arranged in ascending order
Service Vlan
Define a match criterion to match Dscp values
Does not overwrite the previous one
For creating a traffic behavior
Describes the configuration items of creating a behavior
Configuration items of creating a behavior
Creating a traffic behavior
438
Port setup page for a traffic behavior
Traffic directing on the chassis front panel
439
Configuring other actions for a traffic behavior
For setting a traffic behavior
Creating a policy
Configuring classifier-behavior associations for the policy
Describes the configuration items of creating a policy
Configuration items of creating a policy
441
For setting a policy
Applying a policy to a port
Behavior Name
For applying a policy to a port
Configuring queue scheduling on a port
Configuration items of applying a policy to a port
For configuring queue scheduling
WRR
Configuring line rate on a port
Return to Queue scheduling configuration task list
Return to Line rate configuration task list
Configuring priority mapping tables
For configuring line rate on a port
Configuration items of configuring line rate on a port
Configuration items of configuring priority mapping tables
Configuring priority trust mode on a port
For configuring priority mapping tables
Port priority configuration items
For configuring port priority For modifying port priority
Describes the port priority configuration items
447
Return toPriority trust mode configuration task list
448
ACL/QoS configuration examples
ACL/QoS configuration example
Network diagram for ACL/QoS configuration
449
Define a time range covering 800 to 1800 every day
450
Create an advanced IPv4 ACL
451
Define an ACL rule for traffic to the FTP server
452
Create a class
453
Define match criteria
454
455
Configure actions for the behavior
456
Configure classifier-behavior associations for the policy
Create a policy
457
Advantages
PoE configuration
PoE power
PoE overview
Protocol specification related to PoE is Ieee 802.3af
Configuring PoE
Protocol specification
Configuring PoE ports
Port setup PoE port configuration items
461
Configuring non-standard PD detection
PSE setup
462
PoE configuration example
Displaying information about PSE and PoE ports
PoE summary with GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 selected
463
Network diagram for PoE
464
Configure the PoE port supplying power to AP
Related information Conventions
Command conventions
Support and other resources
Contacting HP
Network topology icons
Subscription service
Symbols
GUI conventions
467
Index
Page
Page