INTRODUCTION
1.7.6 RAID 6
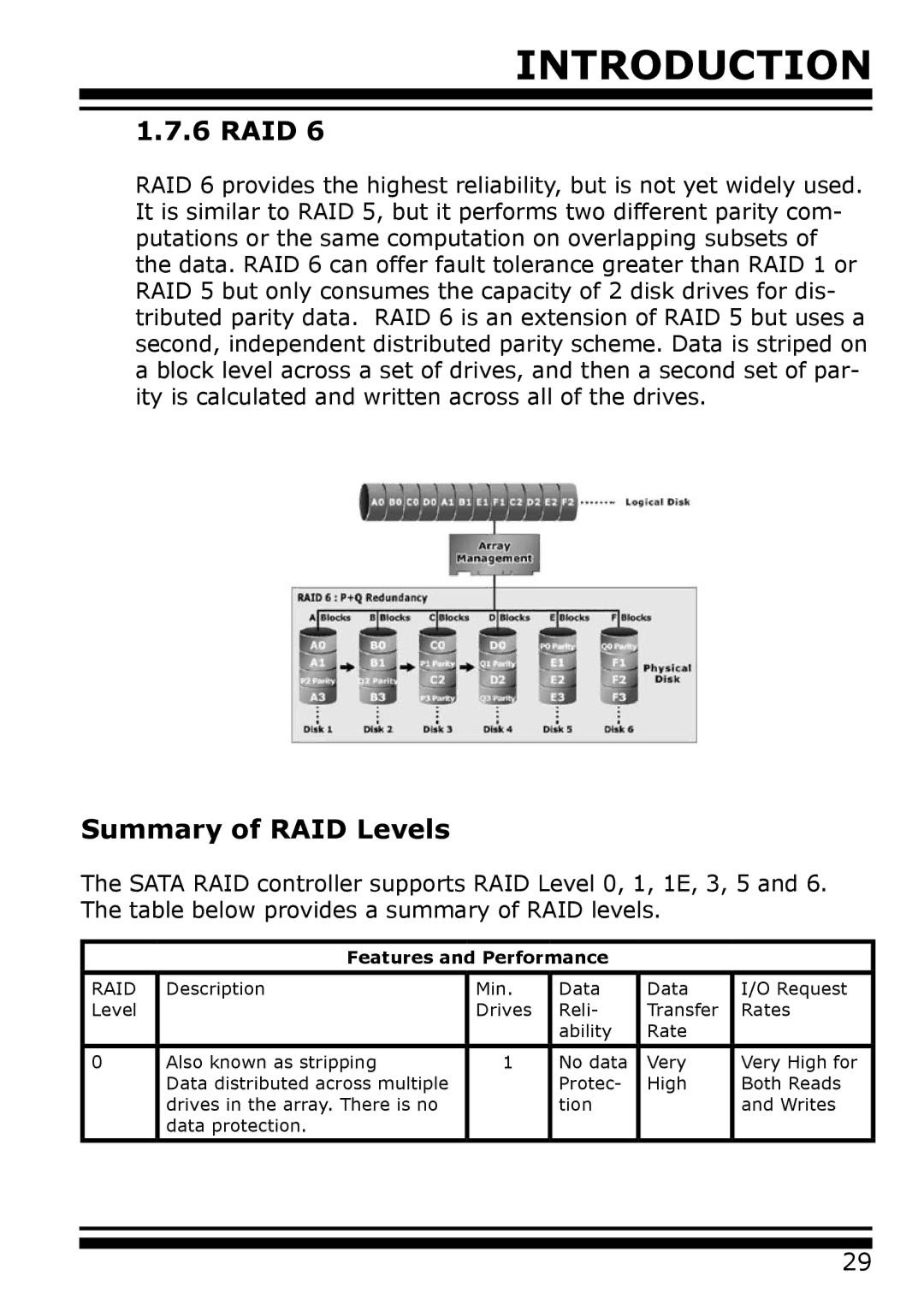
RAID 6 provides the highest reliability, but is not yet widely used. It is similar to RAID 5, but it performs two different parity com- putations or the same computation on overlapping subsets of the data. RAID 6 can offer fault tolerance greater than RAID 1 or RAID 5 but only consumes the capacity of 2 disk drives for dis- tributed parity data. RAID 6 is an extension of RAID 5 but uses a second, independent distributed parity scheme. Data is striped on a block level across a set of drives, and then a second set of par- ity is calculated and written across all of the drives.
Summary of RAID Levels
The SATA RAID controller supports RAID Level 0, 1, 1E, 3, 5 and 6. The table below provides a summary of RAID levels.
Features and Performance
RAID | Description | Min. | Data | Data | I/O Request |
Level |
| Drives | Reli- | Transfer | Rates |
|
|
| ability | Rate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 | Also known as stripping | 1 | No data | Very | Very High for |
| Data distributed across multiple |
| Protec- | High | Both Reads |
| drives in the array. There is no |
| tion |
| and Writes |
| data protection. |
|
|
|
|
29