DSP-100/2000
Users Manual
Nominal Velocity of Propagation (NVP)
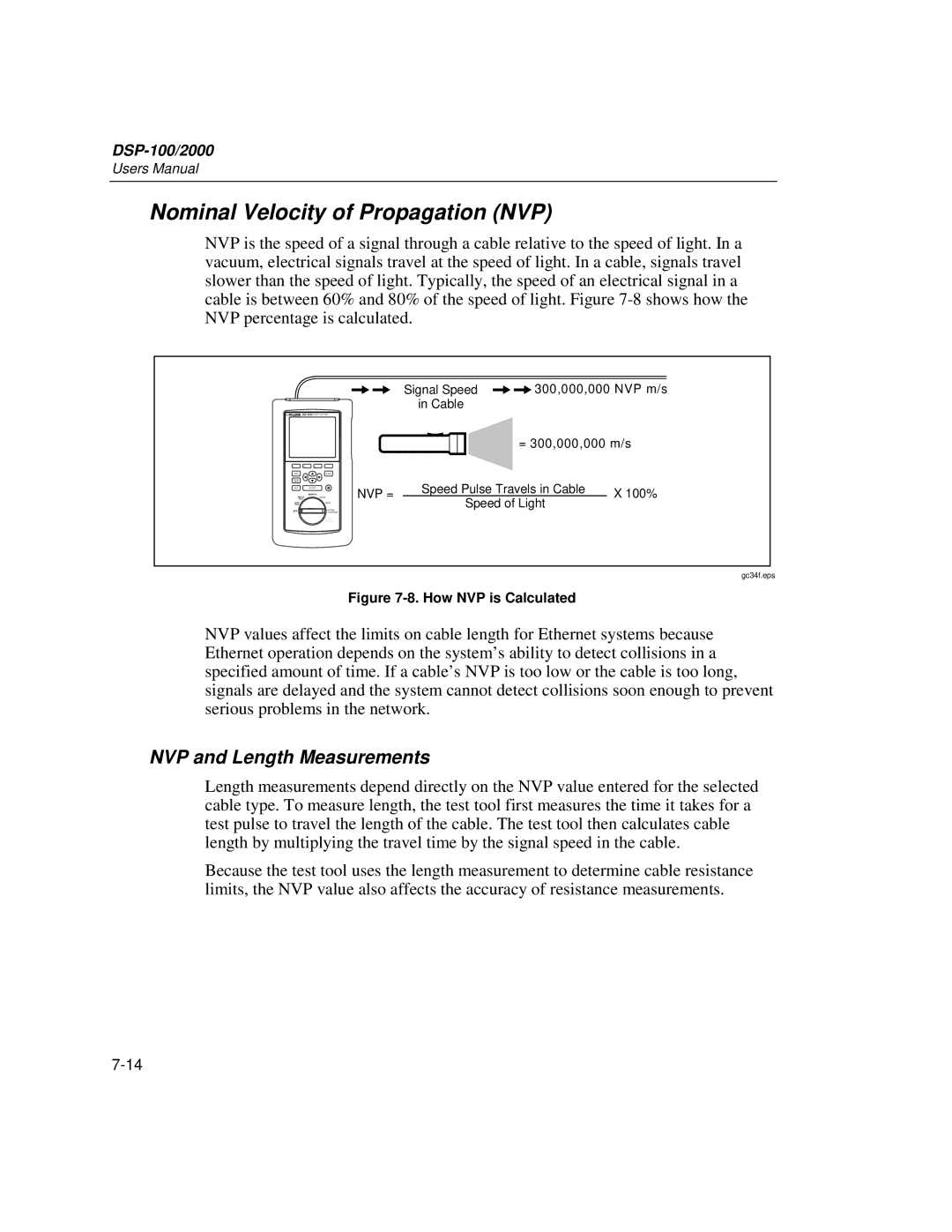
NVP is the speed of a signal through a cable relative to the speed of light. In a vacuum, electrical signals travel at the speed of light. In a cable, signals travel slower than the speed of light. Typically, the speed of an electrical signal in a cable is between 60% and 80% of the speed of light. Figure
Signal Speed ![]() 300,000,000 NVP m/s in Cable
300,000,000 NVP m/s in Cable
![]()
= 300,000,000 m/s
TEST | SAVE |
FAULT
INFO
EXIT | ENTER |
| MONITOR |
SINGLE | SETUP |
TEST |
|
AUTO | |
TEST |
|
NVP = | Speed Pulse Travels in Cable | X 100% |
Speed of Light
OFF | SPECIAL |
FUNCTIONS |
SMART
REMOTE
gc34f.eps
Figure 7-8. How NVP is Calculated
NVP values affect the limits on cable length for Ethernet systems because Ethernet operation depends on the system’s ability to detect collisions in a specified amount of time. If a cable’s NVP is too low or the cable is too long, signals are delayed and the system cannot detect collisions soon enough to prevent serious problems in the network.
NVP and Length Measurements
Length measurements depend directly on the NVP value entered for the selected cable type. To measure length, the test tool first measures the time it takes for a test pulse to travel the length of the cable. The test tool then calculates cable length by multiplying the travel time by the signal speed in the cable.
Because the test tool uses the length measurement to determine cable resistance limits, the NVP value also affects the accuracy of resistance measurements.