Basic Cable Testing 7
Attenuation
Attenuation
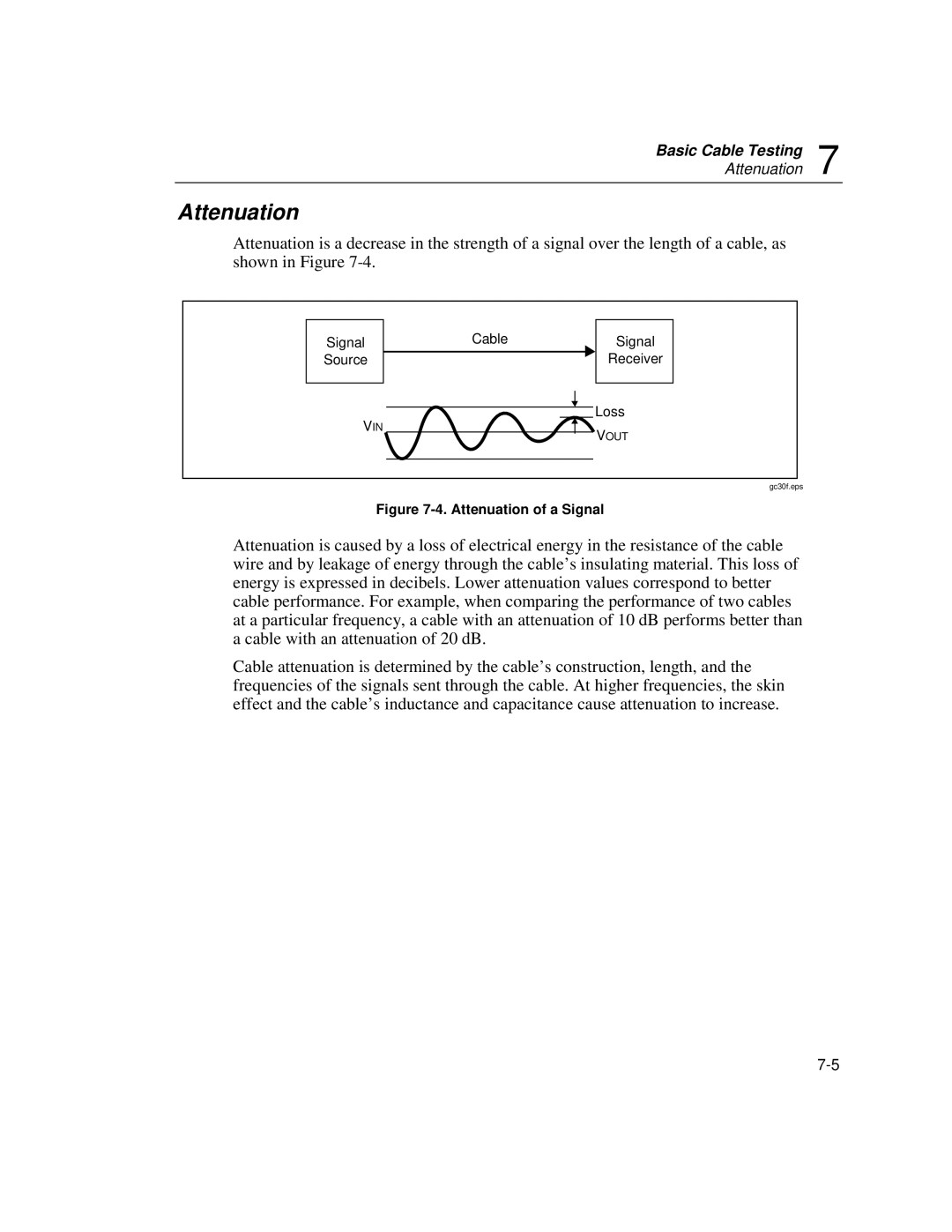
Attenuation is a decrease in the strength of a signal over the length of a cable, as shown in Figure
Signal
Source
VIN
CableSignal Receiver
Loss
VOUT
gc30f.eps
Figure 7-4. Attenuation of a Signal
Attenuation is caused by a loss of electrical energy in the resistance of the cable wire and by leakage of energy through the cable’s insulating material. This loss of energy is expressed in decibels. Lower attenuation values correspond to better cable performance. For example, when comparing the performance of two cables at a particular frequency, a cable with an attenuation of 10 dB performs better than a cable with an attenuation of 20 dB.
Cable attenuation is determined by the cable’s construction, length, and the frequencies of the signals sent through the cable. At higher frequencies, the skin effect and the cable’s inductance and capacitance cause attenuation to increase.