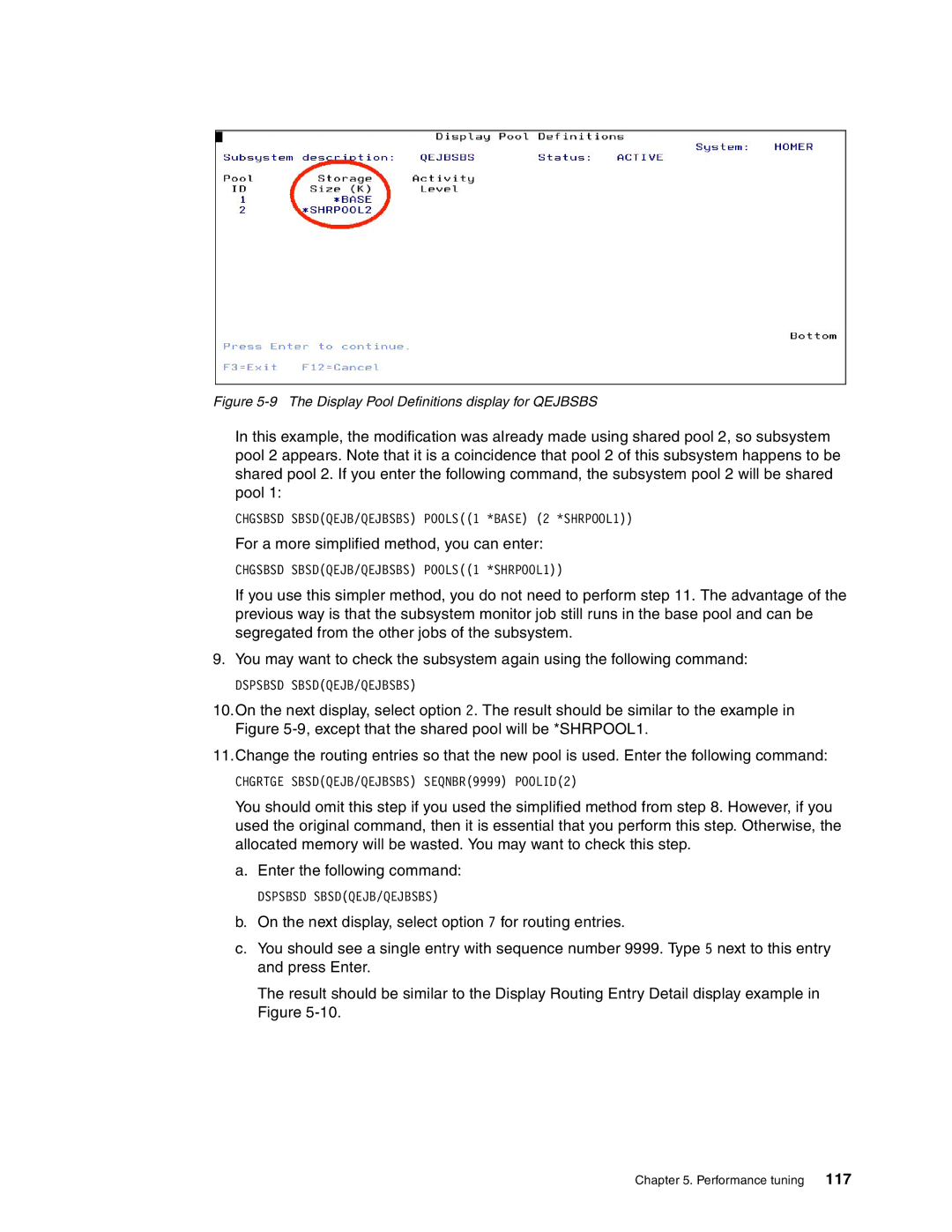
Figure 5-9 The Display Pool Definitions display for QEJBSBS
In this example, the modification was already made using shared pool 2, so subsystem pool 2 appears. Note that it is a coincidence that pool 2 of this subsystem happens to be shared pool 2. If you enter the following command, the subsystem pool 2 will be shared pool 1:
CHGSBSD SBSD(QEJB/QEJBSBS) POOLS((1 *BASE) (2 *SHRPOOL1))
For a more simplified method, you can enter:
CHGSBSD SBSD(QEJB/QEJBSBS) POOLS((1 *SHRPOOL1))
If you use this simpler method, you do not need to perform step 11. The advantage of the previous way is that the subsystem monitor job still runs in the base pool and can be segregated from the other jobs of the subsystem.
9.You may want to check the subsystem again using the following command:
DSPSBSD SBSD(QEJB/QEJBSBS)
10.On the next display, select option 2. The result should be similar to the example in Figure
11.Change the routing entries so that the new pool is used. Enter the following command:
CHGRTGE SBSD(QEJB/QEJBSBS) SEQNBR(9999) POOLID(2)
You should omit this step if you used the simplified method from step 8. However, if you used the original command, then it is essential that you perform this step. Otherwise, the allocated memory will be wasted. You may want to check this step.
a.Enter the following command:
DSPSBSD SBSD(QEJB/QEJBSBS)
b.On the next display, select option 7 for routing entries.
c.You should see a single entry with sequence number 9999. Type 5 next to this entry and press Enter.
The result should be similar to the Display Routing Entry Detail display example in Figure
Chapter 5. Performance tuning 117