Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
THEORY OF OPERATION | ||||
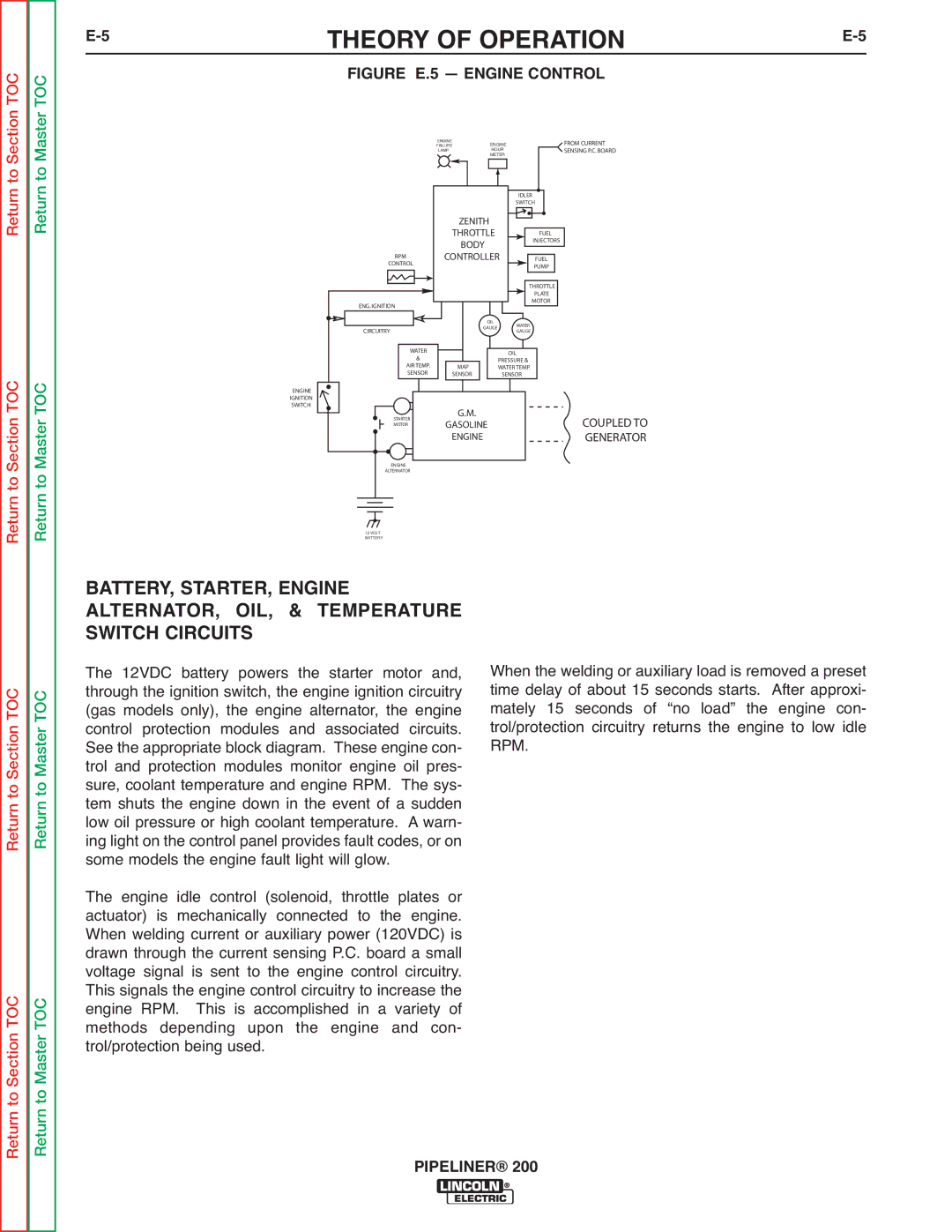
| FIGURE E.5 — ENGINE CONTROL |
| ||
| ENGINE | ENGINE | FROM CURRENT |
|
| FAILURE |
| ||
| LAMP | HOUR | SENSING P.C. BOARD |
|
|
| METER |
|
|
|
|
| IDLER |
|
|
| SWITCH |
| ZENITH |
|
|
| THROTTLE |
| FUEL |
| BODY |
| INJECTORS |
|
|
| |
RPM | CONTROLLER | FUEL | |
CONTROL |
|
| PUMP |
|
|
| THROTTLE |
|
|
| PLATE |
ENG. IGNITION |
|
| MOTOR |
|
|
| |
| OIL |
| WATER |
CIRCUITRY | GAUGE |
| |
| GAUGE | ||
|
| ||
WATER |
|
| OIL |
& |
| PRESSURE & | |
AIR TEMP. |
| ||
MAP | WATER TEMP. | ||
SENSOR | SENSOR |
| SENSOR |
ENGINE
IGNITION
SWITCH
STARTER | G.M. | COUPLED TO | |
GASOLINE | |||
MOTOR | |||
| ENGINE | GENERATOR |
ENGINE
ALTERNATOR
12VOLT BATTERY
Return to Section TOC
to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
BATTERY, STARTER, ENGINE ALTERNATOR, OIL, & TEMPERATURE SWITCH CIRCUITS
The 12VDC battery powers the starter motor and, through the ignition switch, the engine ignition circuitry (gas models only), the engine alternator, the engine control protection modules and associated circuits. See the appropriate block diagram. These engine con- trol and protection modules monitor engine oil pres- sure, coolant temperature and engine RPM. The sys- tem shuts the engine down in the event of a sudden low oil pressure or high coolant temperature. A warn- ing light on the control panel provides fault codes, or on some models the engine fault light will glow.
The engine idle control (solenoid, throttle plates or actuator) is mechanically connected to the engine. When welding current or auxiliary power (120VDC) is drawn through the current sensing P.C. board a small voltage signal is sent to the engine control circuitry. This signals the engine control circuitry to increase the engine RPM. This is accomplished in a variety of methods depending upon the engine and con- trol/protection being used.
When the welding or auxiliary load is removed a preset time delay of about 15 seconds starts. After approxi- mately 15 seconds of “no load” the engine con- trol/protection circuitry returns the engine to low idle RPM.
Return