AIR-CONDITIONER
Contents
10-2
10-1
10-3
10-4
Explanation of illustrated marks
Explanation of indications
Confirmation of warning label on the main unit
Indication Explanation
Never recover the refrigerant into the outdoor unit
∗ For details, refer to the parts list
Do not modify the products
For spare parts, use those specified ∗
Metal section Earth position
Check the following items after reinstallation
Side
Limit even if the refrigerant leaks
Pipe Materials
Safety Caution Concerned to New Refrigerant
Copper pipe Piping
Flare nut
General tools Conventional tools can be used
R410A Conventional air
Used tool Usage
Indoor Unit
Way Air Discharge Cassette Type
Digital Inverter
SP562AT-E SP802AT-E
Super Digital Inverter
RAV SM562BT-E SM802BT-E
Concealed Duct Type
Super Digital Inverter
RAV SM562CT-E SM802CT-E
Under Ceiling Type
Revised Mar
Indoor unit
Twin Type
SP1402AT-E SP1102AT-E
RAV SM563AT-E SM803AT-E
SP562AT-E SP802AT-E
RAV-SM563AT-E, RAV-SM803AT-E
Operation characteristic curve Digital Inverter
Cooling Heating
Current
RAV-SP1102AT-E
Operation characteristic curve Super Digital Inverter
Capacity variation ratio according to temperature
Ratio Capacity
Outdoor temp. ˚C
Tap
Pressure
High
Low Static
Tap Low
Static Pressure Tap
35˚
RAV-SM563UT-E, RAV-SM803UT-E
188
RAV-SM1103UT-E, RAV-SM1403UT-E, RAV-SP1102UT-E
Suction port canvas Separate sold
Dimension
RAV-SM562CT-E, RAV-SM802CT-E, RAV-SM1102CT-E, RAV-SM1402CT-E
Space required for service
365
RAV-SP1102AT-E, RAV-SP1402AT-E
Indoor unit
RAV-SM563UT-E, RAV-SM562BT-E, RAV-SM562CT-E / RAV-SM563AT-E
Outdoor unit
RAV-SM803UT-E, RAV-SM802BT-E, RAV-SM802CT-E / RAV-SM803AT-E
Distributor TCJ sensor
Outdoor unit
Min. Max 5m 50m Ball valve Packed valve Outer dia. Ø a
25 × L180
Outer dia. Ø B Strainer
TCJ
RAV-SM563UT-E, RAV-SM562BT-E, RAV-SM562CT-E / RAV-SP562AT-E
1500cc R410A 2.1 kg Cooling Heating
RAV-SM803UT-E, RAV-SM802BT-E, RAV-SM802CT-E / RAV-SP802AT-E
Compressor DA420A3F 21M R410A 2.95kg Cooling Heating
TCJ sensor Distributor
Inside 2500cc Rotary
L210 FP1.3 flat fin
LM2 3
LM1 3
Color
Identification
Color
Indoor Unit
LM 3
Identification
Diagram
Outdoor Unit Wiring
MCC-5009
Board
MCC-1438
Board
MCC-1531
SUB P.C. board
RAV-SP562AT-E, RAV-SP802AT-E
BLK Black WHI White BLU Blue BRN Brown
Parts name Type Specifications
MP24Z2N
RAV-SM803AT-E
RAV-SM563AT-E
CAM-MD12TF-8
RBC-U21PG W -E2 Ceiling panel
TCB-DP22CE2 Drain up kit
Piping Materials and Joints Used
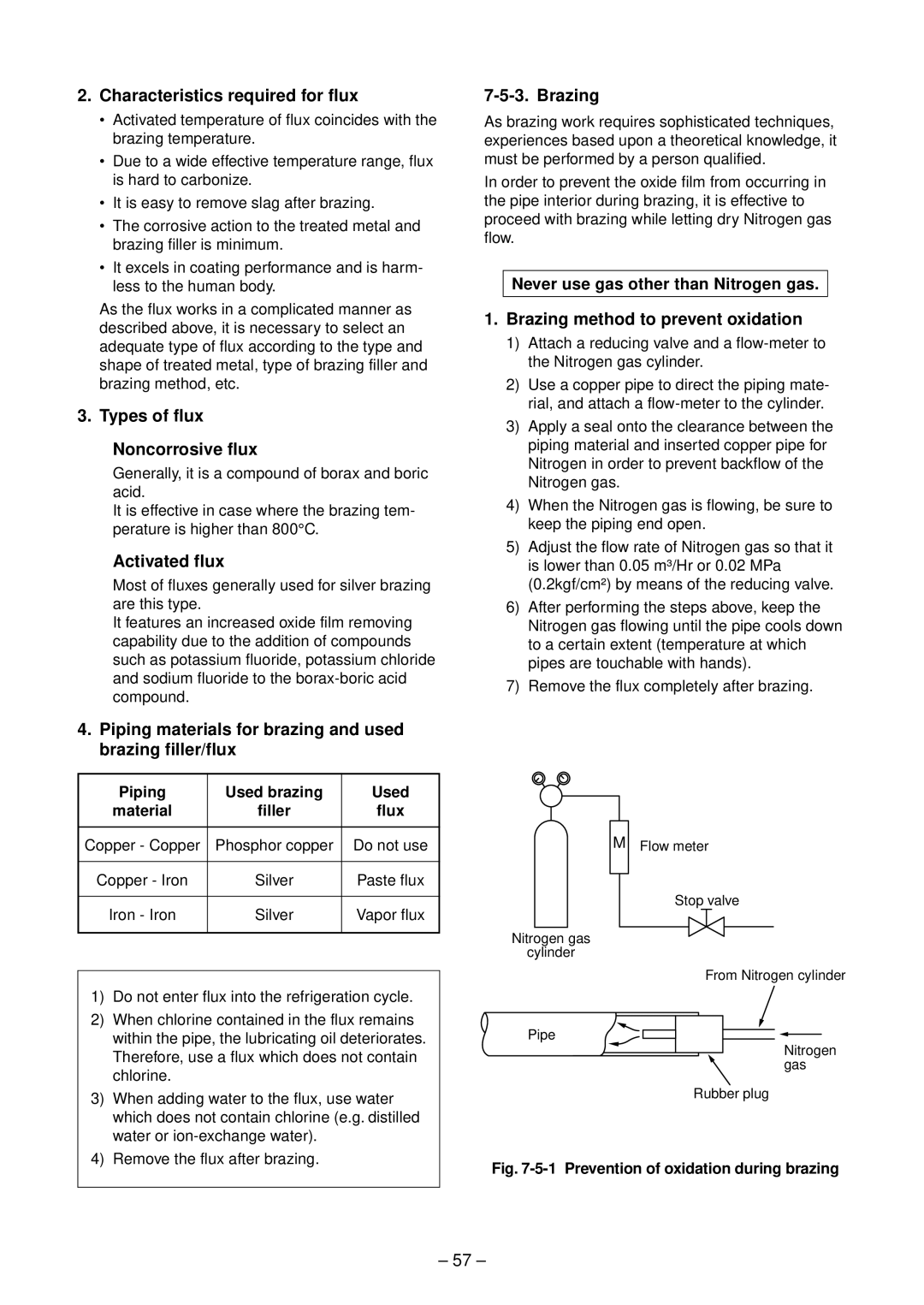
Safety During Installation/Servicing
1 Thicknesses of annealed copper pipes Thickness mm
Processing of Piping Materials
Outer diameter mm R410A R22
12.7 15.9
R410A clutch type Clutch type Wing nut type
Flare tool for Conventional flare tool
R22 clutch type Clutch type Wing nut type
Diameter Width mm
13.0 13.5 12.7 16.2 16.0 12.9 15.9 19.4 19.0 23.3 24.0 19.2
43˚to 45˚
Nm kgfm
Wrenches available on the market
Refer to the 4. Tools
Required Tools
Flux Reason why flux is necessary
Low temperature brazing filler
Materials for Brazing Silver brazing filler
Phosphor bronze brazing filler
Types of flux Noncorrosive flux
Characteristics required for flux
Activated flux
Piping materials for brazing and used brazing filler/flux
Branching pipe for simultaneous operation system
Basic conditions need to reuse the existing pipe
Curing of pipes
Restricted items to use the existing pipes
Existing pipe no * Use a new pipes
Recovery method of refrigerant for RAV-SM563AT-E, SM803AT-E
Work procedure
When recovering refrigerant in case of reinstalla
Indoor Control Circuit
Main Sub master remote controller
Outline of specifications Remarks
Cool
Setting at shipment
Heating Auto
Operation
Heat
Control temp C
Arning
Cooling/dry operation In heating/fan operation
All modes
Frequency fixed In case of wired remote controller
Last push priority
Center
Operation Prohibited
Normal control
Circuit Board
Indoor Print
Ay Air
Concealed Duct Type / Under Ceiling Type
Function Connector Pin Specifications Remarks
Indoor P.C. Board Optional Connector Specifications
Outdoor Controls
Applied
SM803AT-E
MCC-5009
P.C board
Iewed from parts
EEPROM-IC
MCC-1531
RAV
RAV -SP562AT-E, RAV
Ipdu MCC-1438
SP1402AT-E
RAV -SM1103AT-E, RAV -SM1403AT-E
Current release control
Discharge temperature release control
Operation with WE
Outdoor fan control
Allocations of fan tap revolutions rpm
TE ˚C TD ˚C
Trouble of TE sensor
Coil heating control
To ˚C
TE ˚C
Start of heating operation
Defrost control
TE ºC
Zone
Before troubleshooting
Summary of Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting procedure
Ired remote controller type
Trouble Confirmation of lamp display
Error mode detected by indoor and outdoor units
Check Code List
Cause of operation Status of air Condition
Error mode detected by central remote controller
Error mode detected by remote controller
Error Mode Detected by LED on Outdoor P.C. Board
Type a
Type B
E01 error
Troubleshooting Procedure for Each Check Code
E09 error
Check Code
E04 error
E18 error
E10 error
E08, L03, L07, L08 error
L09 error
L30 error
L20 error
P10 error
F10 error
P12 error Only for 4-way air discharge cassette type models
CN333
CN334
P22 error
F02 error
P19 error
P26 error
F01 error
H03 error
P29 error
F06 error
F04 error
F08 error
H02 error
L29 error
H01 error
P03 error
P04 error
Same as others Correct connection of connector
C06 error Central controller
F29 error / 12 error
E03 error Master indoor unit
P31 error Sub indoor unit
100
TA sensor TC, TCJ sensor Caracteristics-2 Caracteristics-1
101
Caracteristics-3
20 TE, TO, TS sensor
102
Replacement Procedure
R2 Replacement of service P.C. board
R1 Readout of the setup data from Eeprom
Contents
103
R3 Writing of the setup contents to Eeprom
105
Memorandum for setup contents Item code table Example
Type Item code
Indoor unit capacity Item code
Wired remote controller
Test Run Setup on Remote Controller
106
RAV-SM563UT-E, RAV-SM803UT-E, RAV-SM562BT-E, RAV-SM802BT-E
Conditioner from the wireless remote controller
Use either Cool or Heat operation mode for test operation
Return Dip switch of the sensor section as before
107
108
Case of wireless remote controller
Item No. DN table Selection of function
109
Indoor unit is controlled by 2 remote controllers
Cabling and Setting of Remote Controller Control
Setup method
110
Monitor Function of Remote Controller Switch
Call of sensor temperature display Contents
111
Order to monitor another error history, push
Calling of error history Contents
112
Group control operation
Setup at Local Site / Others
TCC-LINK Adapter For TCC-LINK Central Control
113
C. Board Switch SW01 Setup
Wiring Specifications
114
Size
115
How to set up central control address number
Address setup procedure
Address Setup
Item code Data at shipment Setup data range
116
System configuration
Address Setup & Group Control
Only turning on source power supply Automatic completion
Automatic address example from unset address No miscabling
Manual setting from remote controller
END
118
119
120
No. Part name Procedure Remarks
Detachment
Attachment
121
122
123
CN102 TCJ sensor 2P Red CN333 Power supply of fan motor
† Fan motor 1. Detachment
Remove nuts fixing the fan motor to Remove it
‡ Drain pan 1. Detachment
124
Body 1 position, and then remove Assembly. Ø4 × 8, 3 pcs
Assembly Perform works of items 1 of , 1 of ‚
Fix the drain pump assembly as before
125
Part name Procedure Remarks
126
Heat
127
128
129
130
131
Motor Remove the connector of the fan
„ Multi blade fan Remove the suction grille
Case side. Then fans come off
132
Heat exchanger support
133
134
135
Procedure Remarks
136
137
Take off fixed screw for the valve mounting
138
By hands so that the fan motor does not
Fall Tighten the flange nut with torque 4.9Nm 50kgf/cm
139
Fan guard
140
Perform works of items 1 of , and ‚
With minus screwdriver along with
141
Clamp
Remove the upper cabinet. ST1T Ø4 × 10L, 6 pcs
142
Discharge port cabinet for the heat
Fin guard Heat exchanger ST1T Ø4 × 10, 2 pcs
143
144
145
146
Motor and the propeller fan
Loosen the flange nut by turning clock
147
148
Product
149
150
‚ Air-outlet cabinet
151
Put the upper left side of the air-outlet
Cabinet on the end plate of heat ex
152
„ Inverter Perform the works in 1 of and ƒ
CN702 PMV Pulse Motor Valve coil
153
Remove connectors and lead wires
154
155
Case of RAV-SP1102AT-E
Case of RAV-SP1402AT-E
156
Pay attention that 4-way valve or PMV is
‰ PMV coil
157
Reactor Perform works of items to „
158
Electric parts box as shown below so that
They do not come to contact with the reac Tor
231
233
225 209 208
159
160
402 404 401 405 403
161
224 212 205 231
162
208 216, 218 205 230
224 212 211 225 209 202 226
229
213, 214, 220 223 207 232 231
164
304 311 306 305 301 307 302 303 310 313 308 309
165
RBC-U21PG W E2
902
166
RAV-SM562BT-E
904
43196012 Bushing 43166002 Remote Controller
901, 902, 903
167
904 901, 902
168
RAV-SM1102BT-E, RAV-SM1402BT-E
402 404 403 406 405401407
169
\Location Part Description
22, 23
44, 45
36, 37, 38,39, 54
33, 34, 35,53, 56
171
404401 407 403 406 402 405
172
404 43158193 Reactor
10, 32
21, 22 14, 16, 17 13, 15, 19
Muffler
173
174
705 701 702 708 707 706 710
3332 15, 16
175
RAV-SM1103AT-E, RAV-SM1403AT-E
176
707 708 706 704 703 701 705 702 710
21,22 16,17
177
43146695 Valve, Pulse, Modulating
178
704 707
179
Inverter 26,27 23,24 28,29
710 706 704
709
180
Drain up Kit
Replacement of Main Parts Sold Separately
181
TCB-DP22CE2
Wireless Remote Control Kit
182
RBC-AX22CE2
This is on installation for 2 HP and 3 HP Products
Required parts for installation work Recommendation
Part name ’ty Specifications/Vendor Remarks
183
Required tools for installation work
Part name Specifications Usage
184
185
Cord heater installation wiring diagram
Cord heater installation work procedure
Photo / Explanatory diagram Procedure
186
Assembly and the sound insulation board
Remove the motor base assembly, partition plate
187
Remove the fixing screws of the heat exchanger
188
189
190
Photo / Explanatory diagram Procedure Assembly
Material SGCC-Z08, Thickness 0.8t
Drawing of thermostat fixing plate
191
Ø3.4 burring hole Upward Ø3.4 burring hole Downward
192
Base Plate
193
RAV-SM1103AT-E, RAV-SM1403AT-E
Check of Concentration Limit
Toshiba Carrier Corporation