October
Issue
NDA-24300
Stock #
Liability Disclaimer
NEAX2400 IPX
Issue No 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109
Issue No
251
Revision Sheet 5/9
403
479
555
Revision Sheet 9/9
Table of Contents
System Operations and Maintenance Manual
Table of Contents
116
Table of Contents
LPM Accommodating UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
NDA-24300TABLE of Contents
Fault Repair Procedures
Hard Time Clock Fault
Routine Maintenance Procedure
Chapter Maintenance Commands
DTF101N
List of Figures
301
List of Figures
List of Figures
NDA-24300LIST of Figures Page xiii Issue
List of Tables
List of Tables
NDA-24300LIST of Tables Page xv Issue
This page is for your notes
NDA-24300CHAPTER
HOW to Follow this Manual
General
Chapter
When replacing a unit/circuit card with a spare
When performing routine maintenance
Introduction
Purpose
Administrative Management Procedures
Basic Knowledge
Summary of This Manual’s Contents
System Configuration
System Configuration
IMG0
3shows the face layout of IMG0
IMG1
4shows the face layout of IMG1
5shows the face layout of IMG 2/3
Module Group
Line Equipment Numbers Lens
U2 U3 MG06 U0 U1
Unit
Group Number Allocations
Group
Total of eight Levels Lv0 Lv7 can be assigned on each Group
Level
11 LP Number Allocations
Local Partition LP Number
System Message 3-E SUP Lock UP Failure Temporary NEC Tokyo
System Messages
IOC CPU EMA
Fault Detecting Function
14 Fault Detection Block Diagram
System Maintenance Outline
Range of Faults Specification
15 General System Block Diagram
16 CPU Controlling Block Diagram
IMG2
17 Speech Path Block Diagram
IMG2 PIM
18 Speech Path Range of Fault
Explanation of Terms
Sense 0~F Kind of Restart Remarks
Precaution about Diagnostic Procedure/Fault Repair Procedure
19 3M Model 8012 Portable Field Service Kit
21 How to Set the ROM in IC Socket
22 How to Clean the Connector Portion
END
How to Follow Diagnostic Procedure/Fault Repair Procedure
Start
System Maintenance Outline
Judgment of fault status
Fault Reporting Method
Reporting Fault to NEC
16LCBE
Forwarding Faulty Circuit Card Method
This page is for your notes
System Messages
System Messages
System Initialize
Message no System Message
Message no System Message
Reset Interrupt
B15 B11
➃ Data Load Result after restart
Processing
➂ Related Call Information
Reference See , .2, for the repair procedure
CPU Clock Down
➁ Male-CPU Restart Information FF
SUP
Level Infinite Loop
➇ Data Analyzed by NEC Engineers
➃ System Controlling Port B
➅ CPU Changeover Factors
➆ System ALM
➀ Information on Self-CPU Restart
After detection of a clock fault
Memory Failure
= CPU #0/CPU #1
➂ B-level Infinite Loop
B1-Level Infinite Loop Permanent
➀ ➁ ➂
B1-Level Infinite Loop Temporary
➀ Mate-CPU Restart Information
Mate CPU Failure
➀ ➁ ➂ ➃
Abnormal Interrupt
Both TSW Failure Permanent
TSW Failure Permanent
Detected B7 b6
➀ TSW system in which a fault is
Both TSW Write Failure
➂ Data Analyzed by NEC Engineers
TSW Write Failure
➁ Clock status of No TSW
➀ TSW card in which a fault is
Both TSW Clock Failure
TSW Clock Failure
➀ ➁ ➂ ➃ ➄
Both PLO Failure
DCS Input Route Route Of Input Clock
➁ Valid Information bit for Scan Data
PLO Failure
System Messages
➁ Kind of failure
➀ MG number of fault detection
Module Group Down Failure
NON
TSW ACT Change Report
➆~➉ Status of ST-BY side TSW card
➂~➅ Status of ACT side TSW card
Dlkc Data Transfer Failure Permanent
➀ System status of faulty Dlkc card
➂ Details on Switching Network
Dlkc Data Transfer Failure Temporary
Connected With Primary Oscillator M-OSC External Clock
PLO Restore
Location
➀ Faulty Circuit Card Mounting
Level Infinite Loop Permanent
➁ PM Restart Type
Level Infinite Loop Temporary
Lock-Up Failure Permanent
Lock-Up Failure Temporary
➀ Faulty Circuit Card Location
48V Over Current
Busy state and stops supplying power
➀ Location of faulty PM
Ground Failure
➀ Location of faulty circuit card
➁ Location of faulty circuit card
Valid only when the kind of fault is 08H
➀ Location of PM Lens with a fault
➁ Kind of fault
➂ Time Slot No. of fault This data is
➂ ➃ ➂ ➃
Digital Line Failure
➀ Location of faulty line
Digital Line Restore
This message displays when a digital line fault is restored
Detection
➀ Unit and MG number of fault
Both TSW Ready Failure
TSW Ready Failure
Detection Reference See , .4, for the repair procedure
Dlkc Ready Failure
➀ Details on faulty Dlkc card
MUX Ready Failure
➀ Unit and MG number for MUX card with ready fault
➁ MG and system number for faulty MUX card
Reference See , .3 and .4, for the repair procedure
Both MUX Ready Failure
➀ Unit and MG number for MUX card with the ready fault
PCI Card Failure
➄ Error status on PCI slot
➀ Detection of PCI restoration
PCI Card Failure Recovered
Slot
➄ Details on error restoration PCI
NON Fixed NON
Reference See , , for the repair procedure
System Failure
➀ Probable cause for failure
RGU & Howler Failure
Line Load Control Start
Line Load Control Stop
➄ The called station number
When type of connection is Station connection
Bad Call Notification
➁ ➃ Station number see table b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
➅ Remote Route No
When type of connection is Trunk connection
➄ Remote Route No
➇ Not used ➈ Time Slot Number of Link ➉ Not used
➆ Called Trunk No
B4-b7
When type of connection is ACD Trunk connection
System Messages
➀ Test Item b0-b3 is valid only for Outgoing trunk test
STA-Test Connection Data
Error no Meaning
Error Numbers and Their Meanings
= SST, WT = SDT = TRG = Sdtt
➇ Tested Route No
➀ ➁ ➂ ➃ ➄ ➅➆ ➇ ➈ ➉ 11
Emergency Call
Assigned at Attendant Desk Console
Emergency Control Start
➀ Route Selection Time Pattern No
➀ Suspension of Emergency Control
Emergency Control Stop
Calling station No. See table
When calling party is Station
Abnormal Call Duration Data
➀ Calling party information
➃ Called party information
When calling party is ATTCON/DESKCON
When calling party is Trunk
Route No. and Trunk No. See table
OG Call to outside IC Call from outside
➄ Called Party Information
Station to Station Call
Type of called party 00 = Station 01 = Attendant Console
FS = 0, FE = 0/1
Smdr Output Buffer Overflow Alarm
➀ Detail Information B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
➃ Overflow Rate
FS = 1, FE =
➂ Overflow Rate
FS = 3, FE =
FS = 2, FE =
➁ Smdr Group No
➂ Port No
➀ Detail Information
Smdr Output Buffer Overflow Release
➁ Load Status
System Initialize With Data Load
System Messages
System Initialize
CPU MBR Key Turn on
CPU MBR Key Turn OFF
➀ System status of TSW card
TSW MBR Key Turn on
TSW MBR Key Turn OFF
Operation
TSW PLO Key Turn on
TSW PLO Key Turn OFF
➀ Frame No. and its kind
Almc MB Key Turn on
Almc MB Key Turn OFF
PM MB Key Turn on
➀ Location of faulty Line/Trunk card b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
PM MB Key Turn OFF
NCU MB Key Turn on
➁ Location of faulty PFT card
NCU MB Key Turn OFF
➀ Performed Diagnosis Item
Cyclic Diagnosis Normal
Index
00H Routine Diagnosis Start
➀ Performed Diagnosis Item
➁ Pending Diagnosis Menu SYS1
➂ Verification of Drive Number
10H Program Memory Verification Normal End
➀ Routine Diagnosis
➁ Information on HD
➂ Verification of Data Memory
20H Data Memory Verification Normal End
➁ Verification of HD
Changeover
30H TSW ACT/STBY Changeover Normal End
➁ Active TSW system after
40H CPU ACT/STBY Changeover Normal End
Ineffective Hold
50H No Trunk Ineffective Hold
➁ MG and Unit of No. of Trunk
70H Call Forwarding Memory Clear Normal End
A0H Periodic Back-up Normal
➁ Information on Periodic Backup
➂ Backup Data to No system
➃ Backup Data to No system
C0H Detection of Remaining Link Normal End
For Release 4 or later
Cyclic Diagnosis Information Error Detected
➀ Detected Error Item B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
➃ Data analyzed by NEC Engineers
10H Program Memory Verification Discrepancy
Diagnosis ➁ Verification of HFD number
Diagnosis ➁ Verification Impossible of HD
11H Program Memory Verification Impossible HFD Fault
➀ Error detection by Routine
➃ Data analyzed by NEC Engineers ➄ Error Drive
12H Program Memory Verification Impossible Fault at CPU side
Diagnosis ➁ Verification of HFC
20H Data Memory Verification Discrepancy
➄ Single Code
21H Data Memory Verification Impossible HFC Fault
➃ Error Type B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Diagnosis ➁ HFC Impossible Verification
➅ Data analyzed by NEC Engineers ➆ Error Drive
➂ -➅MUX card ACT-side linkage condition
30H TSW ACT/STBY Changeover Failure
➁ Active TSW No
➆ -➉MUX card Stby linkage condition B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
MUX card ACT-side linkage condition B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
31H TSW ACT/STBY Changeover Failure MUX Fault
Detected Error Item
Active TSW No
➆ -➉MUX card Stby linkage condition B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Diagnosis
41H CPU ACT/STBY Changeover Failure
42H CPU ACT/STBY Changeover Failure
43H CPU ACT/STBY Changeover Failure PCI Fault
➁ ACT system after changeover
➂ Lens of Ineffective Hold Trunk G, LV
50H Trunk Ineffective Hold Detected
Diagnosis ➁ Lens of Trunk Ineffective Hold MG, U
51H Trunk Ineffective Hold Detected and Released
➄ ➅ ➆ ➇ ➈ 11➉12
52H Trunk Ineffective Hold Detected Impossible
Was stopped
70H Call Forwarding Memory Clear NG
Abnormal End
A0H Periodic Backup Abnormal End
Error detection by Routine
Diagnosis Information of Periodic Backup
Refer to No. ➂ Refer to No.➃ Refer to No.➄
C0H Detection of Remaining Link Abnormal End
➁ ED Error Data
PLO MB Key Turn on
PLO MB Key Turn OFF
13-A CCH Clock Failure
➀ Location of faulty CCH/DCH card
CCH C-Level Infinite Loop Failure Permanent
13-B
13-C CCH C-Level Infinite Loop Failure Temporary
CCH Lock-Up Failure Permanent
13-D
13-E CCH Lock-Up Failure Temporary
CCH B-Level Infinite Loop Failure Permanent
13-F
13-G CCH B-Level Infinite Loop Failure Temporary
➁ Data Analyzed by NEC Engineers
13-H
CCS Link Failure Permanent
➂ Probable cause for failure
Ccitt Factor Error
CCS Link Failure Temporary
13-I
➂ Probable cause for the failure
FLT ID Ccitt Factor Error
Restoration From CCS Link Failure
➁ CKT No. of faulty circuit
13-J
13-K CCH Reset Interrupt Failure
➀ Accommodated location B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
This message displays when a digital line failure occurs
➁ Kind of Fault B7b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
13-N
13-O Digital Line Failure
13-P
➀ Accommodated location
13-Q DRU Battery Operation
➀ Accommodated location
13-R
DRU Line Operation
➂ Location of faulty circuit card
13-Z Power Failure
➀ MG No. and Unit No. of fault detection
➁ Kind of Power
➁ Lens of VPS with the failure
This message displays when a VPS failure is detected
15-A
VPS Failure Temporary
15-B VPS Failure Permanent
➀ Lens of VPS with the failure
VPS Restore
15-C
Become all busy
16-A Inside Trunk All Busy
➀ Intra-Office trunks that have
Trunk Name
Route
Trunk Name Route
➂ Virtual Tie Line Call Header
16-B Virtual Tie Line Set Report
➁ Virtual Tie Line Call Header
Accommodated Location
16-C
Virtual Tie Line Cancel Report
➀ Virtual Tie Line Call Header
16-E Virtual Tie Line Set Time Out
Reason Class Kind Data Reason Kind Value
Call Source
System Messages Reason Class Kind Data Reason Kind Value
Invalid message class
Case of Station OG/ATT OG/ATT Tandem Connection
16-F
Sender Start Time Out
➆ OG route number Hex B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
➄ Tenant No. of calling station Hex. b7 OP data 0/1
➅ Optn data
Number of digits dialed by caller
➇ Oprt data
➈ Trunk No. of OG trunk
➉ Trunk No. of sender
➁ IC route number Hex
Number dialed by caller See table B6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1
Case of Tandem Connection
➀ Type of connection
➂ Oprt data
➇ Oprt data
Number dialed by caller See table B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
IOC0 IOC1
➀ Faulty Port No
16-K Port Line OFF
16-L
Port Line Restore
16-M Hard Clock Failure
16-N
Hard Clock Restore
16-T IOC Failure Temporary
This message displays when the IOC card fails
➁ Cause for fault
IOC Failure Permanent
16-U
16-X Station Exchanged Report
➀ Error code
Error Code HEX Failure
➁ Tenant No. of calling station
B4-b7 B0-b3
➁ CKT No
17-A
CCH MBR Key Turn on
➀ Location of CCH/DCH card B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
17-B CCH MBR Key Turn OFF
➀ Location of CCH/DCH card
17-C
CCH MB Key Turn on
17-D CCH MB Key Turn OFF
➀ Tenant No B7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 ➁ Changing Method
17-H
Day/Night Change Information
Night Mode 2 available only for Japan
IOC MB Key Turn on
17-O
17-P IOC MB Key Turn OFF
IOC MBR Key Turn on
17-Q
17-R IOC MBR Key Turn OFF
➀ Condition of Dch
23-P
DCH Back-Up Automatic Change Start/End
System Messages
DCH Back-Up Manual Change Start/End
23-Q
System Messages
➁ Scan Data
23-Y
MUX Clock Failure
➂ Scan Data
23-Z Both MUX Clock Failure
➀ MUX card location
➀ Port No. of the MAT logged in/out b0-b2 I/O Port No
This message displays when the MAT is log-in or log-out
26-N
MAT Log
➃ User Group No. UGN Hex
When a call is originated from a station
26-R Call Trace
Output Data Hex Actual Meaning Blank
➉ User Group No. UGN Hex
Information on Called Party Informer
When a call is originated from a trunk
Detailed meanings are as follows
➀ ➁ ➂ ➃ ➄ ➅ ➇➆
26-V LAN Interface Error Report
Error Code Output Data Definition Hex
Not used
Kind of Error
Details on Detected Error
12 ~ 24 Not used
When 9 =05 OAI / 07 MIS
26-W LAN Interface Release Report
➈ Application Type
When ➈=03 Smdr / 04 MCI
➉ Device Number of recovered client PC Recovery Information
➁ RLS Data
33-A MUX Clock Restore
➀ MG Module Group
SDT Alarm Warning
➁ Details on alarm
33-B
=-/VC-11 Path Trouble
➂ Alarm-detected HW
Repair Procedure
33-C
SDT Alarm Trouble
Repair Procedure
NDA-24300CHAPTER
➁ Details on the fault
33-D SDT Alarm Restore
➁ Detailed information
33-E
SDT Interface Change Notify
This page is for your notes
Circuit Card Mounting Face Layout
Unit/Circuit Card Replacement Procedure
LPM Accommodating Unit/Circuit Card Replacement Procedure
Precaution
LANIPZ-PC19 GATEPZ-GT16
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Reference Item Remarks
Operating Procedures
PZ-IO27 Note
CPR Replacement Procedure
How to Replace the CPU
Removal of Front Panel and Top Cover from CPR
Circuit Card Accommodation into the New CPR
Lani PZ-PC19
Isagt PZ-GT13
Reattachment of CPR Top Cover and Front Panel
Accommodation of New CPR into LPM
Insertion of New HFD into CPR
By using the two screws, fasten the new HFD onto the CPR
Replacement Procedure
Refer to -2for CPR face layout Refer to -3to replace the CPU
Section
Palm connector yet
IMG0 lamp on the DSP flashes
EMA SUP lamp on the EMA card goes OFF
Top Cover Front Panel
10 Insertion of Isagt and Lani Cards
11 Reattachment of CPR Top Cover and Front Panel
CPR
LPM
13 Insertion of New HFD Into CPR
EMA Card Replacement Procedure
YES
END
OPE lamp on the IOC card goes
IOC Card Replacement Procedure
Replacement Procedure
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
CPU System Changeover Refer to .1.2 in Chapter
Power Supply Unit Replacement Procedure
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
Keep MB switch UP
Misc Card Replacement Procedure
ALM RST button is used to reset the alarm lamps only
Tswm Accommodating Circuit Card Replacement Procedure
Circuit Card Reference Item Remarks Function Name
Misc BUS
GT Card Replacement Procedure
CPU OPE CPU DSP = OFF
GT Card Replacement Procedure
System changeover of GT from ACT to Stby mode
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
IMG0 CPU DSP = Flash green IMG1-3 CPU DSP = OFF
TSW Card Replacement Procedure
16 System Block Diagram TSW and Other Speech Path Echelons
Use extreme care when operating the keys on the circuit card
TSW Card Replacement Procedure
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
They are all steady-green
TSW ACT lamp on the new card goes OFF
TSW ACT lamp on the new card
Remains OFF
Dlkc Card Replacement Procedure
Refer to -16and Figure
OFF
PLO Card Replacement Procedure
OPE lamp on the new card is OFF
PWR SW Card Replacement Procedure
Misc Card Replacement Procedure
18 Circuit Card Mounting Face Layout of PIM
PIM Accommodating Circuit Card Replacement Procedure
Circuit Card Reference Item Remarks Function Name
Keep MB switch set at UP
1 LC/TRK Circuit Card Replacement Procedure
MUX Card Replacement Procedure
MUX ACT lamp on the new card is red
Refer to -16and Figure
Procedure to Replace Optical Fiber Cable
SDT Card Replacement Procedure
OPE lamp on the PA-SDTA card is steady-green
Procedure to Replace PA-SDTA/PA-SDTB card
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
Green
OPE lamp on the new card is red
OPE lamp on the card goes OFF
PWR Card Replacement Procedure
UNIT/CIRCUIT Card Replacement Procedure
Replacement Procedure Fanu on Topu
Fan Unit Replacement
20 Preparation for Fanu Replacement Fans on Topu
21 How to Replace Fanu Fans on Topu
OFF
Replacement Procedure Fanu in Fan Box
23 How to Replace Fanu Fans in Fan Box
PZ-IO27 PZ-GT16 and PZ-GT13 Isagt
CPR Cooling Fan Replacement
25 Extraction of CPR from LPM
27 How to Remove the Cooling FAN
28 Fuses Used by System
Fuse Replacement
30 Fuse Locations Within System
31 Fuse Location Within Tswm
32 RGU Fuse Blown Fault Flowchart
33 DC -48V Fuse Blown Fault Flowchart
Faulty Item Faulty Situation Reference Section
Fault Repair Procedures
Fan Unit Fault
Fault Repair Procedures
Faulty Situation Reference Section
Line Fault
Line Control
Check Point
Line Fault When Dial Tone DT Cannot Be Heard
Check the faulty line on the MDF
Line Fault When Dialing Results in Wrong Connection
Line Fault When Bell Does Not Ring
When Call Cannot Be Answered and Speech Cannot Be Made
Dterm Fault
END
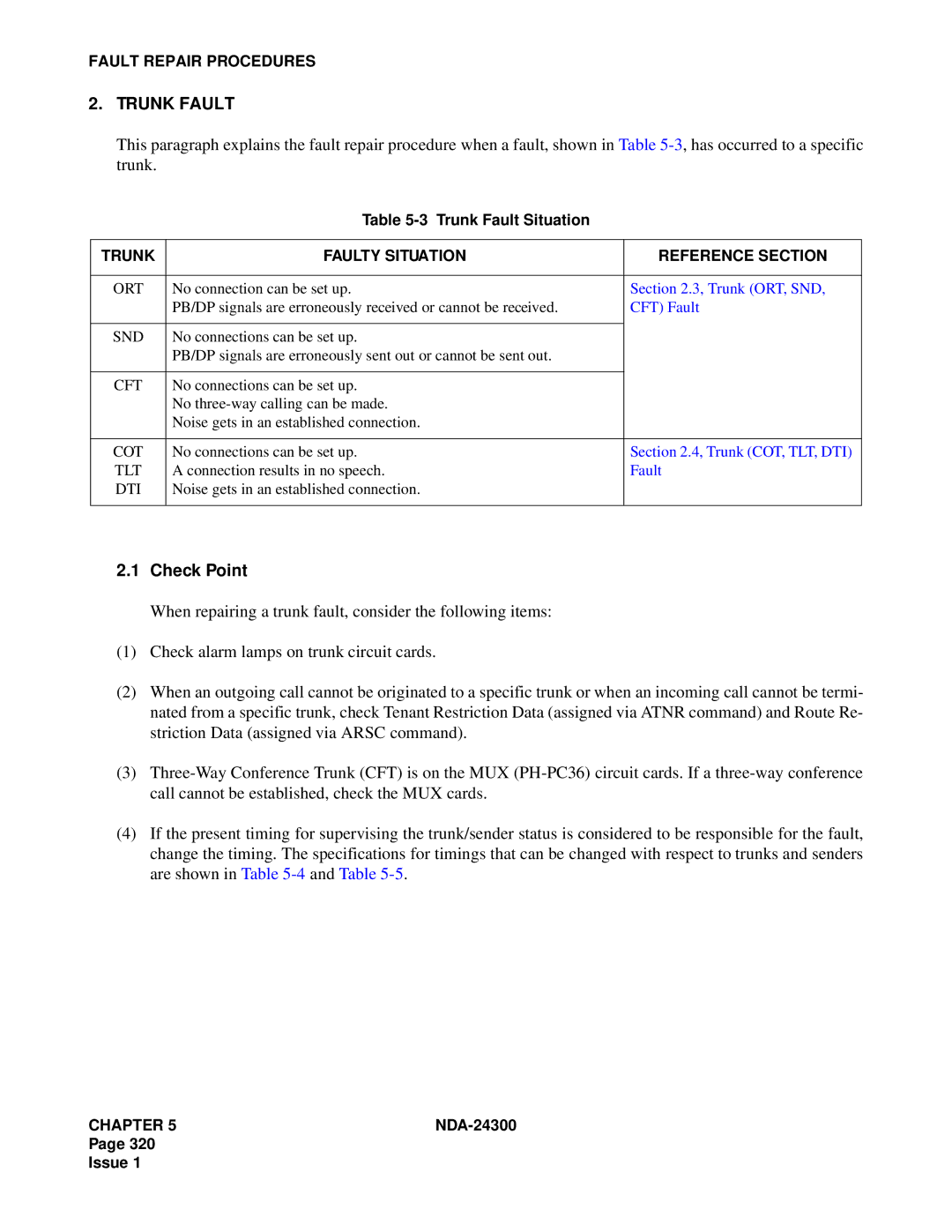
Trunk Faulty Situation Reference Section
Trunk Fault
Timings for Trunks
Timings for Senders
Controlling Trunk Circuit Cards and Speech Path
Trunk Control
Trunk ORT, SND, CFT Fault
Trunk COT, TLT, DTI Fault
Replace the Dterm with a spare
TLT
RA RB TA TB
ATTCON/DESKCON Control
ATTCON/DESKCON Fault
ATT Connector Cabling and Connector Leads Accommodation
ATTCON/DESKCON Fault
ATTCON/DESKCON
Replace the ATTCON/DESKCON with a spare
Fault Situation Reference Section
Unit Fault
Unit Control Block Diagram Dual Configuration
Unit Control Block Diagram Single Configuration
Unit Fault Fault Related to Speech
END
For Single Configuration
END
Unit Fault When Dial Tone DT Cannot Be Heard
Circuit card UP and extract
For Single Configuration
Circuit card UP and extract
Start
Spare, and check it
If the connection is set up, set
Faulty system into Stby
Replace the MUX circuit card with a
Faulty Situation Reference Section
Speech Path TSW System Fault
Speech Path Block Diagram
IMG2 PIM
TSW Write Failure For Dual Configuration
Speech Path System Fault Fault Related to Speech
END
For Single Configuration
END
Speech Path System Fault When Dial Tone DT Cannot Be Heard
Speech Path System Fault Stby Side Has Become Faulty
END
EMA circuit cards
Control System Fault
CPR TSW MUX
CPU Controlling Block Diagram
Lani Isagt
Control System Fault Fault Occurs Intermittently
END
Control System Fault Stby Side Is Faulty
10 Alarm Bus Cable Connections Diagram
IMG
Fault of Alarm Indicating Panel
Alarm Indication Fault
11 Cable Routing for Alarm Indications
Fault That Cannot Be Detected
System configuration
Power Supply Fault
System configuration
16shows the power supply system for PIM
18shows the power supply system for Tswm
Fuse Blown Fault
Circuit Breaker OFF Fault in PWR Supply
Fault Supervision
Fault of Alarm Lamps on PWR Supply
19 Circuit Diagram of Fan Unit and Thermal Unit
FAN Unit Fault
If the voltage is -48
Fan Unit Fault
PIM
20 Dial Tone Connection
Tone Fault
Tone Fault
21 External Hold Tone Supply Block Diagram
22 System Down Fault Repair Sequence
System Down Fault
When Cause for Fault Cannot Be Identified
END
When Faulty Circuit Cards Can Be Assumed From System Message
Ccis Line Control
Common Channel Interoffice Signaling Ccis Line Fault
Check by replacing CCH/CCT card with a spare
Specific CCH/CCT Card Is Faulty
Fault of CCH, DTI and Related Flat Cable
Isdn Line Control
Integrated Service Digital Network Isdn Line Fault
Check by replacing the DCH/PRT card with a spare
Specific DCH/PRT Card Is Faulty
Fault of DCH, DTI, and Related Flat Cable
Start END
Hard Time Clock Fault
This page is for your notes
Kinds of Alarm Indications
Alarm Indications
System Operations
How to Stop Alarm Indications
Alarm Indications on Topu
Lamp Color Function Contents
Automatic Printout to System Message Dedicated Printer
Variable Alarm Indication
Command Command Full Name
Collection of System Messages
Indicating Method
Recovery Procedure
Display on MAT
Indication of Lockout Stations
Rlst
Line Load Control
Operating Procedure
Line Load Control Operations on ATTCON-Cancelling
Cancelling
Line Load Control Key Operations on DESKCON-Setting
11 Line Load Control Indication Deskcon
IOC Line Monitor
Message Content
Line Management
Make-Busy/Make-Busy Cancel of Station and Data Terminal
Class Change and Number Change of Station and Data Terminal
Make-Busy/Make-Busy Cancel of C.O. Line/Tie Line
Station Message Detail Recording System Smdr
Line Management Commands
Transmission Data to Smdr Equipment
Ascii Code Charac Binary Digit Remarks TER HEX
14 Message Format for Outgoing Call
15 Message Format for Incoming Call
16 Message Format for Station-to-Station Call
For an Attendant Orig = 1 Data showing Attendant Number
Data which indicates Call End Time is as follows
Call Start/Call End Time Information
Data which indicates Call Start Time is as follows
Data which indicates the Called Number is as follows
Called Number
Data which indicates the Account Code is as follows
Account Code/Authorization Code
Data which indicates the Authorization Code is as follows
Condition B Information
Route Advance Information
Call Metering Information
Text Format of Centralized Billing Fusion
Kind Contents Outgoing Incoming
System Operations
17 Message Format for Outgoing Call Fusion
18 Message Format for Incoming Call Fusion
19 Message Format for Station-to-Station Call Fusion
Data = 08 Condition B Information
Reference
Data = 02 Calling Party Information Station Number
FPC1
Attcon
Data = 16 Automatic Number Indication
Text sending direction Client Server
Text Format of Smdr TCP/IP Interface
Xxxxx
Type Kind Description Measurement
Traffic Management
Kind of Traffic Measurement
5shows the kinds of traffic measurements
Deskcon
Atrfn
Operating Procedure
Step Asyd Asydn Atrf
21 IPX MAT Menu Display Image Example
Name
Data Output Details on DTFD/DTFDN Command
Full Command Name
Print Log
Data collecting Log
Tool Buttons Collect Data
Stop
Down
Display Area
Save Text File
System Operations
Office Data Preservation
Office Data Management
Office Data Stored Locations
25 Office Data Change Procedure
Office Data Management Procedure
26 Office Data Change Procedure
27 Backup Commands
One-Touch Speed Call Memory Data Management
Individual Speed Calling Data Hddmat command
Data Management Commands
Dcon
Test Operations of Various Kinds
Designated Connection Test Station
Test Item Content of Confirmation Remarks
Designated Connection Test Procedure Register Test Procedure
SRV=SSC, SID=17
Sender Test Procedure
31 3-Party Conference Test Procedure
Party Conference Trunk Test Procedure
32 3-Party Conference Test Connection Diagram
33 Tone Test Procedure/Connection Diagram
Tone Test Procedure
Tone no Kind of Tone Remarks
34 Interrupt Ringing IR Test Procedure/Connection Diagram
Interrupt Ringing IR Test Procedure
35 Trunk Test Procedure
Trunk Test Procedure
36 Trunk Test Connection Diagram
Designated Connection Test DESKCON/ATTCON
Trunk seizure by access code dialing
Spdt
Bad Call Notification
ASYD, SYS1, INDEX86
Routine Diagnosis
Related System Data
INDEX304
INDEX89
INDEX90
Routine Diagnosis Result
Call Forwarding Data Clear See Index
HDD see Index
Belonging Isagt and LANI, are also changed over
System Control Procedures
Does not affect any other systems
37 Switching Network General Block Diagram
38 How to Check LEDs and SW Keys for System Changeover IMG0
39 How to Check LEDs and SW Keys for System Changeover IMG1
IMG 2/3
41 How to Check Status LEDs
Type Operations Remarks
How to Control CPU Block
42 System Block Diagram Switching Network Between CPU and GT
DSP Front View
Manual System Changeover of CPU
45 CPU Changeover via MBR Key
LANIPZ-PC19 ISAGTPZ-GT13
Forced Changeover of CPU
Changeover of Switching Block Type Operations Remarks
How to Control Switching Block
Manual System Changeover of Speech Path System
Dlkc PLO CPR Isagt CPU Lani Isagt PZ-GT13 Lani PZ-PC19
49 TSW/DLKC/MUX in ACT Mode
51 Speech Path System Changeover via Active GT MBR Key
53 Check of Active PLO
Manual System Changeover of PLO
54 PLO in ACT/STBY Mode
55 PLO Changeover via MB Key
Flip the MB key on the PLO card. Refer to Figure
Initialization General
CPU DSP#1 IMG0
System Initialization by Turning on Power Supply
CPU DSP#0
Type Description
System Initialization by Key Operations on Topu
57 Conceptional Diagram of Initial Program Load
58 Related Keys and LEDs for System Initialization
END ON. on Line
Program KEY NON Load
System Data KEY NON Load
DSP of active CPU Is ON. on Line
System Data KEY Load
Program KEY Load
Program KEY Load
System Data KEY → NON Load
Active CPU light steadily green
Lamps on the EMA
System Initialization by Keys on CPU Front Panel
Start EMA PH-PC40
Check ACT0/ACT1
System Initialization by Sinz Command
MB lamp has turned on
Return MB switch to
Previous position after
How to Turn On Whole System
How to Turn ON/OFF Whole System
60 How To Turn OFF the Whole System
How to Turn OFF Whole System
Office Data have been already installed in the HD
Have already been installed in the HD. Office Data has not
Been installed
Procedure #2 see Table
On Line
➀ When Power is OFF ➁ When Power is on OFF Line
Set Sense switch at 1 DM
Line
CPU
Set Sense switch at 2 DM Load Restart on the DSP of active
DM Load Restart on the DSP
Set the Sense switch at
On Line END
This page is for your notes
Flow of Procedures
Routine Maintenance Procedure
Test EQUIPMENT/TOOLS Purpose Remarks
1shows the tools and equipment required for test procedures
Routine Maintenance Procedure
Required Test Equipment and Tools
Time Procedure Reference Section Remarks
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Ambient Conditions in Switch Room Check
Alarm Check
MAT/Printer Check
Collection of System Messages
Display of Locked-out Station
Fan Unit Check
Refer to , Fan Unit Fault, in Chapter
Alarm Tests
Main Power System Check
Trunk RGU Check
Attendant Console Check
ATTCON/DESKCON Check
PM WED
Desk Console Check
System Check
Routine Maintenance Check Lists
Condition And Cause Procedure and Parts Used
Right Connection Test-ATTCON/DESKCON
Test Type Test Item Connection Diagram
Connection test diagrammed to
Trunk/Tie Line
DP/PB
Register/Sender Trunk RST
ORT Function Perform the test by specifying
SND0
RST
Function
Trunk no Sender
Speech Path for Each PIM, and Ringing Generator Unit
Digital Conference Function
Message displays as a result Test
Function Speech Release Remarks Trunk no
PIM1 PIM2 PIM3 PIM4
That the station rings
Mounting Location Check
Module Name Unit Name
Deskcon
Test Item Connection Diagram
Attendant Console ATTCON/DESKCON
Speech Release Deskcon no
Call Termination Call Origination
Attcon
Maintenance Commands
Dteln
Maintenance Commands
Maintenance Commands
Parameters
Allc Assignment of Line Load Control
Functional Outline
Type
Almg Assignment of Alarm Grade Data
LMP
GRD
Atrf Assignment of Traffic Measurement Order
Functional Outline
Bosd Back Up One-Touch Speed Call Memory Data
Result
Cadsd Continuous Assignment of Station Data
Example Input data
STNEND=200
SFC
TEC
=DP/PB
RSC
When Delete is selected in the Type selection list box
Carr Continuous Assignment of Alternative Route Restriction
OG Lgrt
IC Lgrt START/END
IC Lgrt
TKEND=21
When Assign is selected in the Type/KIND selection list box
Catk Continuous Assignment of Trunk Data
Data Entry Result
Tkend
When Delete is selected in the Type/KIND selection list box
Tkstart
TYPE=1 Level →
Details on Trunk Arrangement Type
TYPE=3 Group →
TYPE=5 Unit →
Chapter
Interval Broadcasting Interval
Cbcn Control of Broadcasting for NDM
FPC
FPC of the designated Node Note
Link
Ccse Change of Common Signaling Channel Equipment
CCH Lens
MG=XX, UNIT=X, GROUP=XX
STS1
Cdbu Change of Dch Backup
CNT
STS0
System
Cmod Change of System Mode
Device
=CPU =TSW
Cmwl Control Message Waiting Lamp
Teln
Cmwlt Control Message Waiting Lamps Telephone Number
UGN
=Urgent
Cprs Controlled Alternate PRSCs
Priority Restriction Class N/U
=Normal
Cscl Continuous Change of Station Class
Cstn Continuous Change of Station Number
Dcbd Display of Call Block Entry Data
NDA-24300CHAPTER
CTK
Dcen Display of Connection Trunk Lens Data for LDM
Clens
CRT
Connection Trunk Number 1-4095 Note
Dcon Display of Connection Status
LEN CRT
Connection Route Number 1-1023 Note
Input data New/Old Show Details YES/NO
Dftd Display of System Message Details
Version Issue Date Group 00-23 SP No Digits Ascii 2 digits
Diss Display of Program Issue
Room Class ANX
Dlen Display of Lens Data
Floor
=Ground
=Underground
FLR
Dlsl Display of Lockout Station Lens
This command prints the Lens of stations in lockout state
STN Lens
Dlss Display of Lockout Station Number
Telephone Number max digits
Dlsst Display of Lock Out Station Number Telephone Number
Count
Station Number Max digits
Dltel Display of Telephone Number from Lens for LDM
Telephone Equipment Number
Dntel Display of Telephone Number from Lens for NDM
NID
Network ID Note
Unit U number
Dpkg Display of Setting Port Package
Input Data Module Group MG number
PKG Name
Dpsw Display Package Switch Status
Kind
PMN
Dstn Display of Station Data
Dteln Display of Telephone Number Data for NDM
Shcn
Cpgn
Cpen
Shun
DTF101 Display of Terminal Traffic Data
DTF102 Display of Route Traffic Data
DTF103 Display of Station Peg Count Data
DTF104 Display of Attendant Peg Count Data
DTF105 Display of Route Peg Count Data
DTF201 Display of Service Peg Count Data
DTF301 Display of UCD Route Peg Count Data
DTF302 Display of UCD Group Peg Count Data
DTF303 Display of Station Peg Count Data
DTF501 Display of Attendant Answering Peg Count Data
DTF601 Display of Connection Route Peg Count Data
DTF602 Display of Connection Route Traffic Data
DTF101N Display of Terminal Traffic Data for Fusion Network
DTF102N Display of Route Traffic Data for Fusion Network
DTF103N Display of Station Peg Count Data for Fusion Network
Functional Outline
DTF105N Display of Route Peg Count Data for Fusion Network
DTF201N Display of Service Peg Count Data for Fusion Network
Functional Outline
Functional Outline
Functional Outline
Functional Outline
Functional Outline
Functional Outline
Data Install Procedure
Flinst File Install
HFD0/HFD1
Hddfdd Data Control Between HDD and FDD
Input data System Select
File Name Select Auto Verify Afterward
Hddmat Data Control Between HDD and MAT
Hddmatn Data Control Between HDD and MAT for NDM
Hdfp HDD Format of PBX
=Make Busy Outgoing
Mbct Make Busy of Connection Trunk for LDM
Make Busy Information 0/1
=Make Busy
Mble Make Busy of Lens
Input data MG Unit Group Display data =Make Idle =Make Busy
Mbpm Make Busy of Port Microprocessor
Mbrt Make Busy of Route
Make Idle
Mbrtlr Make Busy of Route-Logical Route Number
Lgrt
Mand as to the Internal route number and its meaning. Note
Port no
Mbsm Make Busy of System Message Printout
Mbst Make Busy of Station
This command assigns the Idle/Busy status of stations
Make Busy/Make Idle Display Data
Exit Click to exit this command
Mbstt Make Busy of Station Telephone Number
Mbtc Make Busy of Trunk-Continuous
=Make Busy Bothway Note
Mbtclr Make Busy of Trunk-Continuous-Logical Route Number
Logical route number allocated to the Route Number. Note
Trunk Number Note
Mbtk Make Busy of Trunk
This command assigns the Idle/Busy status of trunks
Mbtklr Make Busy Trunk-Logical Route Number
Memhdd Data Control Between Memory and HDD
Input data Direction Select MEM to HDD
Memhddn Data Control Between Memory and HDD for NDM
FCH Number
Mfch Make Busy of Fcch
Fchn
Nating Port Microprocessor to MAT
Pmbu Port Microprocessor Back Up
This command clears the fault indications
Ralm Release Alarm
OK/NG
Ralmn Release Alarm for NDM
Status Result of releasing the alarm
Information
Rlst Release Station/Trunk
=LENS
External/Internal Route Number Trunk Number
Rlstt Release of Station/Trunk Telephone Number
Telephone Number Trunk
Connection Trunk
PCN
ERN
GRN
CSN/ZTN
=System Initialize Office Data Load & System Initialize
Sinz System Initialization
Kind of Initialization
=System Initialize
Type 1 By MG
Spts Scanning of Port Status
Exit
Type of Circuit Card Function Name
Port Status Report MG, Unit Display
Type 2 By MG, Unit
= Unassigned Port
Type 3 By MG, Unit, Group
Display of Scanning by Designating Group
Idle = Idle
Trunk Class
TCL
Srts Scanning of Route Status
Number of Idle/Busy TK
Srtslr Scanning of Route Status-Logical Route Number
Interval Interval Time of two scan Display Data
Route of Route Number
Area
Xhfd X-RAY HD or FDD Diagnosis
Function
Message
Fault Drive
Fault Sector