Placement guidelines for the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 65
returns. If the wireless handset is configured to use ESSID of the new WLAN, it automatically discovers the ESSID of the APs operating in broadcast mode.
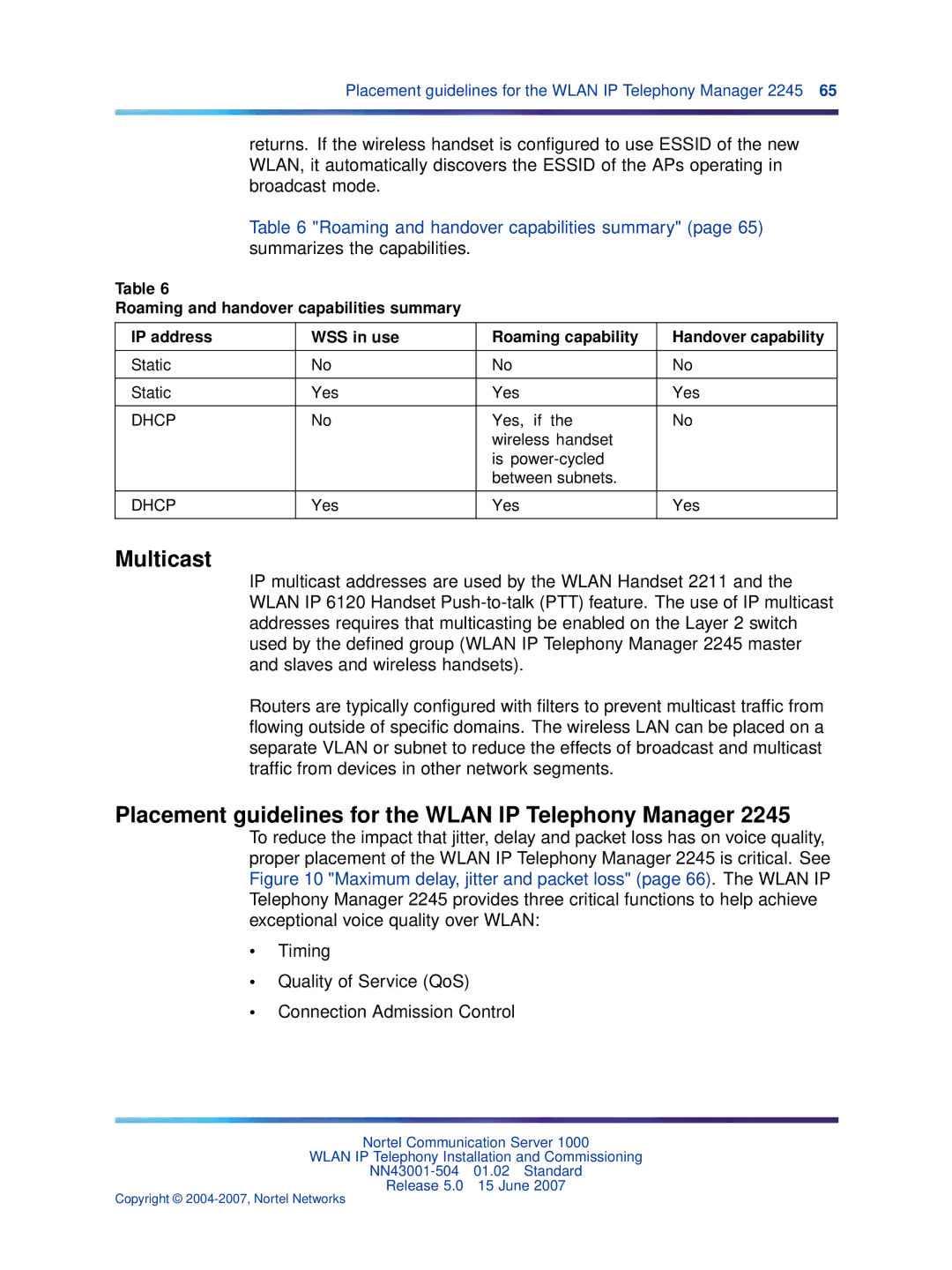
Table 6 "Roaming and handover capabilities summary" (page 65) summarizes the capabilities.
Table 6
Roaming and handover capabilities summary
IP address | WSS in use | Roaming capability | Handover capability |
|
|
|
|
Static | No | No | No |
|
|
|
|
Static | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
|
|
DHCP | No | Yes, if the | No |
|
| wireless handset |
|
|
| is |
|
|
| between subnets. |
|
|
|
|
|
DHCP | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
|
|
Multicast
IP multicast addresses are used by the WLAN Handset 2211 and the WLAN IP 6120 Handset
Routers are typically configured with filters to prevent multicast traffic from flowing outside of specific domains. The wireless LAN can be placed on a separate VLAN or subnet to reduce the effects of broadcast and multicast traffic from devices in other network segments.
Placement guidelines for the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245
To reduce the impact that jitter, delay and packet loss has on voice quality, proper placement of the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 is critical. See Figure 10 "Maximum delay, jitter and packet loss" (page 66). The WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 provides three critical functions to help achieve exceptional voice quality over WLAN:
•Timing
•Quality of Service (QoS)
•Connection Admission Control
Nortel Communication Server 1000
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Release 5.0 15 June 2007