NAT 87
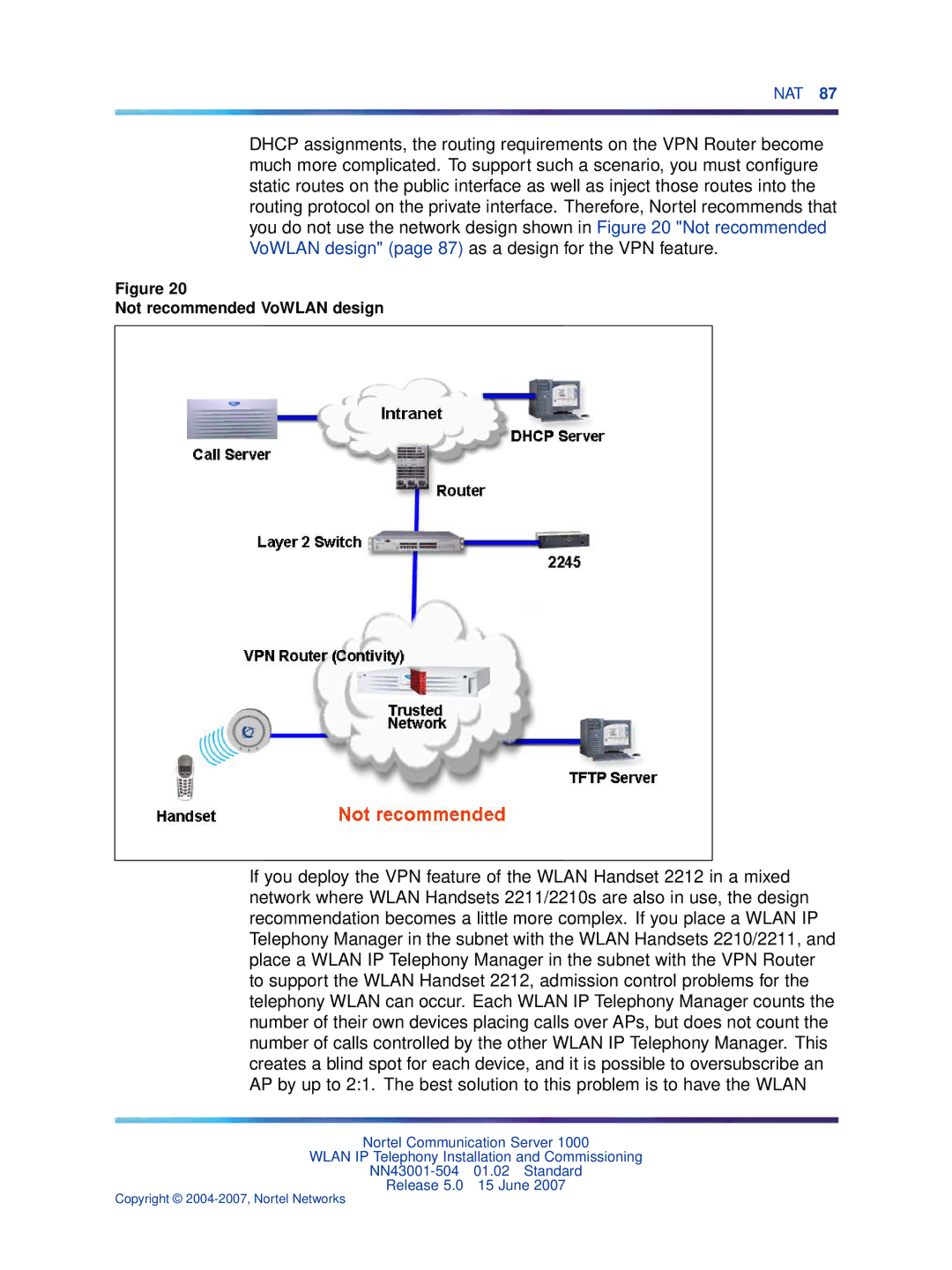
DHCP assignments, the routing requirements on the VPN Router become much more complicated. To support such a scenario, you must configure static routes on the public interface as well as inject those routes into the routing protocol on the private interface. Therefore, Nortel recommends that you do not use the network design shown in Figure 20 "Not recommended VoWLAN design" (page 87) as a design for the VPN feature.
Figure 20
Not recommended VoWLAN design
If you deploy the VPN feature of the WLAN Handset 2212 in a mixed network where WLAN Handsets 2211/2210s are also in use, the design recommendation becomes a little more complex. If you place a WLAN IP Telephony Manager in the subnet with the WLAN Handsets 2210/2211, and place a WLAN IP Telephony Manager in the subnet with the VPN Router to support the WLAN Handset 2212, admission control problems for the telephony WLAN can occur. Each WLAN IP Telephony Manager counts the number of their own devices placing calls over APs, but does not count the number of calls controlled by the other WLAN IP Telephony Manager. This creates a blind spot for each device, and it is possible to oversubscribe an AP by up to 2:1. The best solution to this problem is to have the WLAN
Nortel Communication Server 1000
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Release 5.0 15 June 2007