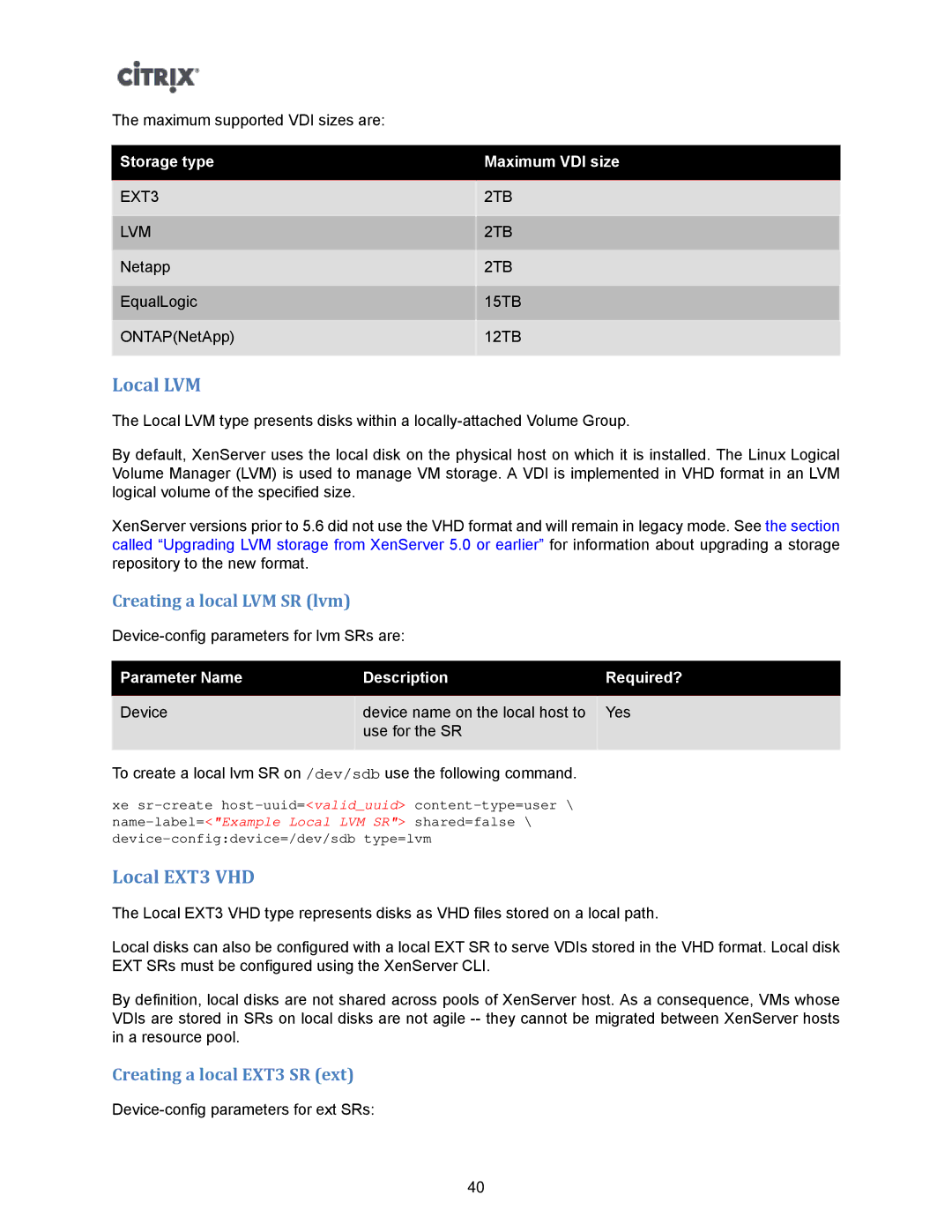
The maximum supported VDI sizes are:
Storage type | Maximum VDI size |
|
|
EXT3 | 2TB |
|
|
LVM | 2TB |
|
|
Netapp | 2TB |
|
|
EqualLogic | 15TB |
|
|
ONTAP(NetApp) | 12TB |
|
|
Local LVM
The Local LVM type presents disks within a
By default, XenServer uses the local disk on the physical host on which it is installed. The Linux Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is used to manage VM storage. A VDI is implemented in VHD format in an LVM logical volume of the specified size.
XenServer versions prior to 5.6 did not use the VHD format and will remain in legacy mode. See the section called “Upgrading LVM storage from XenServer 5.0 or earlier” for information about upgrading a storage repository to the new format.
Creating a local LVM SR (lvm)
Parameter Name | Description | Required? |
|
|
|
Device | device name on the local host to | Yes |
| use for the SR |
|
|
|
|
To create a local lvm SR on /dev/sdb use the following command.
xe
Local EXT3 VHD
The Local EXT3 VHD type represents disks as VHD files stored on a local path.
Local disks can also be configured with a local EXT SR to serve VDIs stored in the VHD format. Local disk EXT SRs must be configured using the XenServer CLI.
By definition, local disks are not shared across pools of XenServer host. As a consequence, VMs whose VDIs are stored in SRs on local disks are not agile
Creating a local EXT3 SR (ext)
40