Network 1 |
Network 3 |
Router |
Network n |
Network 2 |
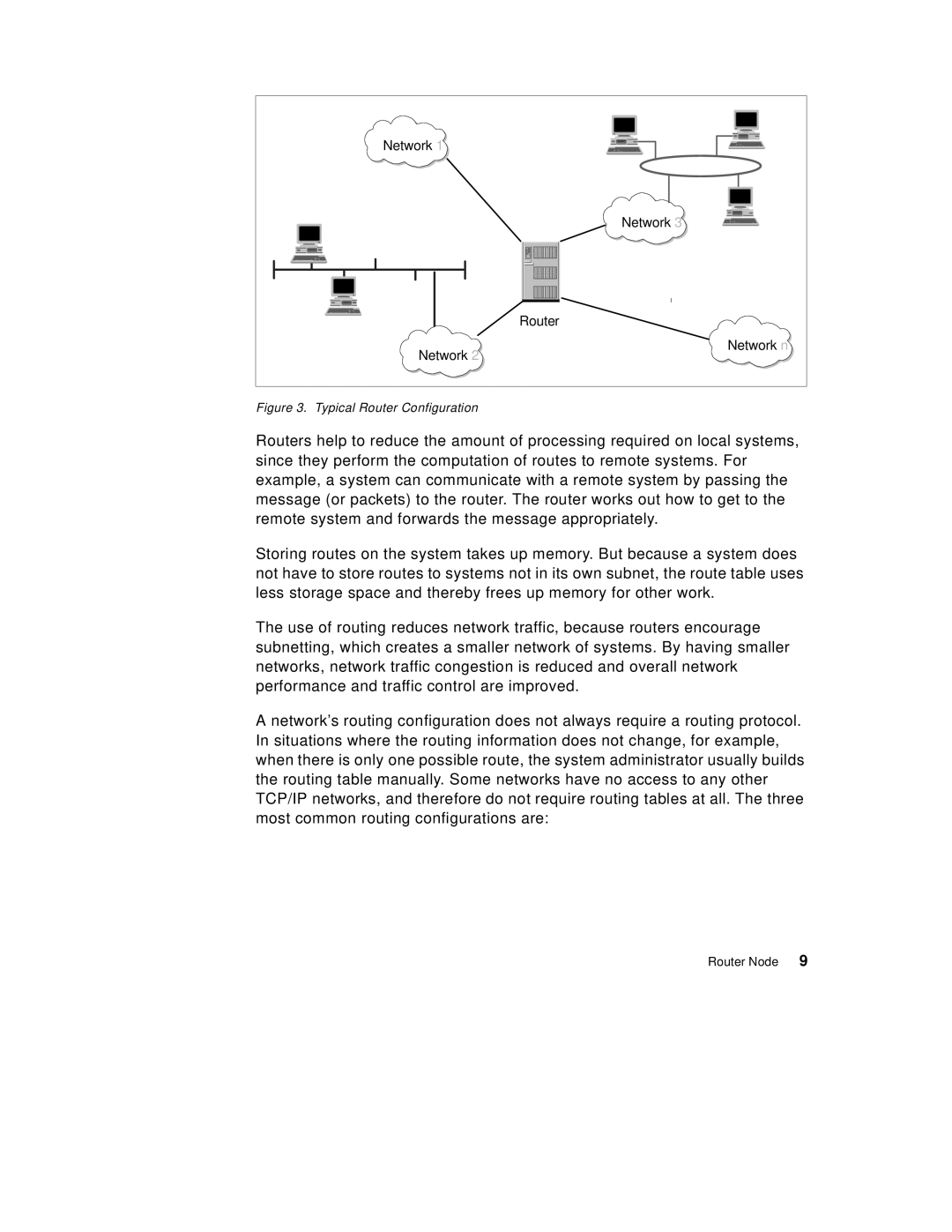
Figure 3. Typical Router Configuration
Routers help to reduce the amount of processing required on local systems, since they perform the computation of routes to remote systems. For example, a system can communicate with a remote system by passing the message (or packets) to the router. The router works out how to get to the remote system and forwards the message appropriately.
Storing routes on the system takes up memory. But because a system does not have to store routes to systems not in its own subnet, the route table uses less storage space and thereby frees up memory for other work.
The use of routing reduces network traffic, because routers encourage subnetting, which creates a smaller network of systems. By having smaller networks, network traffic congestion is reduced and overall network performance and traffic control are improved.
A network’s routing configuration does not always require a routing protocol. In situations where the routing information does not change, for example, when there is only one possible route, the system administrator usually builds the routing table manually. Some networks have no access to any other TCP/IP networks, and therefore do not require routing tables at all. The three most common routing configurations are:
Router Node 9