The second case has proven to be very expensive as well. The RS/6000 SP node was not designed for routing. It is not a
•It takes many CPU cycles to process routing. The CPU is not a dedicated router and is very inefficient when used to route IP traffic (this processing can result in usage of up to 90%).
•It takes a lot of memory to store route tables. The memory on the RS/6000 SP node is typically more expensive than router memory.
The CPU on a node can only drive the system I/O bus at less than 80 megabytes per second, which is less than what a
For these reasons, the performance of routers in handling IP traffic from remote systems to the RS/6000 SP nodes was limited.
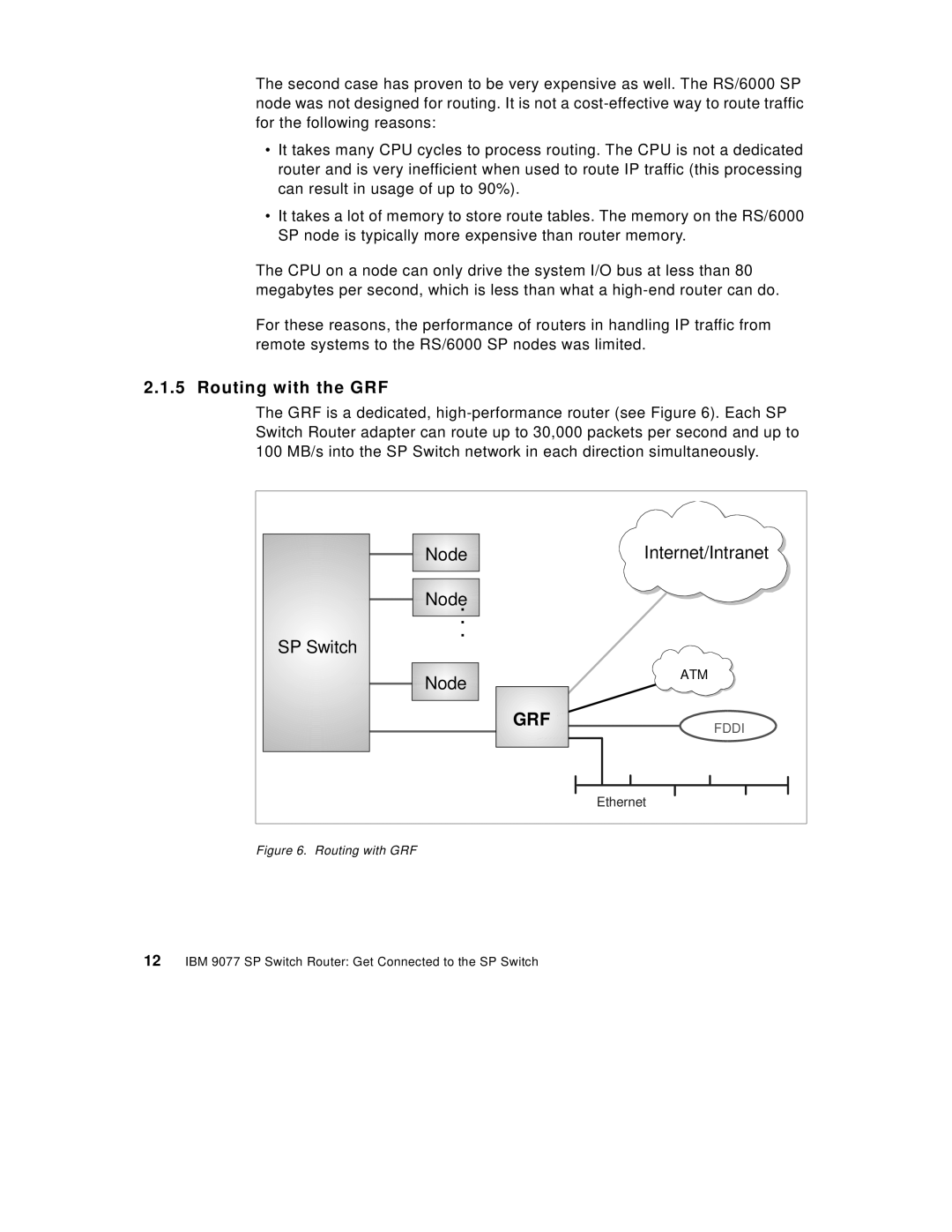
2.1.5 Routing with the GRF
The GRF is a dedicated,
Node |
| Internet/Intranet |
Node |
|
|
. . . |
|
|
SP Switch |
|
|
Node |
| ATM |
|
| |
| GRF | FDDI |
|
| |
|
| Ethernet |