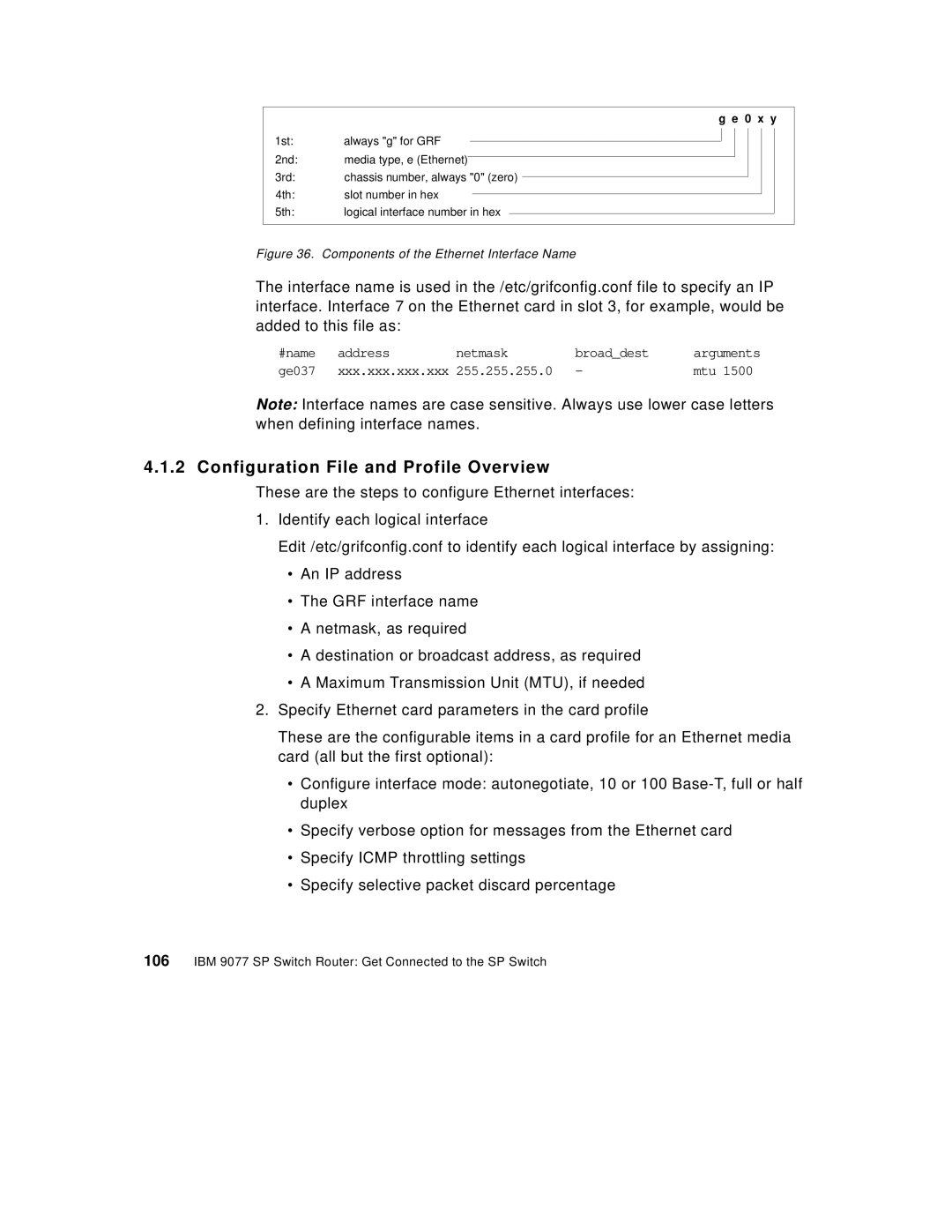
g e 0 x y
1st: | always "g" for GRF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
2nd: | media type, e (Ethernet) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
3rd: | chassis number, always "0" (zero) |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
4th: | slot number in hex |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
5th: | logical interface number in hex |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Figure 36. Components of the Ethernet Interface Name
The interface name is used in the /etc/grifconfig.conf file to specify an IP interface. Interface 7 on the Ethernet card in slot 3, for example, would be added to this file as:
#name | address | netmask | broad_dest | arguments |
ge037 | xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx | 255.255.255.0 | - | mtu 1500 |
Note: Interface names are case sensitive. Always use lower case letters when defining interface names.
4.1.2 Configuration File and Profile Overview
These are the steps to configure Ethernet interfaces:
1.Identify each logical interface
Edit /etc/grifconfig.conf to identify each logical interface by assigning:
•An IP address
•The GRF interface name
•A netmask, as required
•A destination or broadcast address, as required
•A Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU), if needed
2.Specify Ethernet card parameters in the card profile
These are the configurable items in a card profile for an Ethernet media card (all but the first optional):
•Configure interface mode: autonegotiate, 10 or 100
•Specify verbose option for messages from the Ethernet card
•Specify ICMP throttling settings
•Specify selective packet discard percentage