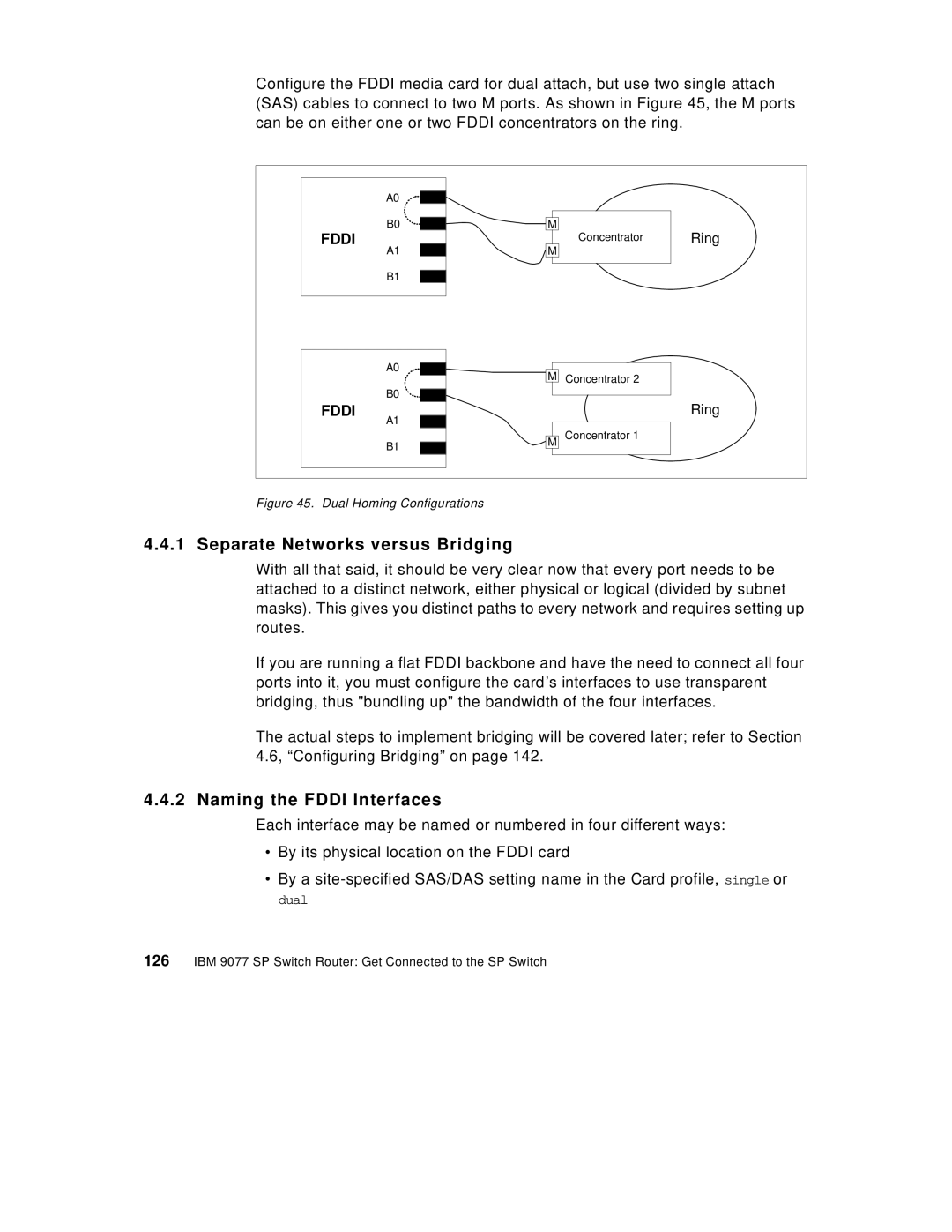
Configure the FDDI media card for dual attach, but use two single attach (SAS) cables to connect to two M ports. As shown in Figure 45, the M ports can be on either one or two FDDI concentrators on the ring.
A0
B0
FDDI
A1
B1
A0
B0
FDDI
A1
B1
M
Concentrator | Ring |
M
M Concentrator 2
Ring
M Concentrator 1
Figure 45. Dual Homing Configurations
4.4.1 Separate Networks versus Bridging
With all that said, it should be very clear now that every port needs to be attached to a distinct network, either physical or logical (divided by subnet masks). This gives you distinct paths to every network and requires setting up routes.
If you are running a flat FDDI backbone and have the need to connect all four ports into it, you must configure the card’s interfaces to use transparent bridging, thus "bundling up" the bandwidth of the four interfaces.
The actual steps to implement bridging will be covered later; refer to Section 4.6, “Configuring Bridging” on page 142.
4.4.2 Naming the FDDI Interfaces
Each interface may be named or numbered in four different ways:
•By its physical location on the FDDI card
•By a