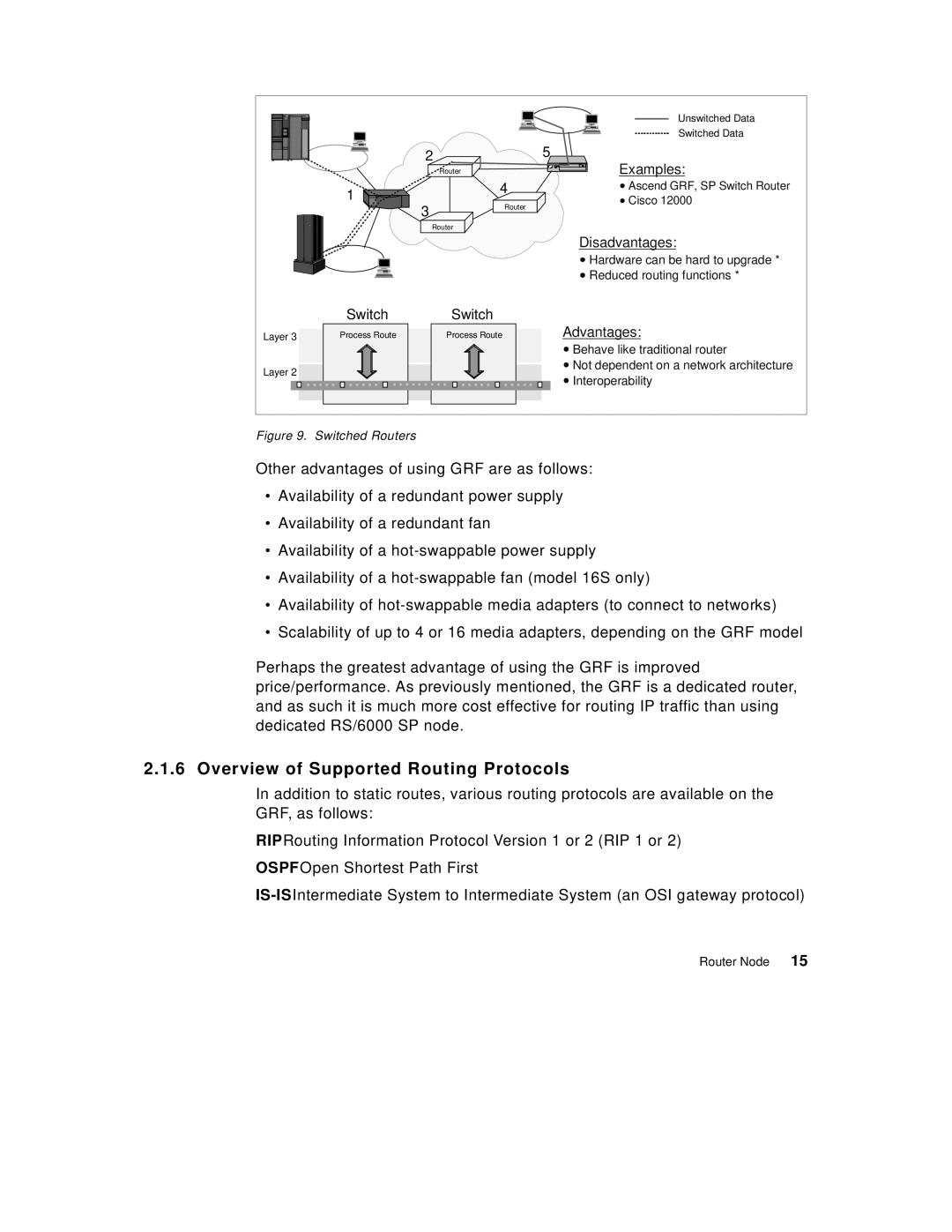
| Unswitched Data |
| Switched Data |
2 | 5 |
|
|
| Router | Examples: |
| 1 |
| 4 | Ascend GRF, SP Switch Router |
|
| Router | Cisco 12000 | |
|
| 3 | ||
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| Router |
|
|
|
|
| Disadvantages: |
|
|
|
| Hardware can be hard to upgrade * |
|
|
|
| Reduced routing functions * |
| Switch |
| Switch |
|
Layer 3 | Process Route |
| Process Route | Advantages: |
|
|
|
| Behave like traditional router |
Layer 2 | Not dependent on a network architecture | |||
Interoperability | ||||
Figure 9. Switched Routers
Other advantages of using GRF are as follows:
•Availability of a redundant power supply
•Availability of a redundant fan
•Availability of a
•Availability of a
•Availability of
•Scalability of up to 4 or 16 media adapters, depending on the GRF model
Perhaps the greatest advantage of using the GRF is improved price/performance. As previously mentioned, the GRF is a dedicated router, and as such it is much more cost effective for routing IP traffic than using dedicated RS/6000 SP node.
2.1.6 Overview of Supported Routing Protocols
In addition to static routes, various routing protocols are available on the GRF, as follows:
RIPRouting Information Protocol Version 1 or 2 (RIP 1 or 2)
OSPFOpen Shortest Path First
Router Node 15