4-4 Administrator’s Handbook
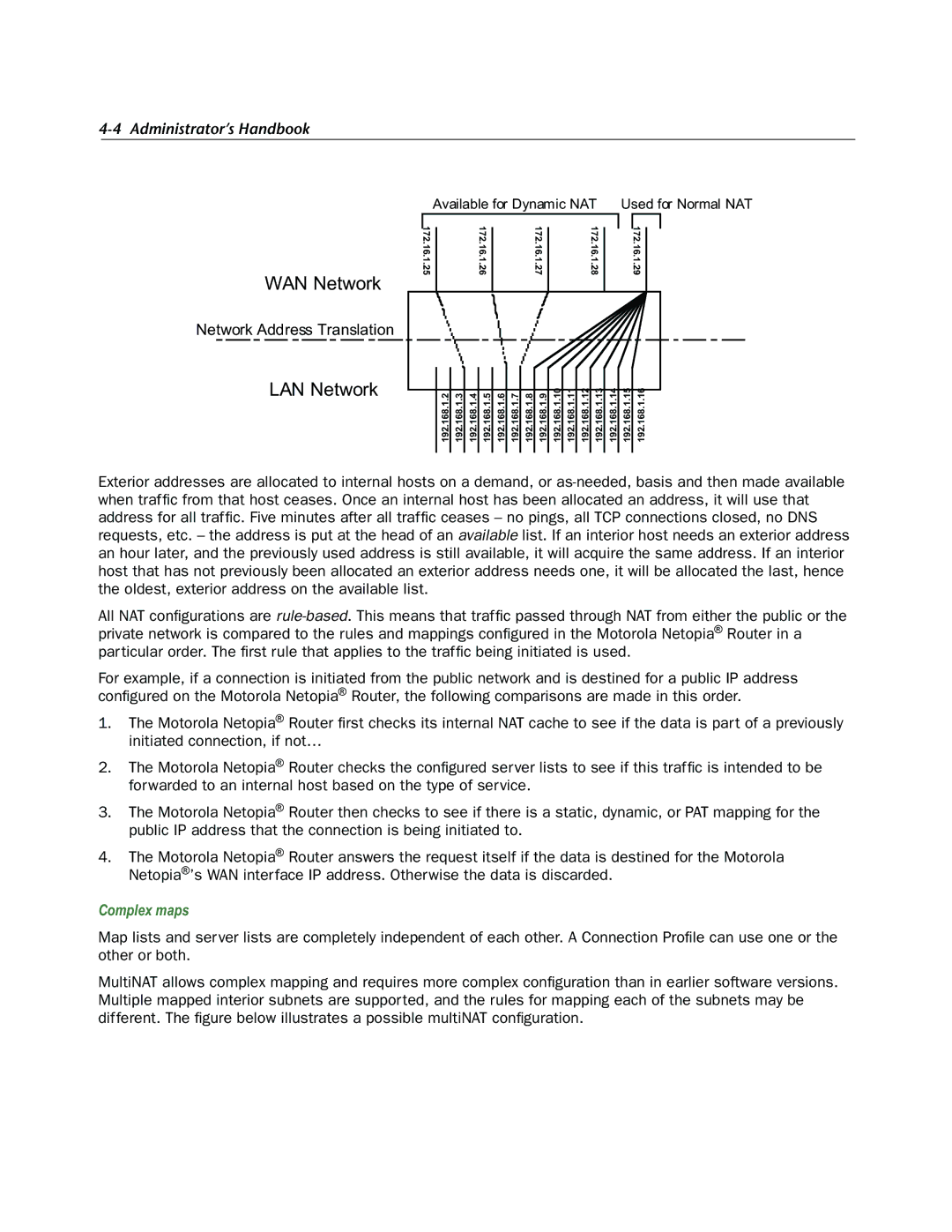
WAN Network
Network Address Translation
LAN Network
|
| Available for Dynamic NAT | Used for Normal NAT | |||||||
| 172.16.1.25 | 172.16.1.26 | 172.16.1.27 | 172.16.1.28 |
|
|
| 172.16.1.29 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
192.168.1.2 | 192.168.1.3 | 192.168.1.4 | 192.168.1.5 | 192.168.1.6 | 192.168.1.7 | 192.168.1.8 | 192.168.1.9 | 192.168.1.10 | 192.168.1.11 | 192.168.1.12 | 192.168.1.13 | 192.168.1.14 | 192.168.1.15 | 192.168.1.16 |
Exterior addresses are allocated to internal hosts on a demand, or
All NAT configurations are
For example, if a connection is initiated from the public network and is destined for a public IP address configured on the Motorola Netopia® Router, the following comparisons are made in this order.
1.The Motorola Netopia® Router first checks its internal NAT cache to see if the data is part of a previously initiated connection, if not…
2.The Motorola Netopia® Router checks the configured server lists to see if this traffic is intended to be forwarded to an internal host based on the type of service.
3.The Motorola Netopia® Router then checks to see if there is a static, dynamic, or PAT mapping for the public IP address that the connection is being initiated to.
4.The Motorola Netopia® Router answers the request itself if the data is destined for the Motorola Netopia®’s WAN interface IP address. Otherwise the data is discarded.
Complex maps
Map lists and server lists are completely independent of each other. A Connection Profile can use one or the other or both.
MultiNAT allows complex mapping and requires more complex configuration than in earlier software versions. Multiple mapped interior subnets are supported, and the rules for mapping each of the subnets may be different. The figure below illustrates a possible multiNAT configuration.