Chapter 4 - Operation and Administration
NOTE
The SNR measurement at the AU is accurate only when receiving transmissions from the applicable SU. If necessary, use the Ping Test utility in the Site Survey menu to verify data transmission.
When the Adaptive Modulation Algorithm is disabled, this parameter will serve to determine Fixed Modulation Level used for transmissions.
The minimum and maximum values for the Maximum Modulation Level are defined by the
VL 900 SUs with HW revision F use a default maximum modulation level of 5. For the rest of the units, the default is the highest supported modulation level (8 for all units with HW revision B or higher, 7 for units with HW revision A).
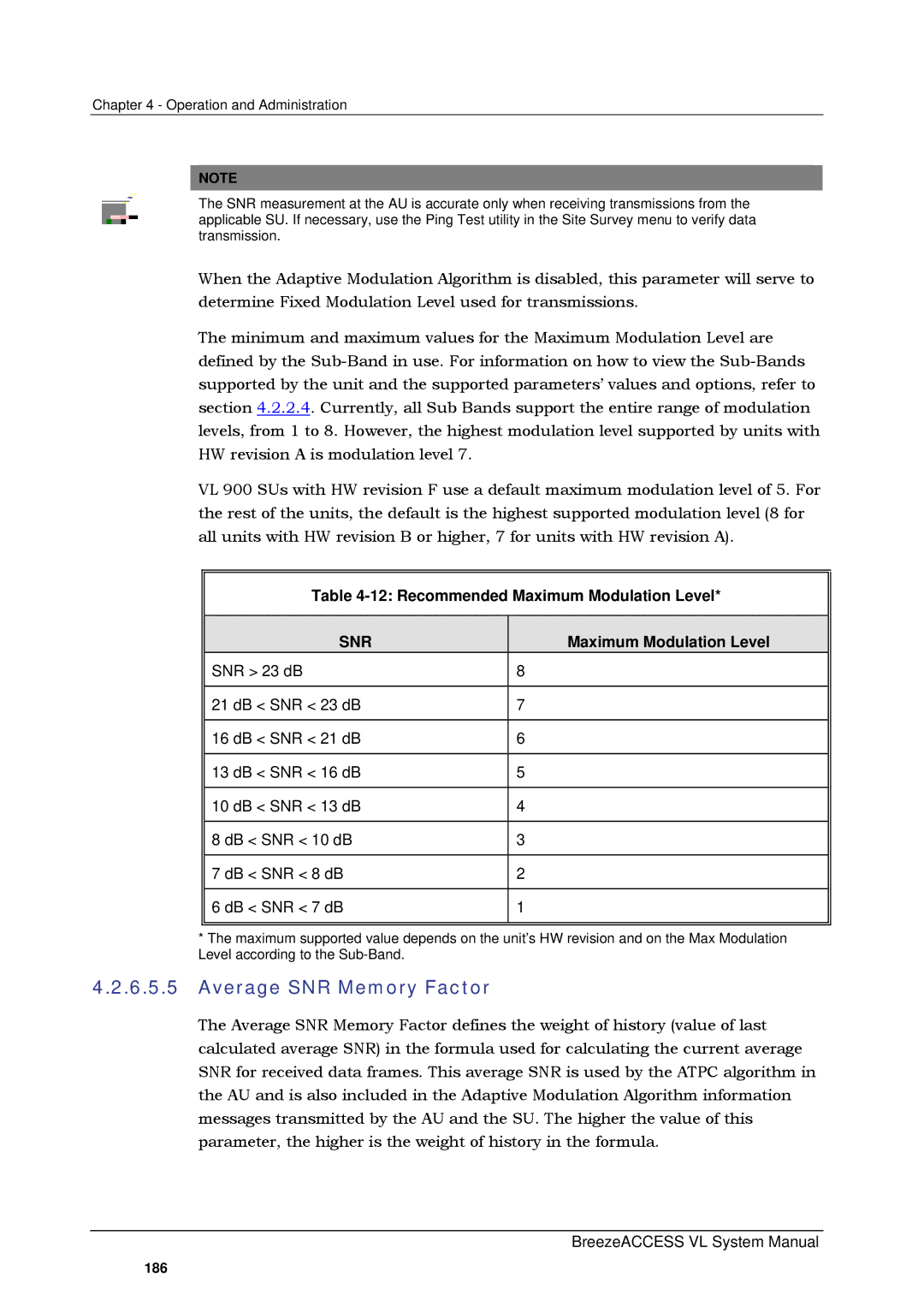
Table 4-12: Recommended Maximum Modulation Level*
SNR | Maximum Modulation Level | |
SNR > 23 dB | 8 | |
|
| |
21 dB < SNR < 23 dB | 7 | |
|
| |
16 dB < SNR < 21 dB | 6 | |
|
| |
13 dB < SNR < 16 dB | 5 | |
|
| |
10 dB < SNR < 13 dB | 4 | |
|
| |
8 dB < SNR < 10 dB | 3 | |
|
| |
7 dB < SNR < 8 dB | 2 | |
|
| |
6 dB < SNR < 7 dB | 1 | |
|
|
*The maximum supported value depends on the unit’s HW revision and on the Max Modulation Level according to the
4.2.6.5.5Average SNR Memory Factor
The Average SNR Memory Factor defines the weight of history (value of last calculated average SNR) in the formula used for calculating the current average SNR for received data frames. This average SNR is used by the ATPC algorithm in the AU and is also included in the Adaptive Modulation Algorithm information messages transmitted by the AU and the SU. The higher the value of this parameter, the higher is the weight of history in the formula.
BreezeACCESS VL System Manual
186