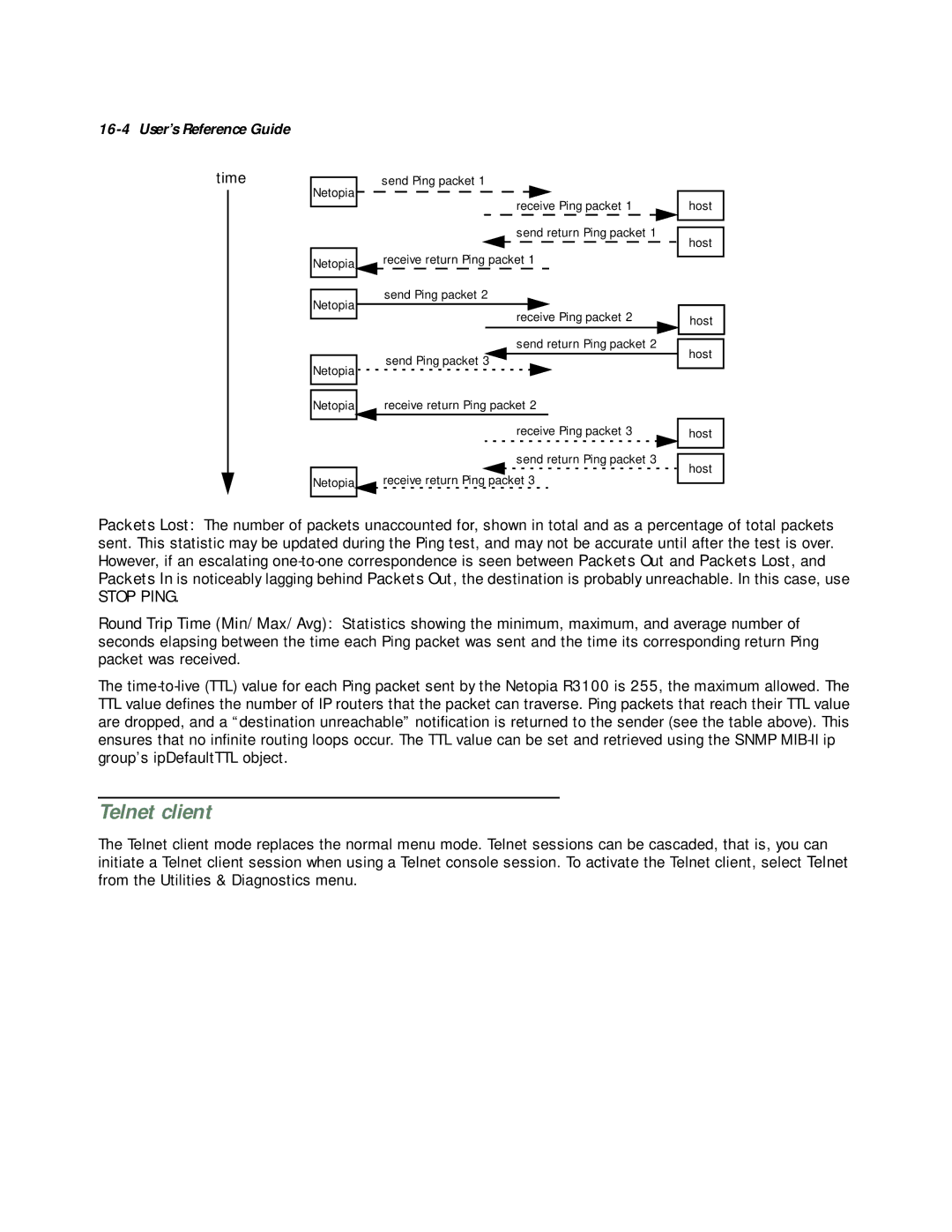
16-4 User’s Reference Guide
time
send Ping packet 1
Netopia ![]()
![]()
receive Ping packet 1
send return Ping packet 1
Netopia![]() receive return Ping packet 1
receive return Ping packet 1
send Ping packet 2
Netopia
|
| receive Ping packet 2 | ||
| ||||
| send Ping packet 3 | send return Ping packet 2 |
| |
|
| |||
|
|
| ||
Netopia |
|
| ||
receive return Ping packet 2 | ||||
| ||||
| ||||
Netopia | ||||
|
| receive Ping packet 3 | ||
|
| |||
|
| send return Ping packet 3 | ||
Netopia | receive return Ping packet 3 | |||
|
|
|
| |
host
host
host
host
host
host
Packets Lost: The number of packets unaccounted for, shown in total and as a percentage of total packets sent. This statistic may be updated during the Ping test, and may not be accurate until after the test is over. However, if an escalating
STOP PING.
Round Trip Time (Min/Max/Avg): Statistics showing the minimum, maximum, and average number of seconds elapsing between the time each Ping packet was sent and the time its corresponding return Ping packet was received.
The
Telnet client
The Telnet client mode replaces the normal menu mode. Telnet sessions can be cascaded, that is, you can initiate a Telnet client session when using a Telnet console session. To activate the Telnet client, select Telnet from the Utilities & Diagnostics menu.