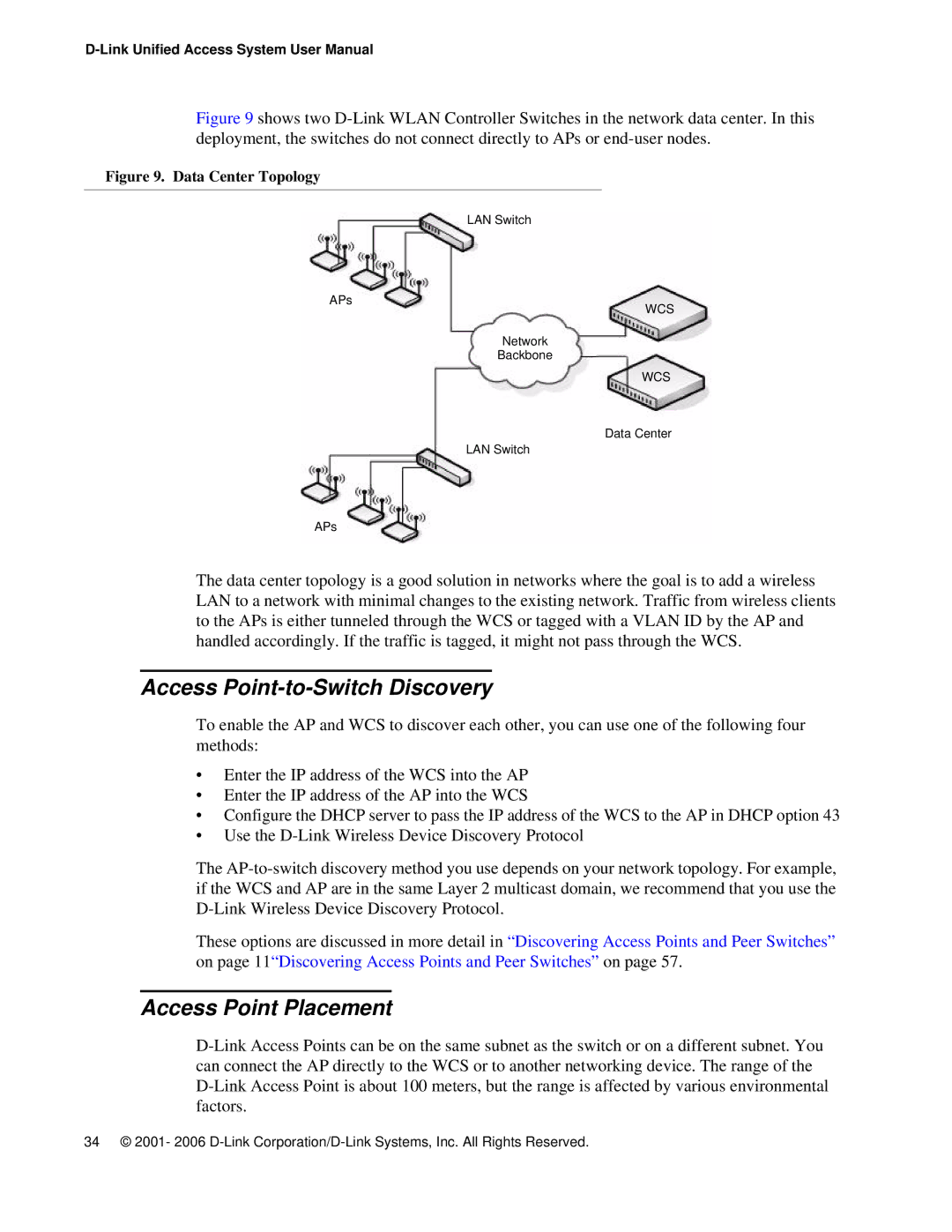
Figure 9 shows two D-Link WLAN Controller Switches in the network data center. In this deployment, the switches do not connect directly to APs or end-user nodes.
Figure 9. Data Center Topology
LAN Switch
APs
WCS
Network
Backbone
WCS
Data Center
LAN Switch
APs
The data center topology is a good solution in networks where the goal is to add a wireless LAN to a network with minimal changes to the existing network. Traffic from wireless clients to the APs is either tunneled through the WCS or tagged with a VLAN ID by the AP and handled accordingly. If the traffic is tagged, it might not pass through the WCS.
Access Point-to-Switch Discovery
To enable the AP and WCS to discover each other, you can use one of the following four methods:
•Enter the IP address of the WCS into the AP
•Enter the IP address of the AP into the WCS
•Configure the DHCP server to pass the IP address of the WCS to the AP in DHCP option 43
•Use the
The
These options are discussed in more detail in “Discovering Access Points and Peer Switches” on page 11“Discovering Access Points and Peer Switches” on page 57.
Access Point Placement
34 © 2001- 2006