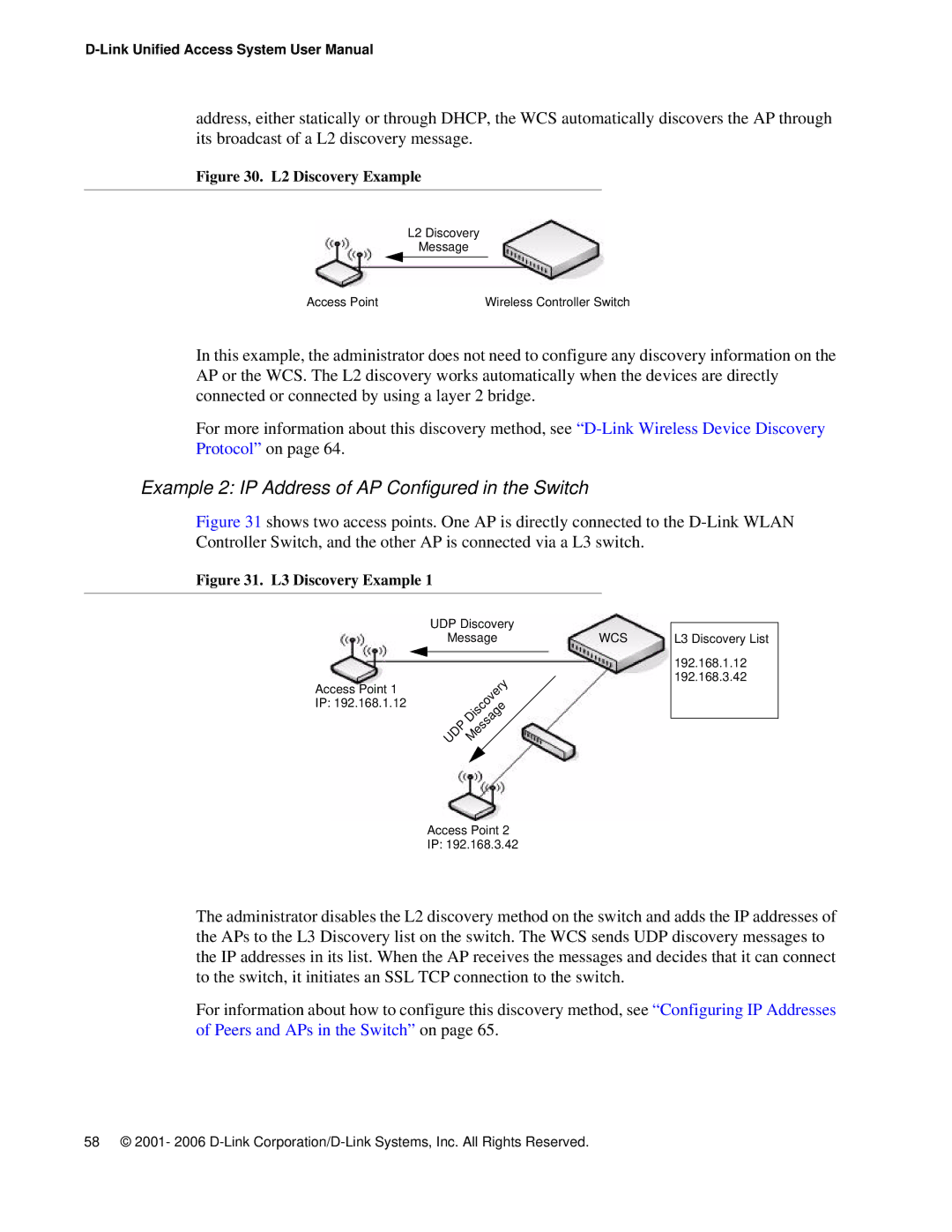
address, either statically or through DHCP, the WCS automatically discovers the AP through its broadcast of a L2 discovery message.
Figure 30. L2 Discovery Example
L2 Discovery
Message
Access Point | Wireless Controller Switch |
In this example, the administrator does not need to configure any discovery information on the AP or the WCS. The L2 discovery works automatically when the devices are directly connected or connected by using a layer 2 bridge.
For more information about this discovery method, see
Example 2: IP Address of AP Configured in the Switch
Figure 31 shows two access points. One AP is directly connected to the D-Link WLAN Controller Switch, and the other AP is connected via a L3 switch.
Figure 31. L3 Discovery Example 1
Access Point 1 IP: 192.168.1.12
UDP Discovery
MessageWCS
|
|
|
| y |
|
|
| r | |
|
| ove |
| |
| Disc | e | ||
P | ag |
| ||
| ss |
|
| |
UD | e |
|
| |
M |
|
|
| |
L3 Discovery List
192.168.1.12
192.168.3.42
Access Point 2
IP: 192.168.3.42
The administrator disables the L2 discovery method on the switch and adds the IP addresses of the APs to the L3 Discovery list on the switch. The WCS sends UDP discovery messages to the IP addresses in its list. When the AP receives the messages and decides that it can connect to the switch, it initiates an SSL TCP connection to the switch.
For information about how to configure this discovery method, see “Configuring IP Addresses of Peers and APs in the Switch” on page 65.
58 © 2001- 2006