HS-100 / HS-100W
Version 10/2005
Copyright 2004 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation
Disclaimer
Trademarks
Certifications
Information for Canadian Users
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
Online Registration
Customer Support
Table of Contents
III
11-1
Viii
27.1
Page
List of Figures
Xiv List of Figures
10-1
Xvi List of Figures
Xvii
Xviii List of Figures
List of Tables
List of Tables
20-3
Xxii List of Tables
Related Documentation
User’s Guide Feedback
¾ ZyXEL Glossary and Web Site
Syntax Conventions
Graphics Icons Key
Dslam
HomeSafe User’s Guide Preface Xxv
Part
Page
HomeSafe Features
Physical Features
Non-Physical Features
Getting to Know Your HomeSafe
Content Filtering
Brute-Force Password Guessing Protection
802.11b Wireless LAN Standard HS-100W only
Firewall
Packet Filtering
Universal Plug and Play UPnP
Call Scheduling
PPPoE
Dhcp Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Upgrade HomeSafe Firmware via LAN
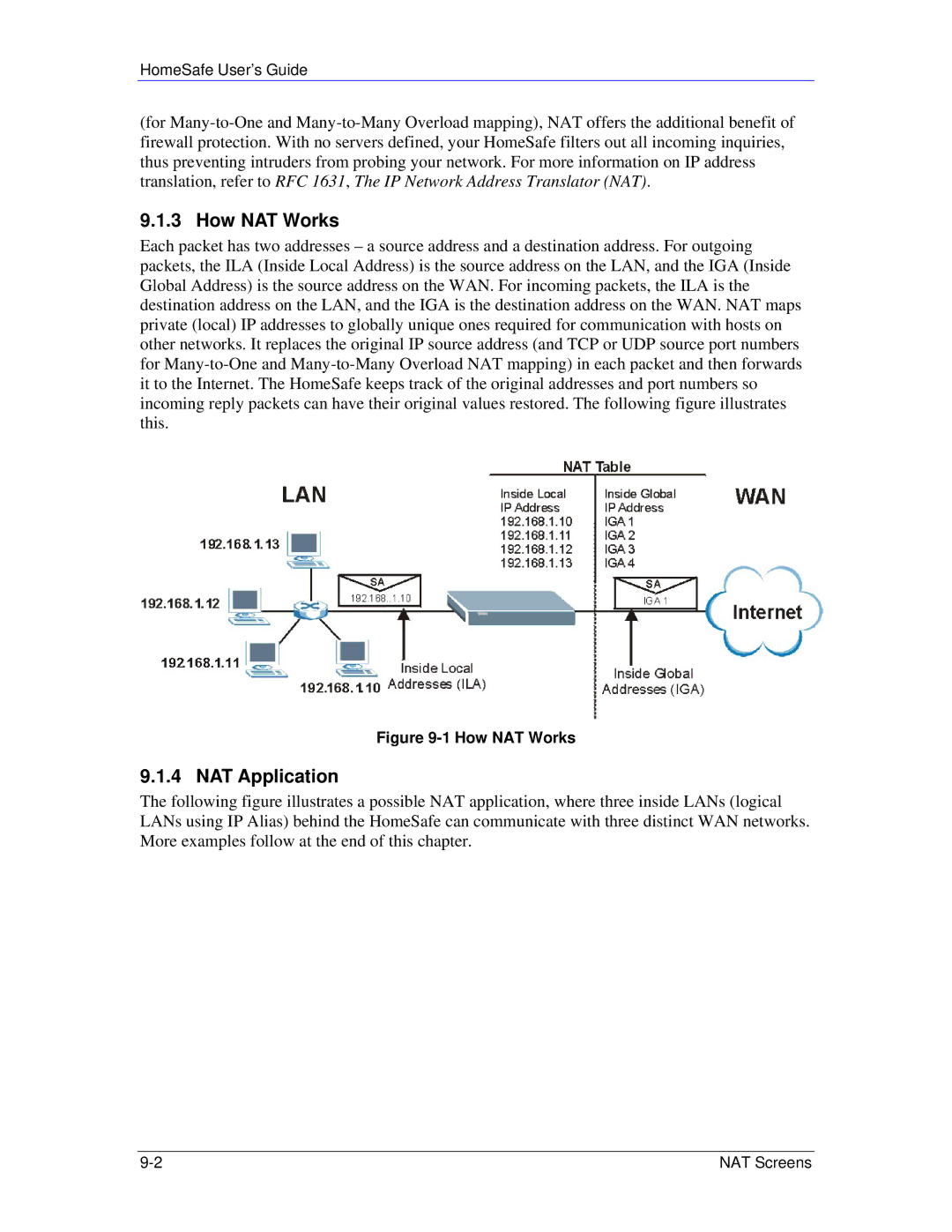
Network Address Translation NAT
Traffic Redirect
Secure Broadband Internet Access via Cable or DSL Modem
Wireless Association List HS-100W only
Applications for the HomeSafe
HomeSafe Parental Control Gateway
Wireless LAN Application
Wireless LAN Application Example
Introducing the Web Configurator
Web Configurator Overview
Accessing the HomeSafe Web Configurator
System Administrator Password Setup
Wlan Setup
Set up your wireless LAN using the second wizard screen
Following table describes the fields in this screen
Wlan Setup Basic Security
Access screen
Essid
Wlan Setup Extended Security
Following table describes the labels in this screen
WEP
Ascii
Internet Configuration Setup
Refer to the chapter on wireless LAN for more information
Internet Configuration Setup ISP Parameters
Internet Access Setup
Internet Access Static IP Address Setup
Dhcp
Internet Configuration Setup Complete
Parental Control Wizard
Parental Control Time Setup
Wizard Parental Control Wizard
10 Wizard Parental Control Time Setup
Parental Control Create or Edit a Profile
Parental Control Profile Information
11 Wizard Create or Edit a Profile
Parental Control User Group
12 Wizard Parental Control Profile Information
Administrator can decide each group’s
Access rights
Parental Control Time Allowance
13 Wizard Parental Control User Group
Parental Control Application Blocking
Parental Control Account Summary
15 Wizard Parental Control Application Blocking
Allowance screen
Parental Control Register for Content Filter
16 Wizard Parental Control Summary
Content Filtering with an External Server
Checking Content Filtering Activation
Content Filter Service Activation
If you click Register Later you will proceed to Figure
Following screen appears after you click Activate in Figure
Accessing the Internet via the HomeSafe Gateway
Content Filter Setup Complete
25 Password Screen
Resetting the HomeSafe
Procedure To Use The Reset Button
HomeSafe Main Menu
Navigation Panel
17 Screens Summary
Link TAB Function
Maintenance
Firewall
Remote Mgmt Telnet
FTP
Page
Connection Wizard General Setup and System Name
Chapter Connection Wizard
Connection Wizard Overview
Domain Name
Connection Wizard General Setup
Connection Wizard Screen
Connection Wizard Wireless LAN Setup Basic Security
Connection Wizard Wireless LAN Setup Extend Security
Ethernet
PPPoE Encapsulation
Connection Wizard Ethernet Encapsulation
Connection Wizard PPPoE Encapsulation
Pptp Encapsulation
Connection Wizard Pptp Encapsulation
WAN IP Address Assignment
Private IP Address Ranges
IP Address and Subnet Mask
DNS Server Address Assignment
WAN MAC Address
Connection Wizard WAN Setup
ISP
Basic Setup Complete
Connection Wizard Finish
10 Connection Wizard Problems
HomeSafe User’s Guide Connection Wizard
System, LAN, Wlan and WAN
Configuring General Setup
Chapter System Screens
System Overview
Click System to open the General screen
Configuring Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS
DynDNS Wildcard
System Ddns
Configuring Password
Configuring Time Setting
System Time Setting
Daylight Savings
Dhcp Setup
Chapter LAN Screens
LAN Overview
Any IP
Multicast
How Any IP Works
Any IP Example Application
Configuring IP
Click LAN to open the IP screen
LAN TCP/IP
Configuring Static Dhcp
LAN Static Dhcp
Configuring IP Alias
LAN IP Alias
LAN IP Alias
Wireless Configuration and Roaming
Wireless LAN Overview
Ibss
2 BSS
Basic Service set
3 ESS
Wireless LAN Basics
1 RTS/CTS
Configuring Wireless
Fragmentation Threshold
Configuring Roaming
RTS/CTS
Requirements for Roaming
Roaming Example
Wireless stations must have the same Essid to
All APs on the same subnet
Allow roaming
Page
Chapter Wireless Security
Wireless Security Overview
WPA-PSK
WPA
Authentication
Wireless Security Relational Matrix
Security Parameters Summary
WEP Overview
WEP Authentication Steps
Preamble Type
Configuring WEP Encryption
Encryption field
User Authentication
Introduction to WPA
Encryption
WPA-PSK Application Example
WPA-PSK application looks as follows
Configuring WPA-PSK Authentication
If wireless station authentication is done
Using a Radius server, the reauthentication
Timer on the Radius server has priority
Wireless Client WPA Supplicants
WPA with Radius Application Example
Configuring WPA Authentication
WPA with Radius Application Example
Wlan Wireless WPA
802.1x Overview
Configuring 802.1x and Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
EAP-MD5 cannot be used with Dynamic WEP Key Exchange
Configuring 802.1x and Static WEP Key Exchange
10 Wlan Wireless 802.1x and Static WEP
Wlan Wireless 802.1x and Static WEP
Wlan Wireless 802.1x and Static WEP
Configuring
Reset
MAC Filter
Following table describes the labels in this menu
Wlan MAC Address Filter
MAC
Configuring Local User Database
Introduction to Local User Database
10 Wlan Local User Database
Active Select this option to activate the user profile
Introduction to Radius
Configuring Radius
EAP Authentication Overview
15 Wlan Radius
11 Wlan Radius
HomeSafe User’s Guide
Page
Configuring Route
Chapter WAN Screens
WAN Overview
TCP/IP Priority Metric
Configuring WAN ISP
Ethernet Encapsulation
Screen shown next is for Ethernet encapsulation
PPPoE Encapsulation
WAN ISP PPPoE Encapsulation
WAN ISP Pptp Encapsulation
Configuring WAN IP
WAN IP Address Assignment
WAN IP
Selected Use Fixed IP Address
Server
Choose Both, None, In Only or Out Only
Configuring WAN MAC
Choose RIP-1 , RIP-2B or RIP-2M
RIP-1
Traffic Redirect WAN Setup
Traffic Redirect
Configuring Traffic Redirect
WAN Traffic Redirect
WAN Traffic Redirect
SUA/NAT and Static Route
Page
Chapter Network Address Translation NAT Screens
NAT Overview
NAT Definitions
What NAT Does
How NAT Works
NAT Application
NAT Mapping Types
Following table summarizes these types
Using NAT
SUA Server
SUA Single User Account Versus NAT
NAT Mapping Types
Port Forwarding Services and Port Numbers
Default Server IP Address
Services and Port Numbers
Services Port Number
Configuring SUA Server
Configuring Servers Behind SUA Example
Configuring Address Mapping
SUA/NAT Setup
Address Mapping
One-to-One and Server mapping types
Configuring Address Mapping
Trigger Port Forwarding
Many-to-One and Server mapping types
Configuring Trigger Port Forwarding
Trigger Port Forwarding Example
Two Points To Remember About Trigger Ports
Following is an example of trigger port forwarding
Only one LAN computer can use a trigger port range at a time
Page
Configuring IP Static Route
Chapter Static Route Screens
Static Route Overview
Click Static Route to open the screen as shown next
Configuring Route Entry
Static Route Edit
NAT Screens 10-3
UPnP, Parental Control and Firewall
How Do I Know If Im Using UPnP?
Chapter UPnP
Universal Plug and Play Overview
UPnP and ZyXEL
Configuring UPnP
Installing UPnP in Windows Example
Click UPnP to display the screen shown next
Installing UPnP in Windows Me
Installing UPnP in Windows XP
Follow the steps below to install UPnP in Windows Me
Follow the steps below to install UPnP in Windows XP
Using UPnP in Windows XP Example
Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device
Internet Connection Properties
Web Configurator Easy Access
Connections Select My Network Places under Other Places
UPnP 11-7
Page
Parental Control Logins
Initial Configuration
Chapter Parental Control
Parental Control Overview
Parental Administrator log
Parental Control Application
Configuring Parental Control
HomeSafe Parental Control Wireless Gateway Application
Parental Control
For content filtering to be activated. See Checking
Content filtering activation
Web site displays a registration successful
Web page. It may take up to another ten minutes
Content Filtering with an External Server
Reset Click Reset to start configuring this screen again
Parental Control Group Edit Filter
Parental Control Group Edit Configuration
Parental Control Filter
Parental Control 12-9
12-10 Parental Control
Parental Control 12-11
How to set how much of the URL
See the Customizing Keyword
Blocking URL Checking section for
HomeSafe checks
Customizing Keyword Blocking URL Checking
Parental Control Edit
Services
Service Description
RLOGINTCP513
PPTPTUNNELGRE0
RCMDTCP512
REALAUDIOTCP7070
Parental Control Edit
Access, you should select the unrestricted
User access will be denied after the End
If you want to allow twenty-four hour
Check box
Parental Control Bypass List
Weekdays or Weekend boxes
Parental Control 12-19
Page
Chapter Firewall
Introduction
Guidelines For Enhancing Security With Your Firewall
Firewall Settings Screen
Firewall Settings
Firewall, NAT and Remote Management
LAN-to-WAN rules
No Log
Log All log all LAN to WAN packets
Services
WAN-to-LAN rules
Firewall Service
Click Clear All to empty the Blocked Service
Remote Management
Page
Only LAN only Neither Disable
Chapter Remote Management Screens
Remote Management Overview
Remote Management Limitations
Configuring WWW
System Timeout
Remote Management and NAT
Configuring Telnet
Telnet Configuration on a TCP/IP Network
Configuring FTP
Remote Management Telnet
Snmp
Remote Management FTP
Snmp is only available if TCP/IP is configured
Snmp Management Model
Configuring Snmp
Supported MIBs
Snmp Traps
Snmp Traps
Remote Management Snmp
Configuring DNS
Remote Management DNS
Configuring Security
Icmp
Remote Management Screens 14-11
Page
HomeSafe User’s Guide VPN Screens 14-1
Logs and Maintenance
Chapter Centralized Logs
View Log
Log Settings
Settings, see section
Log Settings
When Log is Full
Daily
Weekly
Hourly
Chapter Maintenance
Maintenance Overview
Status Screen
Maintenance System Statistics
System Statistics
Maintenance Dhcp Table
Dhcp Table Screen
Any IP Table
Association List
Maintenance Firmware Upload
16.6 F/W Upload Screen
Configuration Screen
Upload Warning
Backup Configuration
Restore Configuration
Maintenance Restore Configuration
Back to Factory Defaults
11 Configuration Restore Successful
14 Factory Defaults
Restart Screen
SMT General Configuration
Page
Chapter Introducing the SMT
SMT Introduction
Main Menu Commands
Navigating the SMT Interface
Operation Keystroke Description
Enter
System Management Terminal Interface Summary
Main Menu Summary
? or ChangeMe
Menu Title Description
Changing the System Password
Menu 23 System Password
Chapter Menu 1 General Setup
General Setup
Procedure To Configure Menu
Field Description Example
Procedure to Configure Dynamic DNS
Select Yes to configure Menu 1.1 Configure Dynamic DNS
Yes
DynamicDNS
User
Specified IP Address field
Chapter Menu 2 WAN Setup
WAN Setup
Introduction to WAN
From the main menu, enter 2 to open menu
Page
Chapter Menu 3 LAN Setup
LAN Setup
Protocol Dependent Ethernet Setup
20.3 TCP/IP Ethernet Setup and Dhcp
Menu 3.2 TCP/IP and Dhcp Ethernet Setup
Menu 3.2 Dhcp Ethernet Setup Fields
Menu 3.2 LAN TCP/IP Setup Fields
Both
RIP-1
RIP-1,RIP-2B or RIP-2M
IP Alias Setup
Physical Network & Partitioned Logical Networks
Wireless LAN Setup
Both, In Only, Out Only or None
Field Description Example Essid
Disable
CH06 2437MHz
RTS
Auto
Configuring MAC Address Filter
Mixed
Configuring Roaming on the HomeSafe
Menu 3.5.1 Wlan MAC Address Filter
10 Menu 3.5.2 Roaming Configuration
Menu 3.5.2 Roaming Configuration
Page
Chapter Internet Access
Introduction to Internet Access Setup
Menu 4 Internet Access Setup Ethernet
Ethernet Encapsulation
Configuring the Pptp Client
Configuring the PPPoE Client
Default
New Fields in Menu 4 Pptp Screen
New Fields in Menu 4 PPPoE screen
21-4 Internet Access
Chapter Remote Node Configuration
Introduction to Remote Node Setup
Remote Node Profile Setup
Ethernet
Alias
Press Enter to go to Menu 11.3 Remote Node Network
Layer Options
Outgoing Authentication Protocol
Nailed-Up Connection
Fields in Menu 11.1 PPPoE Encapsulation Specific
CHAP/PAP
Edit IP
Menu 11.1 Remote Node Profile for Pptp Encapsulation
Remote Node Network Layer Options
Dynamic
Remote Node Filter
SUA Only
Many-to-One and Server
RIP-1/RIP-2B/RIP-2M or None
Traffic Redirect Setup
Menu 11.5 Remote Node Filter Ethernet Encapsulation
22-8 Remote Node Configuration
Chapter Static Route Setup
IP Static Route Setup
23-2 Static Route Setup
Chapter Dial-in User Setup
Dial-in User Setup
Page
Menu 4 Applying NAT for Internet Access
Applying NAT
NAT Setup
Full Feature
Applying NAT in Menus 4
NAT
Address Mapping Sets
SUA Address Mapping Set
Following table explains the fields in this menu
Menu 15.1.255 is read-only SUA Address Mapping Rules
User-Defined Address Mapping Sets
Ordering Your Rules
Menu 15.1.1 First Set
Field Desription Example
Edit
Select Rule item
Configuring a Server behind NAT
Follow these steps to configure a server behind NAT
One-to-One,Many-to-One and Server types
Example 1 Internet Access Only
Following are some examples of NAT configuration
General NAT Examples
Example 2 Internet Access with an Inside Server
Example 3 Multiple Public IP Addresses With Inside Servers
Dynamic Inside Global Address is assigned by the ISP
Enter 1 to configure the Address Mapping Sets
Following figures show how to configure the first rule
Address Translation field in menu 4 or menu 11.3
Then enter 15 from the main menu
Enter 2 in Menu 15 NAT Setup
Example 4 NAT Unfriendly Application Programs
Example 3 Menu
20 Example 4 Menu 15.1.1 Address Mapping Rules
Menu 15.3 Trigger Port Setup
Page
Access Methods
Chapter Enabling the Firewall
Remote Management and the Firewall
Enabling the Firewall
SMT Advanced Management
Chapter Filter Configuration
Introduction to Filters
Filter Structure of the HomeSafe
Execute
Configuring a Filter Set
Abbreviations Used in the Filter Rules Summary Menu
Configuring a Filter Rule
Configuring a TCP/IP Filter Rule
Rule Abbreviations Used
Abbreviation Description
TCP/IP Filter Rule
Field Description Options
Less
Equal
Following figure illustrates the logic flow of an IP filter
Configuring a Generic Filter Rule
Executing an IP Filter
Generic Filter Rule Menu Fields
Example Filter
HomeSafe User’s Guide Generic Filter Rule Menu Fields
10 Example Filter Menu
Filter Types and NAT
Firewall Versus Filters
Applying a Filter
Applying LAN Filters
Applying Remote Node Filters
14 Filtering Remote Node Traffic
Page
Chapter Snmp Configuration
About Snmp
Snmp Configuration
Following table describes the Snmp configuration parameters
Supported MIBs
Snmp Traps
Ports and Permanent Virtual Circuits
Port PVC Permanent Virtual Circuit
Page
System Password
Configuring External Radius Server
Chapter System Security
System Security
29.1.3
Enter 4 to display Menu 23.4 System Security IEEE802.1x
No Access Allowed
Menu 23.4 System Security IEEE802.1x
PSK
Group Data Privacy field
Mode
Management Protocol is selected
System Information and Diagnosis
System Status
Menu 24.1 System Maintenance Status
System Maintenance Status Menu Fields
Menu 1 General Setup
System Information
System Information
To get to the System Information
Menu 24.3.2 System Maintenance Syslog and Accounting
Log and Trace
Console Port Speed
Syslog Logging
System Information and Diagnosis 30-5
Diagnostic
Call-Triggering Packet
System Maintenance Menu Diagnostic
WAN Dhcp
30-8 System Information and Diagnosis
Chapter Firmware and Configuration File Maintenance
Filename Conventions
Filename Conventions
File Type Internal Name External Name Description
Backup Configuration
Using the FTP Command from the Command Line
Example of FTP Commands from the Command Line
Follow the instructions as shown in the next screen
Backup Configuration Using Tftp
General Commands for GUI-based FTP Clients
Command Description
GUI-based FTP Clients
Restore Configuration
Tftp Command Example
Restore Using FTP
Following is an example Tftp command
Uploading Firmware and Configuration Files
Restore Using FTP Session Example
Configuration File Upload
You see the following screen when you telnet into menu
Firmware File Upload
FTP File Upload Command from the DOS Prompt Example
FTP Session Example of Firmware File Upload
Tftp File Upload
Tftp Upload Command Example
Chapter System Maintenance
Command Interpreter Mode
Command Syntax
Command Usage
Call Control Support
Budget Management
Call History
Call History Fields
Time and Date Setting
Time and Date Setting Fields
NTP RFC-1305 the default, is similar to Time RFC-868
Resetting the Time
Daylight Saving field
Page
Chapter Remote Management
Remote Management
LAN Only
Chapter Call Scheduling
Introduction to Call Scheduling
Menu 26.1 Schedule Set Setup
Once
Applying Schedule Sets to a Remote Node PPPoE
Appendices and Index
Page
Troubleshooting
Problem Corrective Action
Appendix a
Control Group Edit screen
Appendix B PPPoE
PPPoE in Action
Benefits of PPPoE
Traditional Dial-up Scenario
Diagram B-2 The HomeSafeas a PPPoE Client
HomeSafeas a PPPoE Client
What is PPTP?
Diagram C-1 Transport PPP frames over Ethernet
Appendix C
Pptp and the HomeSafe
Diagram C-2 Pptp Protocol Overview
Diagram C-3 Example Message Exchange between PC and an ANT
Pptp Protocol Overview
Control & PPP connections
Pptp
Page
Chart 1 System Error Logs
Chart 2 System Maintenance Logs
Appendix D Log Descriptions
LOG Message Description
Chart 3 UPnP Logs
Chart 4 Content Filtering Logs
ID content
Chart 5 Icmp Type and Code Explanations
Type Code Description
Log Commands
Configuring What You Want the HomeSafe to Log
Displaying Logs
Page
Appendix E Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
Windows 95/98/Me
If you need TCP/IP
If you need Client for Microsoft Networks
Checking/Modifying Your Computer’s IP Address
Windows 2000/NT/XP
Click Advanced to go to the Advanced TCP/IP
HomeSafe User’s Guide
Turn on your HomeSafeand restart your computer if prompted
Macintosh OS 8/9
Select Ethernet built-in from the Connect via list
Close the TCP/IP Control Panel
Macintosh OS
Check your TCP/IP properties in the Network window
Select Built-in Ethernet from the Show list
Page
Appendix F Wireless LAN and Ieee
Benefits of a Wireless LAN
Ad-hoc Wireless LAN Configuration
Ieee
Infrastructure Wireless LAN Configuration
Diagram F-1 Peer-to-Peer Communication in an Ad-hoc Network
Diagram F-2 ESS Provides Campus-Wide Coverage
Page
Appendix G Wireless LAN With Ieee
Deployment Issues with Ieee
Security Flaws with Ieee
Advantages of the Ieee
Diagram G-1 Sequences for EAP MD5-Challenge Authentication
Appendix H Types of EAP Authentication
EAP-TTLS Tunneled Transport Layer Service
EAP-MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm
EAP-TLS Transport Layer Security
Difficulty Wireless Security
Certificate Client
Certificate Server
Dynamic Key
Antenna Characteristics
Appendix Antenna Selection and Positioning Recommendation
Types of Antennas For Wlan
Positioning Antennas
Appendix J Brute-Force Password Guessing Protection
Chart 6 Brute-Force Password Guessing Protection Commands
Example
Page
Ideal Setup
Triangle Route Problem
Triangle Route Solutions
Appendix K Triangle Route
How To Configure Triangle Route
Diagram K-3 IP Alias
Diagram K-4 Gateways on the WAN Side
Gateways on the WAN Side
Appendix L Index
BSS
Ibss
See NAT
See Ttls
Wlan