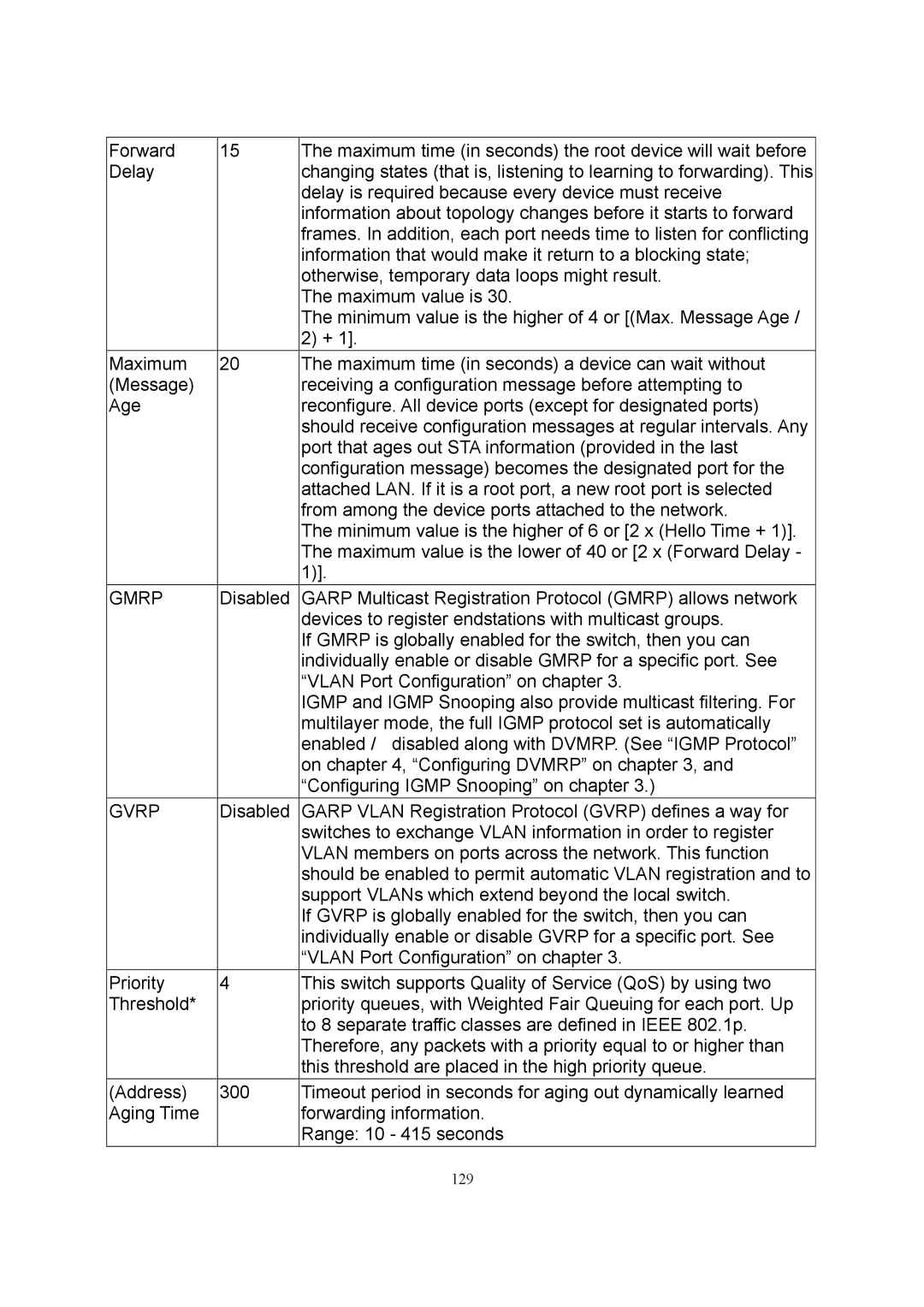
Forward | 15 | The maximum time (in seconds) the root device will wait before |
Delay |
| changing states (that is, listening to learning to forwarding). This |
|
| delay is required because every device must receive |
|
| information about topology changes before it starts to forward |
|
| frames. In addition, each port needs time to listen for conflicting |
|
| information that would make it return to a blocking state; |
|
| otherwise, temporary data loops might result. |
|
| The maximum value is 30. |
|
| The minimum value is the higher of 4 or [(Max. Message Age / |
|
| 2) + 1]. |
Maximum | 20 | The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without |
(Message) |
| receiving a configuration message before attempting to |
Age |
| reconfigure. All device ports (except for designated ports) |
|
| should receive configuration messages at regular intervals. Any |
|
| port that ages out STA information (provided in the last |
|
| configuration message) becomes the designated port for the |
|
| attached LAN. If it is a root port, a new root port is selected |
|
| from among the device ports attached to the network. |
|
| The minimum value is the higher of 6 or [2 x (Hello Time + 1)]. |
|
| The maximum value is the lower of 40 or [2 x (Forward Delay - |
|
| 1)]. |
GMRP | Disabled | GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP) allows network |
|
| devices to register endstations with multicast groups. |
|
| If GMRP is globally enabled for the switch, then you can |
|
| individually enable or disable GMRP for a specific port. See |
|
| “VLAN Port Configuration” on chapter 3. |
|
| IGMP and IGMP Snooping also provide multicast filtering. For |
|
| multilayer mode, the full IGMP protocol set is automatically |
|
| enabled / disabled along with DVMRP. (See “IGMP Protocol” |
|
| on chapter 4, “Configuring DVMRP” on chapter 3, and |
|
| “Configuring IGMP Snooping” on chapter 3.) |
GVRP | Disabled | GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) defines a way for |
|
| switches to exchange VLAN information in order to register |
|
| VLAN members on ports across the network. This function |
|
| should be enabled to permit automatic VLAN registration and to |
|
| support VLANs which extend beyond the local switch. |
|
| If GVRP is globally enabled for the switch, then you can |
|
| individually enable or disable GVRP for a specific port. See |
|
| “VLAN Port Configuration” on chapter 3. |
Priority | 4 | This switch supports Quality of Service (QoS) by using two |
Threshold* |
| priority queues, with Weighted Fair Queuing for each port. Up |
|
| to 8 separate traffic classes are defined in IEEE 802.1p. |
|
| Therefore, any packets with a priority equal to or higher than |
|
| this threshold are placed in the high priority queue. |
(Address) | 300 | Timeout period in seconds for aging out dynamically learned |
Aging Time |
| forwarding information. |
|
| Range: 10 - 415 seconds |
Page 129
Image 129