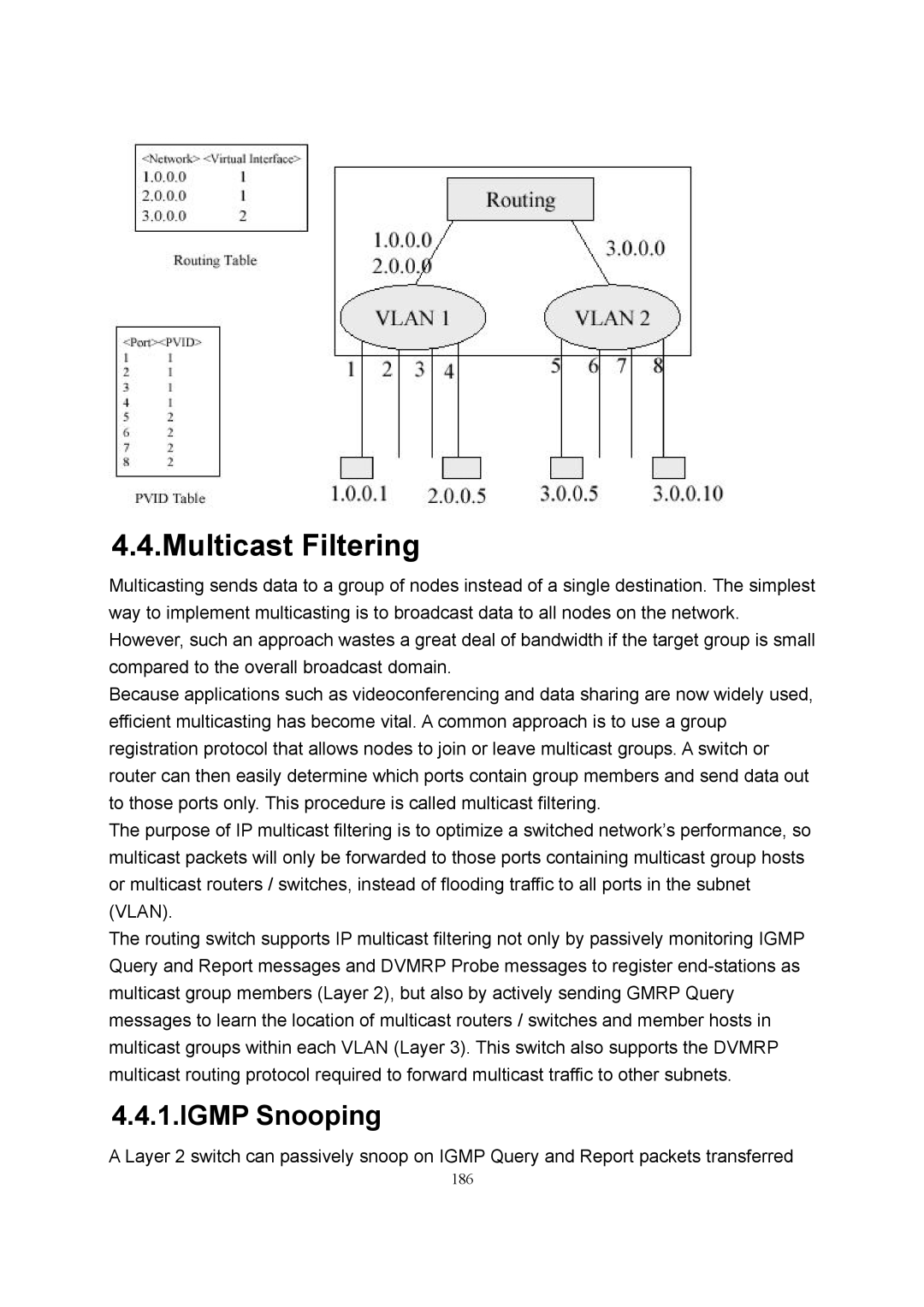
4.4.Multicast Filtering
Multicasting sends data to a group of nodes instead of a single destination. The simplest way to implement multicasting is to broadcast data to all nodes on the network. However, such an approach wastes a great deal of bandwidth if the target group is small compared to the overall broadcast domain.
Because applications such as videoconferencing and data sharing are now widely used, efficient multicasting has become vital. A common approach is to use a group registration protocol that allows nodes to join or leave multicast groups. A switch or router can then easily determine which ports contain group members and send data out to those ports only. This procedure is called multicast filtering.
The purpose of IP multicast filtering is to optimize a switched network’s performance, so multicast packets will only be forwarded to those ports containing multicast group hosts or multicast routers / switches, instead of flooding traffic to all ports in the subnet (VLAN).
The routing switch supports IP multicast filtering not only by passively monitoring IGMP Query and Report messages and DVMRP Probe messages to register
4.4.1.IGMP Snooping
A Layer 2 switch can passively snoop on IGMP Query and Report packets transferred
186