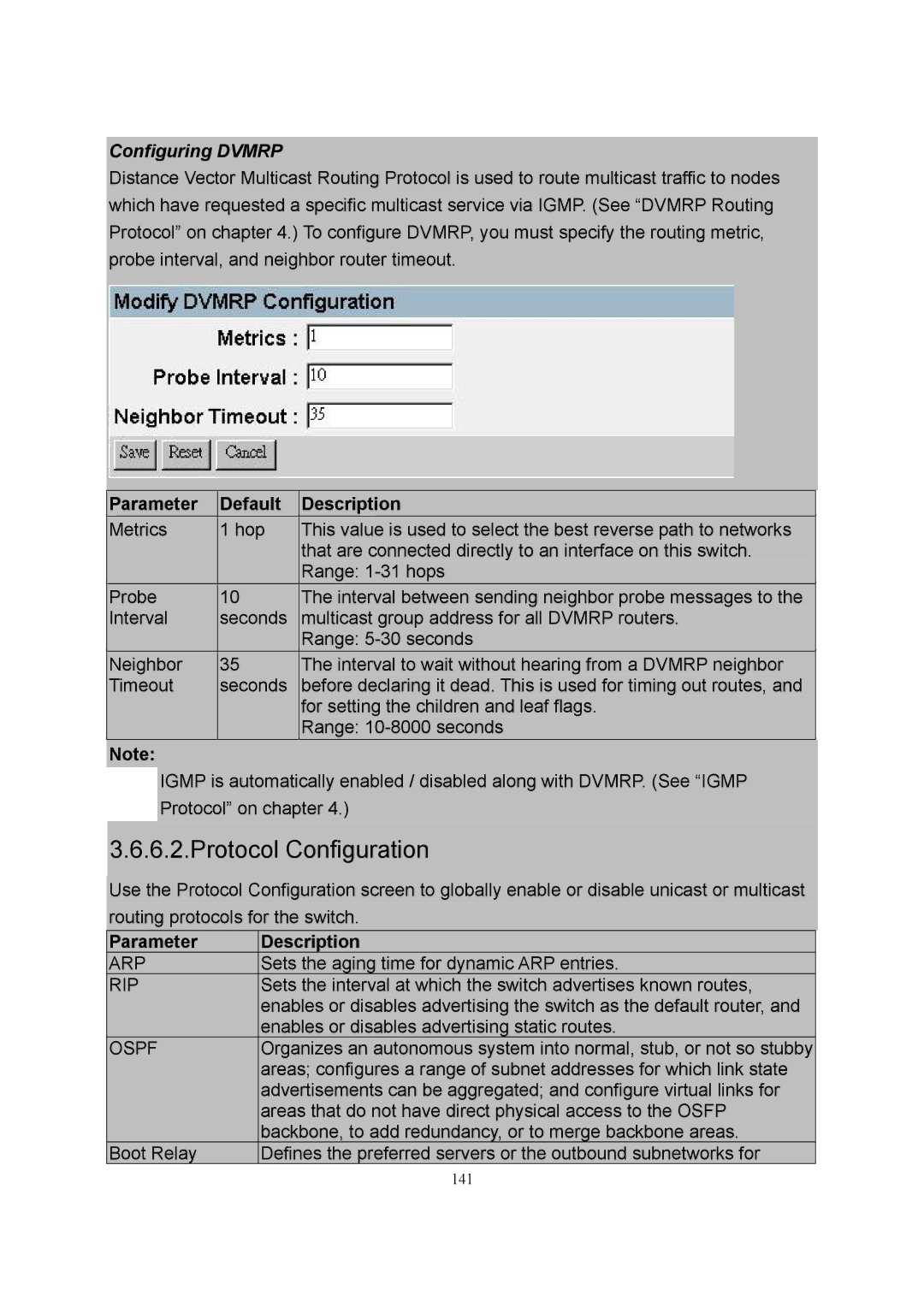
Configuring DVMRP
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol is used to route multicast traffic to nodes which have requested a specific multicast service via IGMP. (See “DVMRP Routing Protocol” on chapter 4.) To configure DVMRP, you must specify the routing metric, probe interval, and neighbor router timeout.
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|
|
| |||
| Metrics | 1 hop | This value is used to select the best reverse path to networks |
|
|
|
| that are connected directly to an interface on this switch. |
|
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Probe | 10 | The interval between sending neighbor probe messages to the |
|
| Interval | seconds | multicast group address for all DVMRP routers. |
|
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Neighbor | 35 | The interval to wait without hearing from a DVMRP neighbor |
|
| Timeout | seconds | before declaring it dead. This is used for timing out routes, and |
|
|
|
| for setting the children and leaf flags. |
|
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Note: |
|
|
|
IGMP is automatically enabled / disabled along with DVMRP. (See “IGMP Protocol” on chapter 4.)
3.6.6.2.Protocol Configuration
Use the Protocol Configuration screen to globally enable or disable unicast or multicast routing protocols for the switch.
Parameter | Description |
ARP | Sets the aging time for dynamic ARP entries. |
RIP | Sets the interval at which the switch advertises known routes, |
| enables or disables advertising the switch as the default router, and |
| enables or disables advertising static routes. |
OSPF | Organizes an autonomous system into normal, stub, or not so stubby |
| areas; configures a range of subnet addresses for which link state |
| advertisements can be aggregated; and configure virtual links for |
| areas that do not have direct physical access to the OSFP |
| backbone, to add redundancy, or to merge backbone areas. |
Boot Relay | Defines the preferred servers or the outbound subnetworks for |
141