SN
Age
The link state sequence number, used to remove previous duplicate LSAs.
The number of seconds since this LSA was originated.
Displaying the Neighbor Table
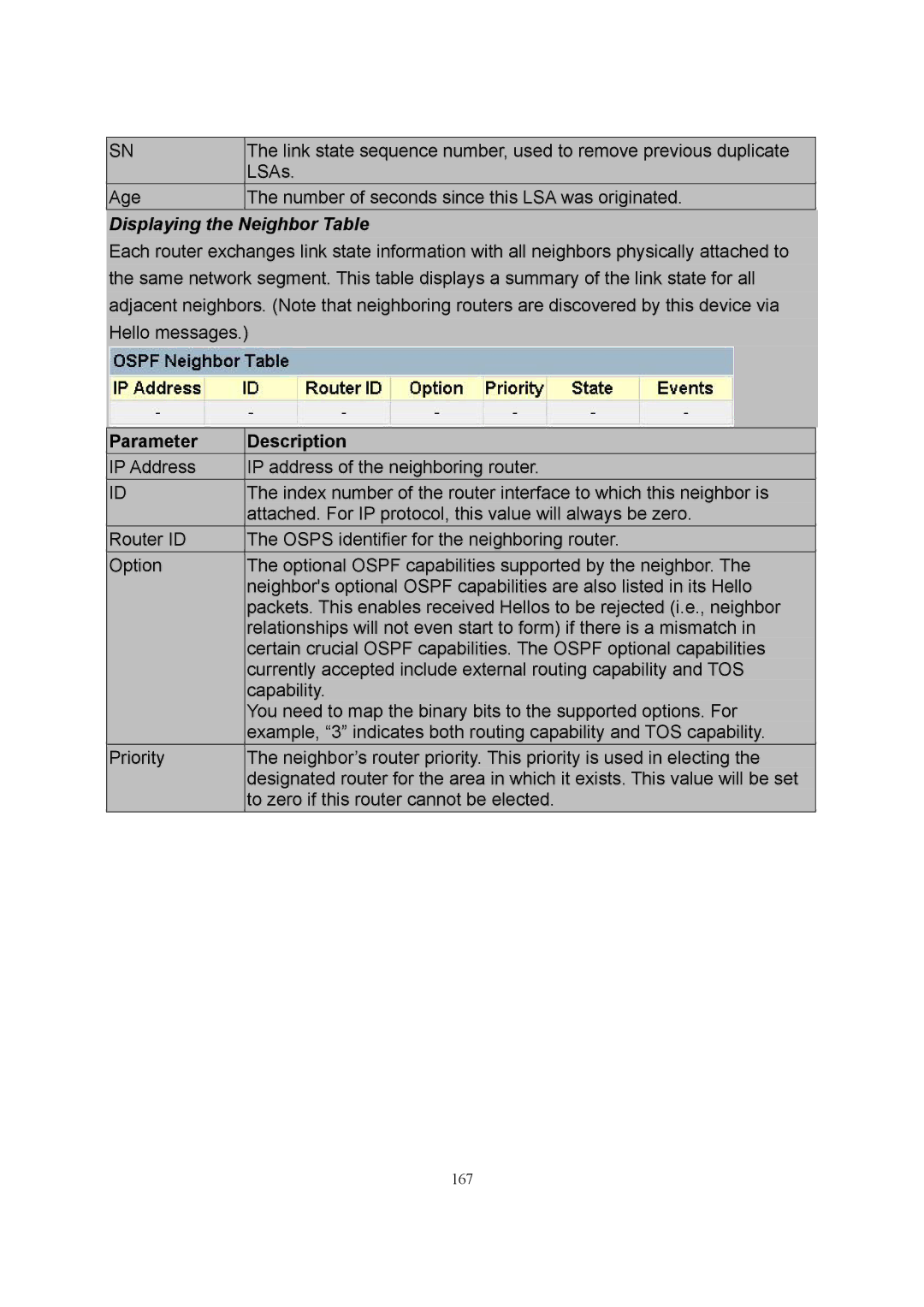
Each router exchanges link state information with all neighbors physically attached to the same network segment. This table displays a summary of the link state for all adjacent neighbors. (Note that neighboring routers are discovered by this device via Hello messages.)
| Parameter | Description |
|
|
| ||
| IP Address | IP address of the neighboring router. |
|
| ID | The index number of the router interface to which this neighbor is |
|
|
| attached. For IP protocol, this value will always be zero. |
|
| Router ID | The OSPS identifier for the neighboring router. |
|
| Option | The optional OSPF capabilities supported by the neighbor. The |
|
|
| neighbor's optional OSPF capabilities are also listed in its Hello |
|
|
| packets. This enables received Hellos to be rejected (i.e., neighbor |
|
|
| relationships will not even start to form) if there is a mismatch in |
|
|
| certain crucial OSPF capabilities. The OSPF optional capabilities |
|
|
| currently accepted include external routing capability and TOS |
|
|
| capability. |
|
|
| You need to map the binary bits to the supported options. For |
|
|
| example, “3” indicates both routing capability and TOS capability. |
|
| Priority | The neighbor’s router priority. This priority is used in electing the |
|
|
| designated router for the area in which it exists. This value will be set |
|
|
| to zero if this router cannot be elected. |
|