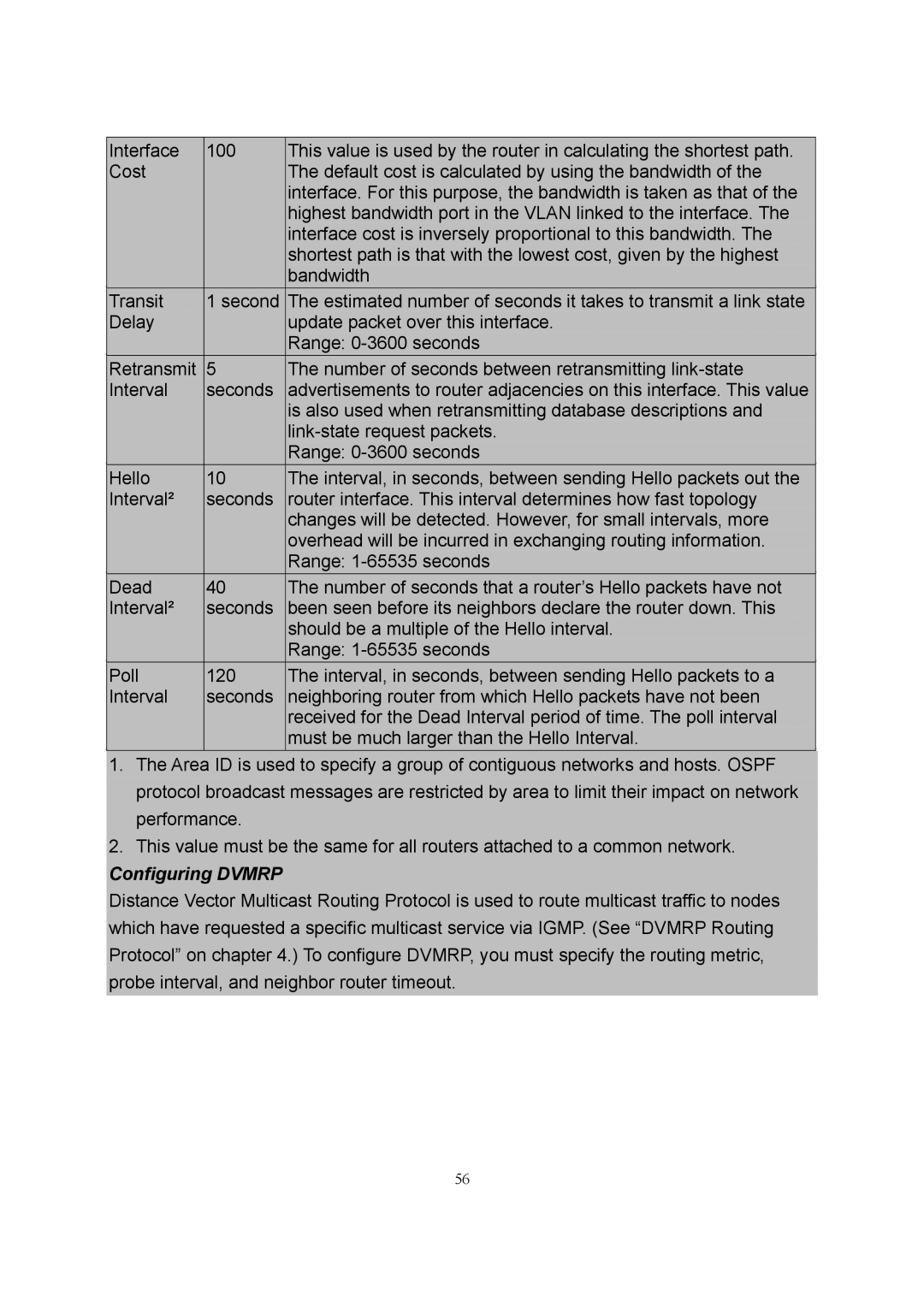
| Interface | 100 | This value is used by the router in calculating the shortest path. |
|
|
| |||
| Cost |
| The default cost is calculated by using the bandwidth of the |
|
|
|
| interface. For this purpose, the bandwidth is taken as that of the |
|
|
|
| highest bandwidth port in the VLAN linked to the interface. The |
|
|
|
| interface cost is inversely proportional to this bandwidth. The |
|
|
|
| shortest path is that with the lowest cost, given by the highest |
|
|
|
| bandwidth |
|
| Transit | 1 second | The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state |
|
| Delay |
| update packet over this interface. |
|
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Retransmit | 5 | The number of seconds between retransmitting |
|
| Interval | seconds | advertisements to router adjacencies on this interface. This value |
|
|
|
| is also used when retransmitting database descriptions and |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Hello | 10 | The interval, in seconds, between sending Hello packets out the |
|
| Interval² | seconds | router interface. This interval determines how fast topology |
|
|
|
| changes will be detected. However, for small intervals, more |
|
|
|
| overhead will be incurred in exchanging routing information. |
|
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Dead | 40 | The number of seconds that a router’s Hello packets have not |
|
| Interval² | seconds | been seen before its neighbors declare the router down. This |
|
|
|
| should be a multiple of the Hello interval. |
|
|
|
| Range: |
|
| Poll | 120 | The interval, in seconds, between sending Hello packets to a |
|
| Interval | seconds | neighboring router from which Hello packets have not been |
|
|
|
| received for the Dead Interval period of time. The poll interval |
|
|
|
| must be much larger than the Hello Interval. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.The Area ID is used to specify a group of contiguous networks and hosts. OSPF protocol broadcast messages are restricted by area to limit their impact on network performance.
2.This value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network.
Configuring DVMRP
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol is used to route multicast traffic to nodes which have requested a specific multicast service via IGMP. (See “DVMRP Routing Protocol” on chapter 4.) To configure DVMRP, you must specify the routing metric, probe interval, and neighbor router timeout.
56