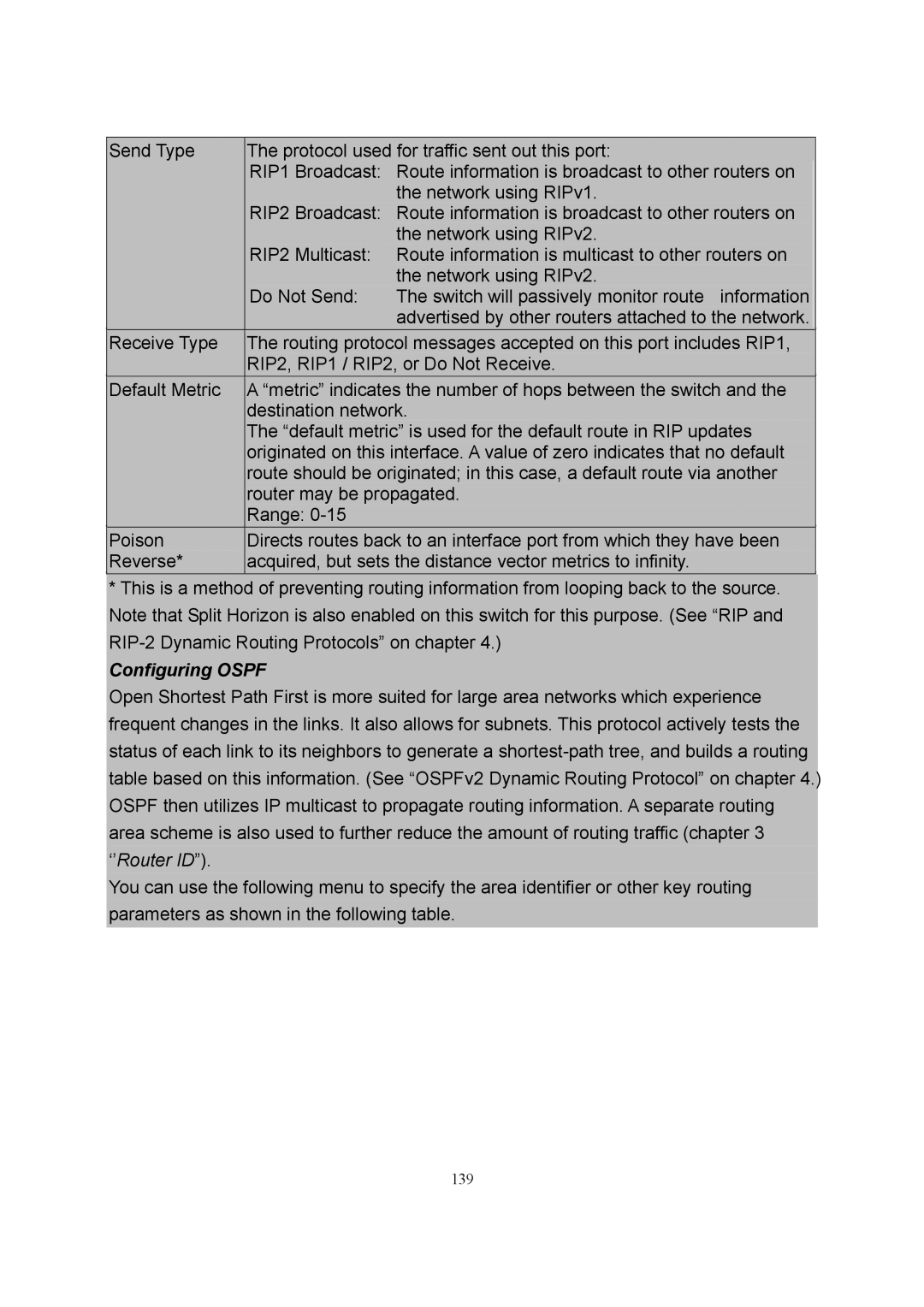
| Send Type | The protocol used for traffic sent out this port: |
| |
|
| |||
|
| RIP1 Broadcast: | Route information is broadcast to other routers on |
|
|
|
| the network using RIPv1. |
|
|
| RIP2 Broadcast: | Route information is broadcast to other routers on |
|
|
|
| the network using RIPv2. |
|
|
| RIP2 Multicast: | Route information is multicast to other routers on |
|
|
|
| the network using RIPv2. |
|
|
| Do Not Send: | The switch will passively monitor route information |
|
|
|
| advertised by other routers attached to the network. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Receive Type | The routing protocol messages accepted on this port includes RIP1, |
| |
|
| RIP2, RIP1 / RIP2, or Do Not Receive. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| Default Metric | A “metric” indicates the number of hops between the switch and the |
| |
|
| destination network. |
| |
|
| The “default metric” is used for the default route in RIP updates |
| |
|
| originated on this interface. A value of zero indicates that no default |
| |
|
| route should be originated; in this case, a default route via another |
| |
|
| router may be propagated. |
| |
|
| Range: |
|
|
| Poison | Directs routes back to an interface port from which they have been |
| |
| Reverse* | acquired, but sets the distance vector metrics to infinity. |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
*This is a method of preventing routing information from looping back to the source. Note that Split Horizon is also enabled on this switch for this purpose. (See “RIP and
Configuring OSPF
Open Shortest Path First is more suited for large area networks which experience frequent changes in the links. It also allows for subnets. This protocol actively tests the status of each link to its neighbors to generate a
You can use the following menu to specify the area identifier or other key routing parameters as shown in the following table.