Configuring OSPF
Open Shortest Path First is more suited for large area networks which experience frequent changes in the links. It also allows for subnets. This protocol actively tests the status of each link to its neighbors to generate a shortest path tree, and builds a routing table based on this information. (See “OSPFv2 Dynamic Routing Protocol” on chapter 4.) OSPF then utilizes IP multicast to propagate routing information. A separate routing area scheme is also used to further reduce the amount of routing traffic (chapter
2 ”Protocol Configuration”).
You can use the following menu to specify the area identifier, or other key routing parameters as described in the following table.
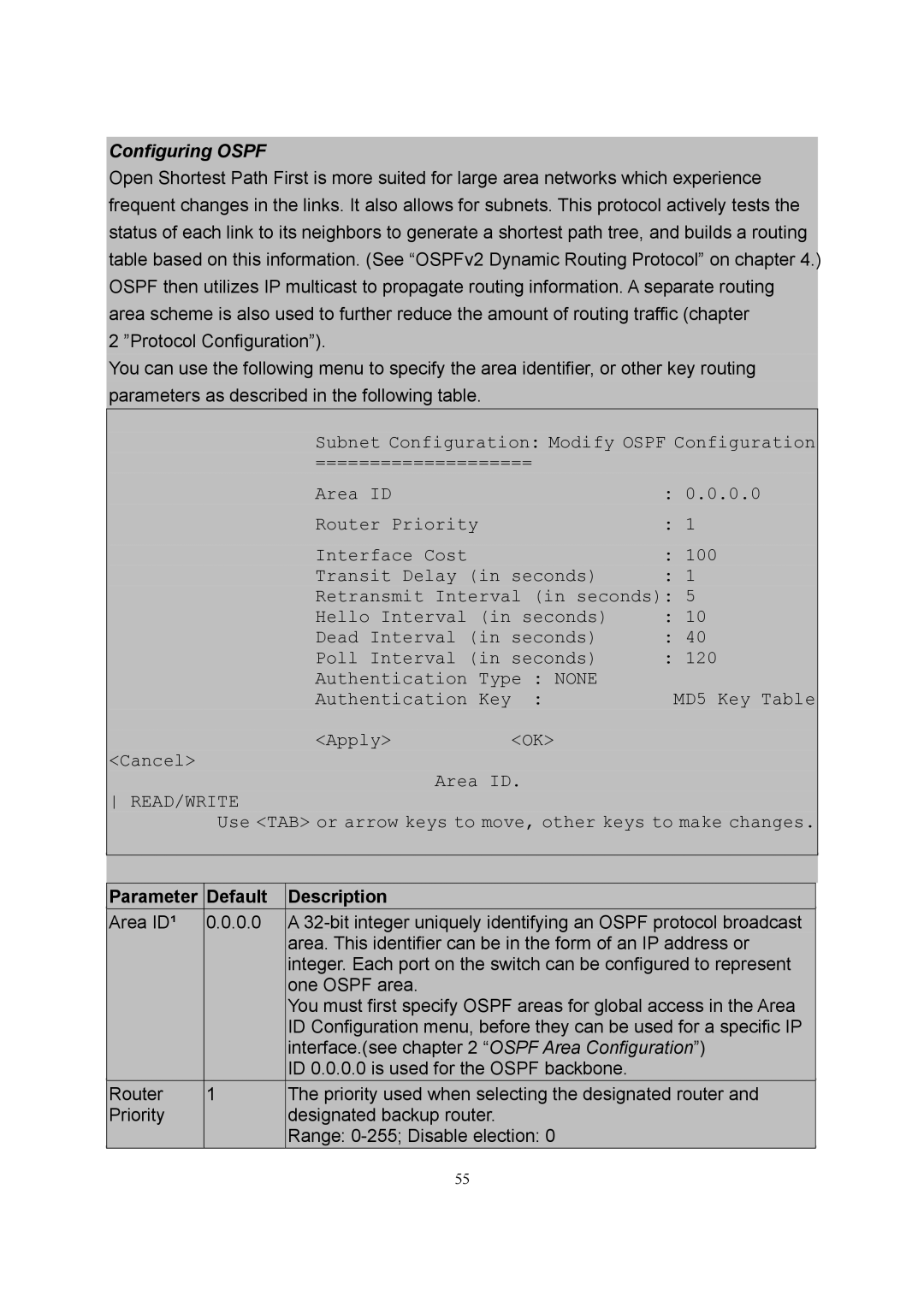
Subnet Configuration: Modify OSPF Configuration
====================
Area ID |
| : | 0.0.0.0 |
Router Priority |
| : | 1 |
Interface Cost |
| : | 100 |
Transit Delay (in seconds) | : | 1 | |
Retransmit Interval (in seconds): | 5 | ||
Hello Interval | (in seconds) | : | 10 |
Dead Interval (in seconds) | : | 40 | |
Poll Interval (in seconds) | : | 120 | |
Authentication | Type : NONE |
| MD5 Key Table |
Authentication | Key : |
| |
<Apply> | <OK> |
|
|
<Cancel>
Area ID.
READ/WRITE
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
|
|
|
Parameter | Default | Description |
Area ID¹ | 0.0.0.0 | A |
|
| area. This identifier can be in the form of an IP address or |
|
| integer. Each port on the switch can be configured to represent |
|
| one OSPF area. |
|
| You must first specify OSPF areas for global access in the Area |
|
| ID Configuration menu, before they can be used for a specific IP |
|
| interface.(see chapter 2 “OSPF Area Configuration”) |
|
| ID 0.0.0.0 is used for the OSPF backbone. |
Router | 1 | The priority used when selecting the designated router and |
Priority |
| designated backup router. |
|
| Range: |
|
|
|
55