4.2.Layer 3 Switching
The two major functions provided by a Layer 3 switch include IP Switching and Routing Path Management. When the switch is set to multilayer mode (chapter 2 ”Setting the System Operation Mode”), it acts as a routing switch, with support for standard IP routing and the ability to pass traffic between VLANs as required. However, when the switch is first set to multilayer mode, no default routing is defined. As with all traditional routers, the routing function must first be configured to work. (RIP: chapter 2 , 3 “Configuring RIP”; OSPF: chapter 2 ,3 “Configuring OSPF”).
4.2.1.Initial Configuration
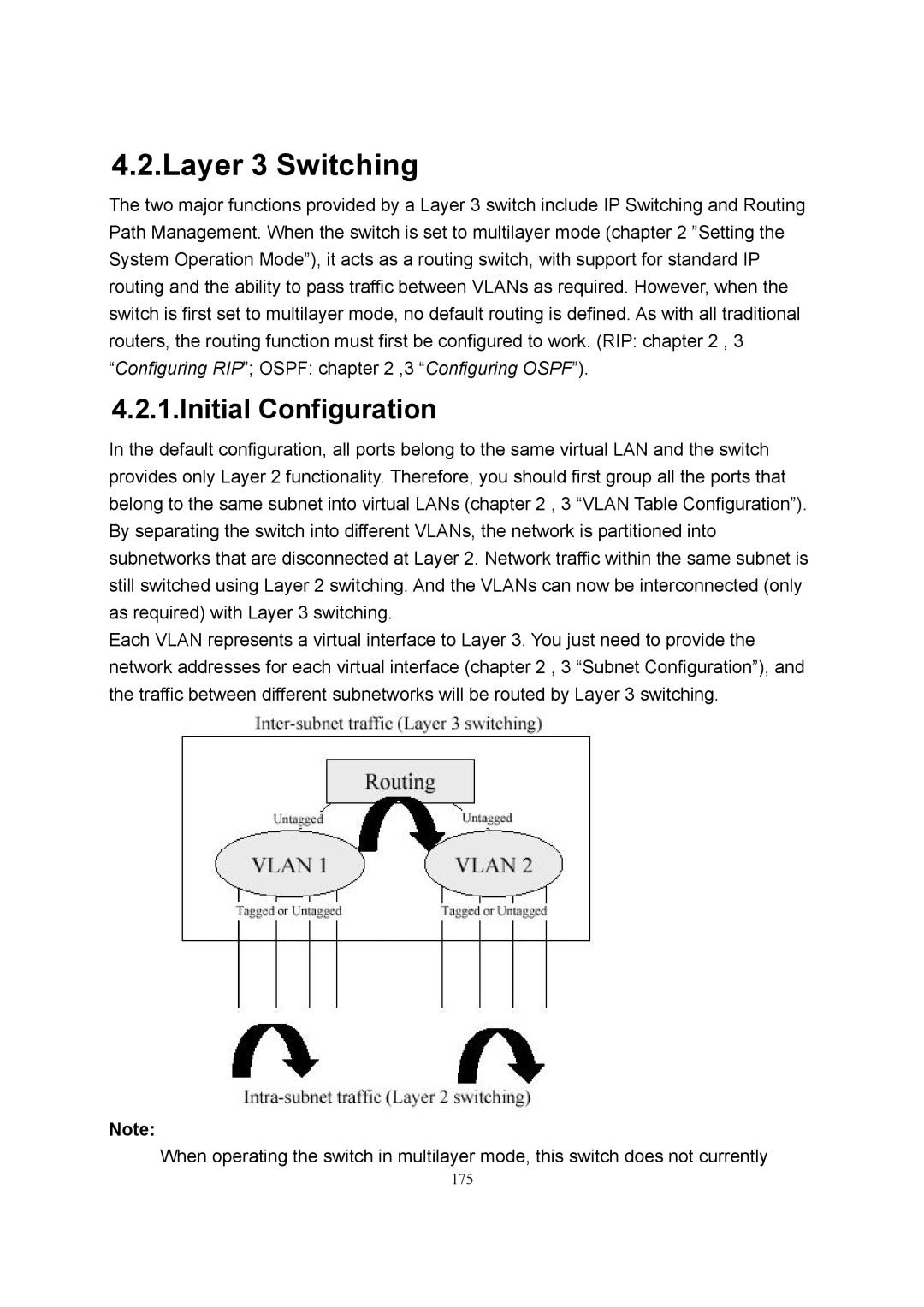
In the default configuration, all ports belong to the same virtual LAN and the switch provides only Layer 2 functionality. Therefore, you should first group all the ports that belong to the same subnet into virtual LANs (chapter 2 , 3 “VLAN Table Configuration”). By separating the switch into different VLANs, the network is partitioned into subnetworks that are disconnected at Layer 2. Network traffic within the same subnet is still switched using Layer 2 switching. And the VLANs can now be interconnected (only as required) with Layer 3 switching.
Each VLAN represents a virtual interface to Layer 3. You just need to provide the network addresses for each virtual interface (chapter 2 , 3 “Subnet Configuration”), and the traffic between different subnetworks will be routed by Layer 3 switching.
Note:
When operating the switch in multilayer mode, this switch does not currently
175