Devices’ Features and Data Paths | Clock Synchronization Interface |
|
|
Clock Synchronization Interface
AdvancedTCA systems provide a telecom clock synchronization interface which allows to synchronize elements within a telecommunication network. The telecom clock synchronization interface consists of three redundant clock buses (CLK1, CLK2 and CLK3) which are available at the system backplane. Each clock bus is implemented as a differential pair of MDS/LDS signals which connects to each system slot.aaa
In compliance with the AdvancedTCA PICMG 3.0 specification, CLK1 and CLK2 are used as system clocks and CLK3 is used as reference clock.a
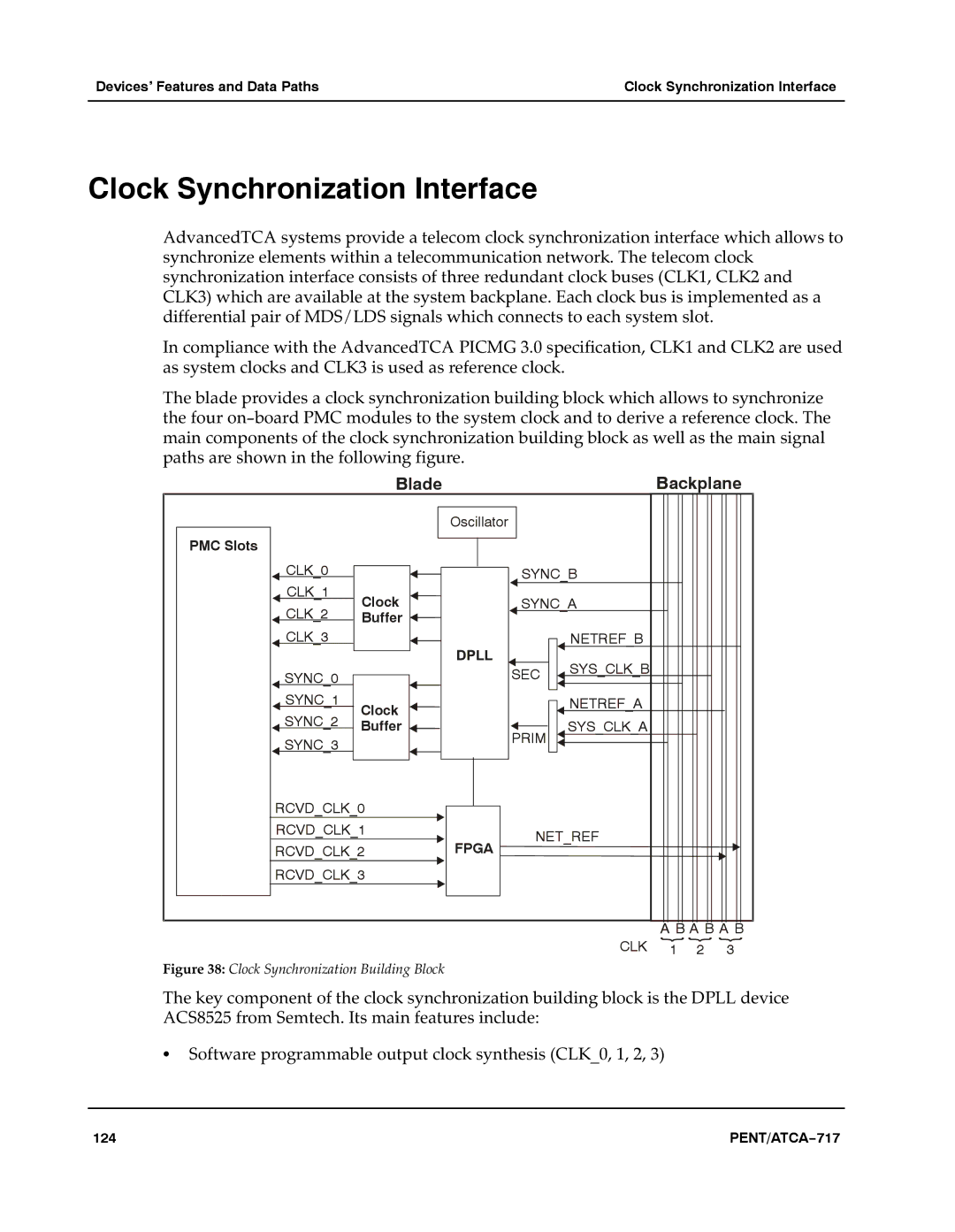
The blade provides a clock synchronization building block which allows to synchronize the four on−board PMC modules to the system clock and to derive a reference clock. The main components of the clock synchronization building block as well as the main signal paths are shown in the following figure.aaa
PMC Slots
| Blade |
|
|
| Backplane | ||
|
| Oscillator |
|
|
|
|
|
CLK_0 |
|
| SYNC_B |
|
|
| |
CLK_1 | Clock |
| SYNC_A |
|
|
| |
CLK_2 |
|
|
|
| |||
Buffer |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
CLK_3 |
|
|
| NETREF_B |
|
|
|
SYNC_0 |
|
| SEC | SYS_CLK_B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
SYNC_1 | Clock |
|
| NETREF_A |
|
|
|
SYNC_2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Buffer |
| PRIM | SYS_CLK_A |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
SYNC_3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
RCVD_CLK_0 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
RCVD_CLK_1 |
| NET_REF |
|
|
| ||
RCVD_CLK_2 | FPGA |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
| |||
RCVD_CLK_3 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| A B A B A B | ||
|
|
|
| CLK | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Figure 38: Clock Synchronization Building Block
The key component of the clock synchronization building block is the DPLL device ACS8525 from Semtech. Its main features include:
SSoftware programmable output clock synthesis (CLK_0, 1, 2, 3)
124 | PENT/ATCA−717 |