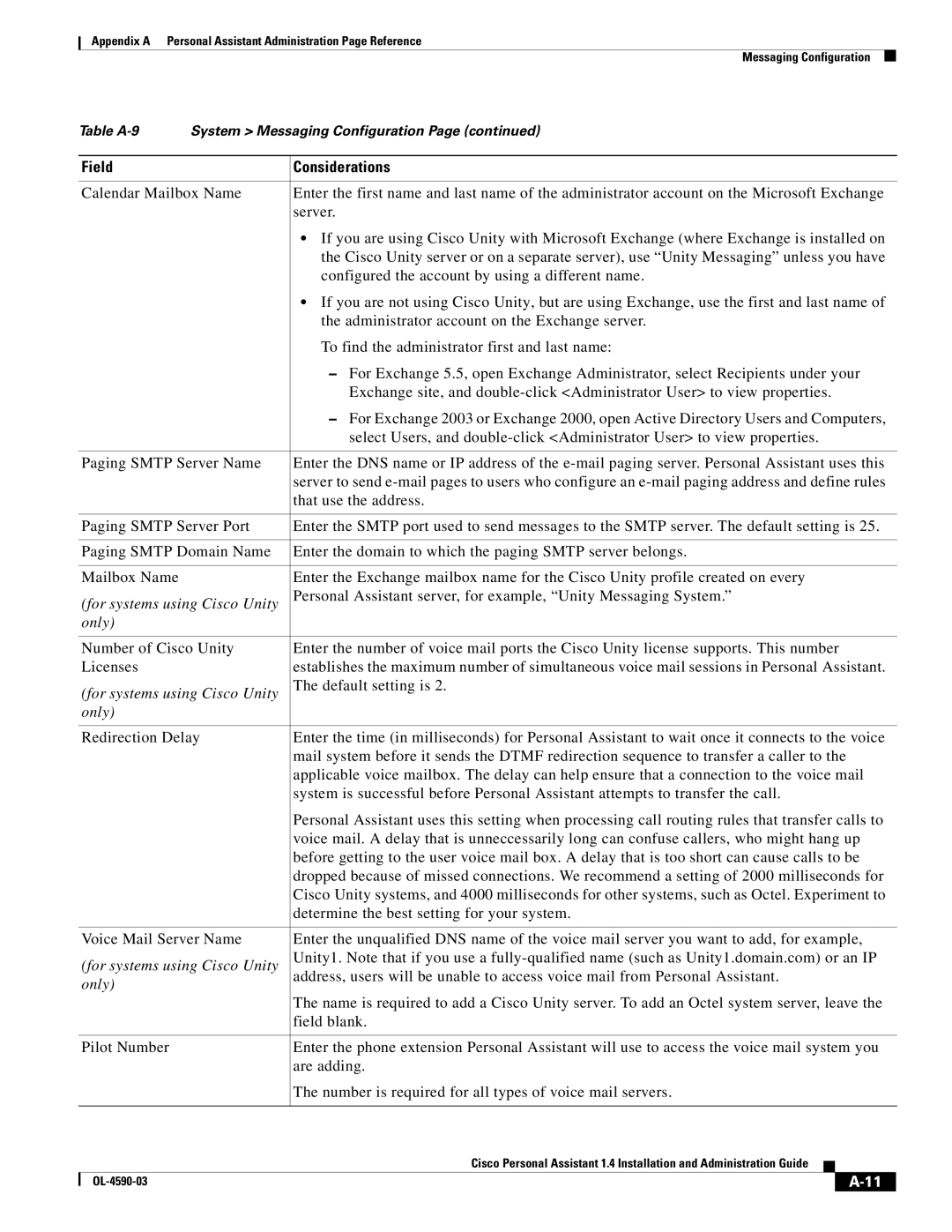
1.4 specifications
Cisco Systems 1.4 represents a notable advancement in the company's portfolio of networking solutions, emphasizing enhanced performance, security, and scalability. This version is designed to cater to the changing landscape of networking demands, particularly in hybrid and cloud environments.One of the standout features of Cisco Systems 1.4 is its enhanced security protocols. With cyber threats on the rise, Cisco has integrated advanced security measures, including end-to-end encryption and improved threat detection measures. These features help organizations safeguard their data against breaches and unauthorized access, a critical concern in today’s digital age.
Another significant characteristic of Cisco Systems 1.4 is its support for advanced network automation. By leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), this version automates routine networking tasks, such as configuring and monitoring network devices. This not only streamlines operations but also reduces human error, thereby enhancing overall network reliability and efficiency.
The addition of new collaboration tools is another highlight. Cisco's commitment to facilitating seamless communications is evident, with improved features that enable better integration of voice, video, and messaging services. The unified communications experience allows businesses to foster teamwork, regardless of location.
Moreover, Cisco Systems 1.4 supports the latest networking technologies, including Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). These technologies enable greater flexibility in network management, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to changing requirements and optimize their resources effectively.
Scalability is a key feature in Cisco Systems 1.4, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes. The architecture allows for easy expansion and integration with existing systems, ensuring a smooth transition as organizations grow.
In addition to these technological advancements, Cisco Systems 1.4 boasts a user-friendly interface, making it accessible for IT professionals and enhancing productivity. The intuitive controls and dashboards facilitate quick troubleshooting and management.
In summary, Cisco Systems 1.4 stands out with its robust security features, advanced automation capabilities, seamless collaboration tools, support for modern networking technologies, and superior scalability. Collectively, these characteristics position this version as a formidable solution for modern networking challenges, fostering innovation and efficiency in various industries.